When Should I Be Tested
All sexually active gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men should be tested regularly for STDs. The only way to know your STD status is to get tested . Having an STD makes it easier to get HIV or give it to others, so its important that you get tested to protect your health and the health of your partner. CDC recommends sexually active gay and bisexual men test for
- HIV
- Syphilis
- Hepatitis B
- Hepatitis C if you were born between 1945 to 1965 or with risk behaviors
- Chlamydia and gonorrhea of the rectum if youve had receptive anal sex or been a bottom in the past year
- Chlamydia and gonorrhea of the penis if you have had insertive anal sex or received oral sex in the past year and
- Gonorrhea of the throat if youve given oral sex in the past year.
Sometimes your doctor or health care provider may suggest a herpes blood test. If you have more than one partner or have had casual sex with people you dont know, you should be screened more often for STDs and may benefit from getting tested for HIV more often . Your doctor can offer you the best care if you discuss your sexual history openly. Talk with your doctor about getting vaccinations for Hepatitis A and B, and HPV.
Just Diagnosed Next Steps After Testing Positive For Gonorrhea Or Chlamydia
If youve just found out that you have gonorrhea or chlamydia, you may be trying to figure out what to do next. Here are the three most important steps that you can take:
WHY?Many people with gonorrhea and chlamydia dont have symptoms. Why does this matter? Because an untreated infection can lead to serious and permanent health problems, even if you never have symptoms. Gonorrhea and chlamydia can be cured with the right medicine from your doctor. Just make sure you take all of your medicine exactly as your doctor tells you to.
WHERE?Your regular doctor can prescribe antibiotics to cure the STD. But if you dont have insurance or want to see someone else for treatment, there are other low-cost or free options. You can get tested and treated at your local health departments STD clinic, a family planning clinic, a student health center, or an urgent care clinic. You can also find a clinic using GetTested and ask if they offer treatment for gonorrhea and chlamydia.
- In women, untreated chlamydia or gonorrhea can cause pelvic inflammatory disease which can lead to health problems like ectopic pregnancy or infertility .
- In men, chlamydia and gonorrhea can cause a painful condition in the tubes attached to the testicles. In rare cases, this may prevent him from being able to have children.
- Untreated chlamydia or gonorrhea may also increase your chances of getting or giving HIV the virus that causes AIDS.
New Guidelines For Chlamydia Gonorrhoea And Syphilis
Growing antibiotic resistance forces updates to recommended treatment for sexually transmitted infections
30 AUGUST 2016 | GENEVA New guidelines for the treatment of three common sexually transmitted infections have been issued by the World Health Organization in response to the growing threat of antibiotic resistance.
Chlamydia, gonorrhoea and syphilis are all caused by bacteria and they are generally curable with antibiotics. However, these STIs often go undiagnosed and they are becoming more difficult to treat, with some antibiotics now failing as a result of misuse and overuse. It is estimated that, each year, 131 million people are infected with chlamydia, 78 million with gonorrhoea, and 5.6 million with syphilis.
Resistance of these STIs to the effect of antibiotics has increased rapidly in recent years and has reduced treatment options. Of the three STIs, gonorrhoea has developed the strongest resistance to antibiotics. Strains of multidrug-resistant gonorrhoea that do not respond to any available antibiotics have already been detected. Antibiotic resistance in chlamydia and syphilis, though less common, also exists, making prevention and prompt treatment critical.
The new recommendations are based on the latest available evidence on the most effective treatments for these three sexually transmitted infections.
Don’t Miss: When To Get Tested For Chlamydia After Treatment
What Are The Schools Teaching
A growing body of research suggests that federal efforts to encourage abstinence-only sex education do not prepare young people to avoid unwanted pregnancies or STDs.
Robinson pointed out that funding increased for sexual education that promotes abstinence, even in the Obama era. “Abstinence-only” is now called “sexual risk avoidance” and gets $35 million from the federal government, spread out among school districts in the U.S. But Robinson says, it’s not even clear what’s being taught, if anything, on sexual health from school to school.
“The onus is on the principal to see curriculum is being taught,” Robinson said. “Some principals don’t do . There is not enough funding for surveillance to go around to schools to see what is being taught.”
These Conditions Are Dangerous But Preventable
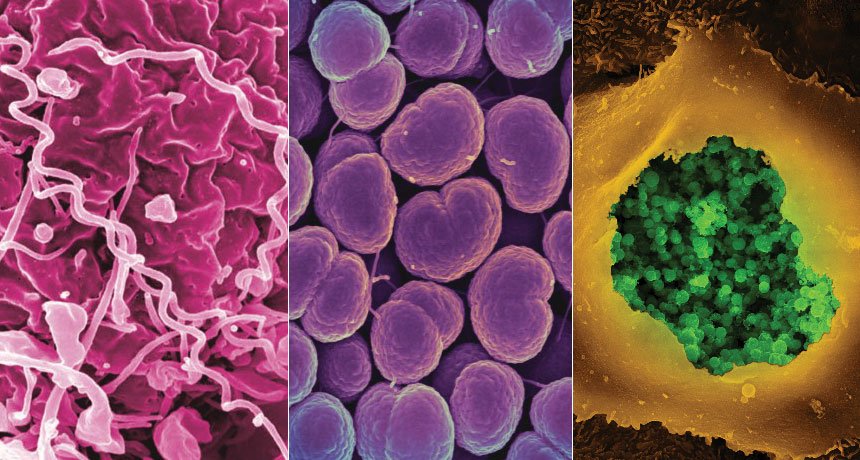
All of these conditions are preventable with safer sex measures like monogamous sexual relationships and condom use. While theyre also all generally curable with antibiotics, they may not be for long: Rising rates of antibiotic resistance mean that doctors around the world are finding it more difficult to find effective treatment.
STDs that go undiagnosed or untreated can lead to infertility, chronic pain and an increased risk for HIV, according to the CDC. The trouble with spotting these bacterial infections is that they can be symptomless or have symptoms like strange discharge, burning during urination, sores or pain that can be mistaken for other conditions. This makes regular screening an important part of STD prevention.
Don’t Miss: Herbal Remedies For Chlamydia And Gonorrhea
Some Stds Go Hand In Hand
Researchers have determined through the years that some STIs are very likely to occur alongside each other.
The chlamydia and gonorrhoea pairing mentioned above is one such example.
Syphilis and gonorrhoea is another common pairing. In fact, famous Scottish surgeon John Hunter concluded that both were caused by the same pathogen in 1767. Today, we know this isnt the case. Hunters research was probably flawed due to the fact that he obtained samples from an individual suffering from both syphilis and gonorrhoea at the time. Since Hunter was considered an important medical authority, however, his conclusion was considered valid and it didnt get challenged for a long period of time.
There are numerous factors that increase the risk of getting two STDs at the same time and being more vulnerable to sexually transmitted pathogens.
If you already have one STD, you become more susceptible to getting others. HIV positive individuals, for example, are more likely than HIV-negative people to get other STDs and vice versa. Syphilis, for example, causes the appearance of open genital sores. When the HIV virus comes in contact with such open wounds, it can pass on more effortlessly. In the other scenario, HIV weakens the immune system and reduces the bodys capability of fighting off a virus or a bacterium.
Which Stds Are Causing The Most Concern
Gonorrhea is far and away the most pressing concern. Currently, thereâs only one CDC-recommended treatment for it: a combination of two powerful antibiotics, azithromycin and ceftriaxone.
Syphilis and chlamydia have also begun to show resistance to antibiotics in some parts of the world, though Klausner says there are several treatment options for both.
STDs, which donât always have symptoms, can cause serious complications if left untreated:
- Gonorrhea can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease , which causes inflammation of the ovaries, the fallopian tubes, and the uterus, which can ultimately lead to infertility. In men, it can cause infection of the testes and sterility. In rare cases, gonorrhea can spread to your blood or joints, which can be life-threatening. Untreated gonorrhea may increase your risk of HIV.
- Chlamydia can also cause PID in women, which may result in permanent damage. Though men seldom have long-term complications from untreated chlamydia, it can lead to sterility in rare cases.
- Syphilis, in its early stages, can cause chancre sores, rashes, fever, swollen lymph glands, and other symptoms. If left untreated for years, it can eventually damage the brain, heart, liver, and other organs, causing paralysis, numbness, blindness, dementia, and death.
Pregnant women with untreated STDs have a higher chance of stillbirth and newborn death, according to the World Health Organization. STDs can also affect babies during delivery.
Read Also: Antibiotics To Treat Chlamydia And Gonorrhea
How Chlamydia Is Passed By An Infected Person And Why Certain Body Parts Are More Likely To Be Infected
Chlamydia is transmitted sexually, via bodily fluids. It can be passed through vaginal, penile, and anal contact, and it can be passed through oral sex as well though thatâs less risky. It can also be transmitted using sex toys.
Conditions necessary for transmission
For transmission to occur, chlamydia-containing bodily fluid must make contact with a type of tissue that is in the cervix, urethra, rectum, and eyes.
Why chlamydia infection is more common in certain body parts
People are more likely to get chlamydia in the rectum, cervix, or urethra than in the mouth. This may be because of differences in immune response in the local area, microscopic tears in the vaginal, penile, or anal area caused by friction during sex, and/or differences in the tissues that line these organs .
Syphilis And Gonorrhea On The Rise In The South Zone
SOUTH ZONE Alberta Health Services is concerned about an apparent spike in syphilis and gonorrhea in the South Zone, prompting a reminder of the importance of safe sex practices among all sexually-active age groups, including seniors.
Between January and March of 2018, 11 cases of gonorrhea were documented in the South Zone which is two more than were reported in all of 2017.
It is not unusual for individuals who have a sexually-transmitted infection to have more than one STI at the same time. HIV, gonorrhea, syphilis, and chlamydia are all examples of STIs.
Recently, three new cases of gonorrhea were identified in the South Zone. Individuals with gonorrhea may have numerous sexual contacts – both known to them and anonymous – who have been potentially exposed.
An STI is also sometimes referred to as an STD . They are caused by a bacteria, virus, or parasite passed from one person to another through unprotected sexual contact.
The role of Public Health is to follow up with the known sexual contacts of people who are diagnosed with STIs to let them know they may have been exposed and to provide information on how to get tested.
New social media tools enable people to communicate quickly to arrange anonymous sexual encounters, resulting in increased difficulty in tracking STIs. When people dont know their sexual partners identities, it makes it difficult to contact partners for follow-up testing and treatment.
– 30 –
You May Like: Can You Die From Chlamydia
In Both Males And Females
Complications that may be seen in anyone include:
- Other STIs. Chlamydia and gonorrhea both make you more susceptible to other STIs, including human immunodeficiency virus . Having chlamydia can also increase your risk of developing gonorrhea, and vice versa.
- Reactive arthritis . Also called Reiters syndrome, this condition results from an infection in your urinary tract or intestines. Symptoms of this condition cause pain, swelling, or tightness in your joints and eyes, and a variety of other symptoms.
- Infertility. Damage to reproductive organs or to sperm can make it more challenging or, in some cases, impossible to become pregnant or to impregnate your partner.
When A Person Infected With Chlamydia Is Contagious
- Chlamydia can be transmitted by an infected person immediately after they become infected.
- Chlamydia infection can be passed regardless of whether the infected person has symptoms.
- The infected person will continue to be contagious until seven days after they finish treatment âit doesnât matter whether they have any signs or symptoms of the disease.
Don’t Miss: What Is Chlamydia In Men
Rising Std Rates Reflect Our National Spending Priorities
The increase in STD rates is directly attributable to a decrease in funding for health clinics that can screen and treat people, as opposed to any recent change in sexual behavior among certain demographic groups, says Dr. Jeffrey Klausner, an HIV and infectious diseases expert at the UCLA School of Medicine and Public Health.
Historically, when weve invested in prevention and control, weve been able to greatly reduce infections, said Klausner. For instance, venereal disease control became a national priority during World War II because STDs were disabling soldiers. During this time, doctors discovered the cure for syphilis and the army embarked on a major public health campaign that included condom distribution and STD education.
Unfortunately, the U.S. hasnt been able to keep up with this baby boomer-era progress. From the CDC report:
Not that long ago, gonorrhea rates were at historic lows, syphilis was close to elimination, and we were able to point to advances in STD prevention, such as better chlamydia diagnostic tests and more screening, contributing to increases in detection and treatment of chlamydial infections. That progress has since unraveled. The number of reported syphilis cases is climbing after being largely on the decline since 1941, and gonorrhea rates are now increasing. This is especially concerning given that we are slowly running out of treatment options to cure .
Failure To Complete Treatment
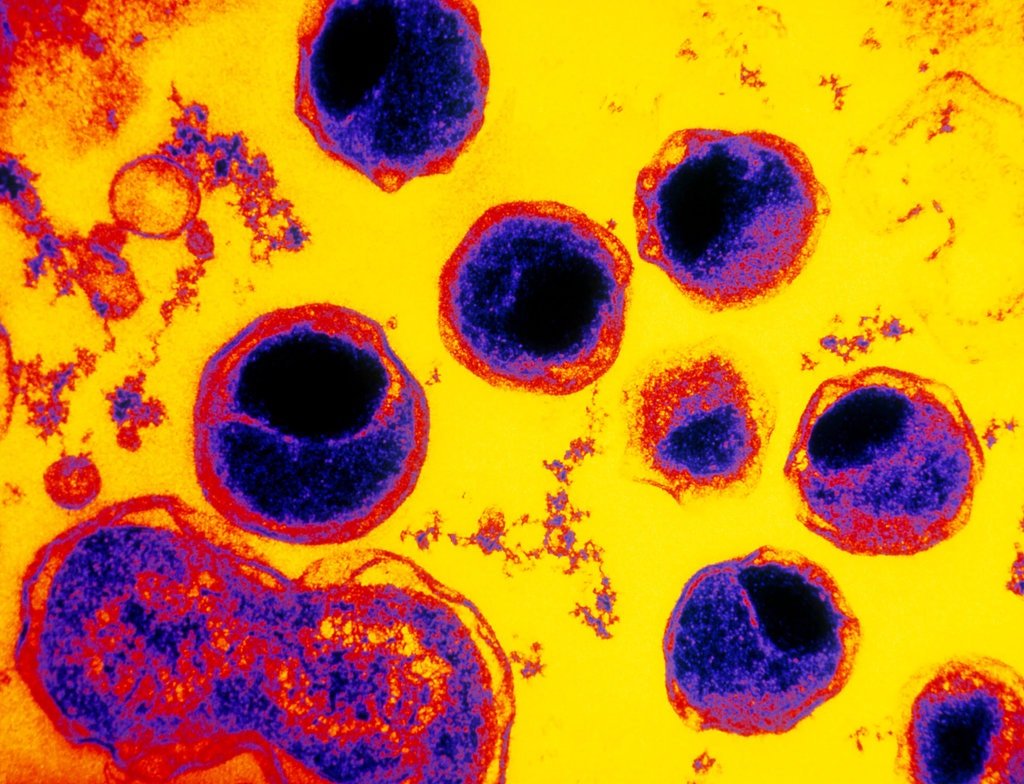
If you don’t take all of your antibiotics, you may not fully get rid of an infection. In addition, failing to finish your medication can cause problems such as antibiotic resistance. This means that the medication may not work as well if you need to take it again.
Due to high rates of incomplete therapy, antibiotic-resistant gonorrhea may one day turn a relatively uncomplicated STD into one that is difficult, if not impossible, to cure.
To help combat this, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention now recommends a dose of ceftriaxone be given for the treatment of uncomplicated gonorrhea infections.
You May Like: How Long Can A Person Have Chlamydia
Less Money Fewer Clinics Less Culturally Competent Care
Following the release of the CDC surveillance report, the National Coalition of STD Directors said that “steep increases in STDs are largely due to federal, state, and local funding cutbacks,” and called on Congress to increase funding for CDC’s STD prevention services by $70 million, “the bare minimum it will take to support an effective response to this crisis.”
A recent report conducted by the public health research group Trust for America’s Health estimated that 55,000 jobs were cut from local public health departments from 2008 to 2017. The CDC has reported that budget cuts resulting in clinic closures, higher caseloads, and a lack of patient follow-up have affected half of local STD-prevention programs in recent years.
“Since 2003 the STD prevention line at the CDC was either cut or flat funded every year,” said Matt Prior, M.P.H., director of communications at NCSD. “These programs are operating at a 40% reduction in funding since 2003, adjusted for inflation. To us it’s clear that public health workforce reaches fewer people today.”
Infectious disease experts know that access to care is a key determinant in whether a person will get tested and treated, and there are many drop-offs even for people who are able to access care.
How Herpes Is Transmitted
Direct skin-to-skin contact is necessary for herpes to be passed. When a herpes blister on the skin of the infected person makes contact with their partnerâs skin, it can rupture. The fluids in it contain a high concentration of herpes virus. The risk of transmission during the infected personâs first outbreak is greater because that is when the virus is most highly concentrated in the blisters.
You May Like: Can You Not Get Chlamydia From Someone That Has It
Who Is At Risk And How Can They Prevent It
Any person who is sexually active has a risk of STIs. A person can transmit or contract STIs through oral, anal, or vaginal sexual intercourse.
To prevent contracting either of these infections, a person should use barrier methods, such as condoms, and get tested regularly.
Even when they do not cause any symptoms, these infections can cause complications.
If a person does not seek treatment for gonorrhea, for example, there may be a of contracting HIV. They may also contract disseminated gonococcal infections.
Contracting Chlamydiaand Transmitting It To Othersthrough Oral Sex
You need to understand several things about chlamydia to determine how likely it is that you will get chlamydia from oral sex:
- How chlamydia is passed from one person to another
- After contracting chlamydia, when will a person become infectious
- Who is at higher risk for chlamydia
- How giving versus receiving oral sex affects your risk
Let discuss each portion in more details!
Read Also: How To Get Tested For Chlamydia Female
Facts About The Contagiousness Of Gonorrhea
- Someone whose mouth is exposed often to fluids from the vagina or penis is more likely to contract gonorrhea. This is even more true if the fluids are swallowed.
- Someone who has more than five sexual partners in their lifetime is more likely to get gonorrhea. Clearly, the number of different partners matters.
- Gonorrhea can be transmitted immediatelyâas soon as a person becomes infected with it.
- It doesnât matter if the infected person has symptoms of gonorrheaâtheyâre still contagious.
- An infected person can transmit the infection as long as they have it i.e., until theyâre cured, which is seven days after they finish treatment. Again, it doesnât matter if they have signs or symptoms of the infection.
What Happens During A Gonorrhea Test
If you are a woman, a sample may be taken from your cervix. For this procedure, you will lie on your back on an exam table, with your knees bent. You will rest your feet in supports called stirrups. Your health care provider will use a plastic or metal instrument called a speculum to open the vagina, so the cervix can be seen. Your provider will then use a soft brush or plastic spatula to collect the sample.
If you are a man, your provider may take a swab from the opening of your urethra.
For both men and women, a sample may be taken from a suspected area of infection, such as the mouth or rectum. Urine tests are also used for both men and women.
Some gonorrhea tests can be done with an at-home STD test kit. If your health care provider recommends at-home testing, be sure to follow all directions carefully.
Your health care provider may order tests for other STDs when you get a gonorrhea test. These may include tests for chlamydia, syphilis, and/or HIV.
Don’t Miss: How Do They Test For Chlamydia