What To Think About
To prevent reinfection, don’t have sex until any partner that might be infected is tested and treated.
Some people who have gonorrhea also have chlamydia. The Public Health Agency of Canada recommends that drug treatment for gonorrhea also include antibiotics that are effective in treating chlamydia. For more information, see the topic Chlamydia.
Pelvic inflammatory disease is a serious complication of gonorrhea that can lead to infertility, chronic pelvic pain, and ectopic pregnancy. To prevent PID, prompt treatment of gonorrhea is important. For more information, see the topic Pelvic Inflammatory Disease .
Disseminated gonococcal infection occurs when the gonorrhea infection spreads to sites other than the genitals, such as the joints, skin, heart, or blood. Treatment of DGI usually requires hospitalization and antibiotic treatment given intravenously or into a muscle .
Your doctor must report to the local health unit that you have gonorrhea.
Why Is It Important To Treat Chlamydia
If left untreated chlamydia is unlikely to go away. It can be passed onto sexual partners and can cause serious harm. Women can get cervicitis or pelvic inflammatory disease. This can result in permanent damage to the fallopian tubes, which may lead to infertility or ectopic pregnancy. Chlamydia also can cause a reactive arthritis. Men can suffer with urethritis , this can spread to the contents of the scrotal sac – epididymis and testicles. This causes pain, and in severe cases infertility. Men can also get a reactive arthritis.
What Happens To Those Who Dont Get Treated
Since more than 50% of the infected dont experience any signs of chlamydia, many people unknowingly pass their infection onto their partner and leave it to manifest in their system for years.
Even though chlamydia is not a life-threatening infection, if left untreated, it can cause serious health problems. For women, untreated chlamydia can move up into the fallopian tubes and womb and cause pelvic inflammatory disease . If it travels to the uterus as well, it can lead to endometritis.
In time, these diseases will become a serious problem and can cause:
- Infertility
- Increased risk of developing HIV
- Joint pain
Any prolonged damage to the reproductive tissues can cause irreversible damage, and once it gets to this stage, chlamydia can be a serious burden, and infertility can no longer be treated.
In men, the infection can affect the testes and spread to the reproductive tract. When it gets to this area, the infection can cause serious inflammation, swelling, fever, and pain. However, if left untreated, it can have the same consequences as in women, and that is infertility.
Thats why its crucial to get on-time treatment and regularly get tested for chlamydia even if you dont notice any signs or symptoms.
Also Check: What Are Some Treatments For Chlamydia
Why Do You Have To Wait 3 Months To Retest For Chlamydia
In fact, women who become reinfected with chlamydia have an even higher risk for PID and ectopic pregnancy than those with a first infection. Due to these risks, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that any person who tests positive for chlamydia be retested three months after treatment.
What Happens If I Get Chlamydia When I’m Pregnant

- Chlamydia during pregnancy has been associated in very rare cases with problems such as premature birth, and infection of the uterus lining after the birth.
- It can be passed to the baby during the birth and before the baby is born. This can cause inflammation and discharge in the babys eye and/or pneumonia.
- You may be offered a chlamydia test as part of your antenatal care.
- Chlamydia can be treated with antibiotics when youre pregnant and when youre breastfeeding. The antibiotics wont harm the baby, but do tell the doctor or nurse that youre pregnant or breastfeeding.
- Youll be advised to have another test after you complete your treatment.
You May Like: How To Know If You Get Rid Of Chlamydia
Who Should Be Tested For Chlamydia
Any sexually active person can be infected with chlamydia. Anyone with genital symptoms such as discharge, burning during urination, unusual sores, or rash should refrain from having sex until they are able to see a health care provider about their symptoms.
Also, anyone with an oral, anal, or vaginal sex partner who has been recently diagnosed with an STD should see a health care provider for evaluation.
Because chlamydia is usually asymptomatic, screening is necessary to identify most infections. Screening programs have been demonstrated to reduce rates of adverse sequelae in women.31,41 CDC recommends yearly chlamydia screening of all sexually active women younger than 25, as well as older women with risk factors such as new or multiple partners, or a sex partner who has a sexually transmitted infection.40 Rectal chlamydia testing can be considered for females based on sexual behaviors and exposure. 40 Pregnant women under 25 or older pregnant women at increased risk for chlamydia should be screened during their first prenatal visit and again during their third trimester.40 Women diagnosed with chlamydial infection should be retested approximately 3 months after treatment.40 Any woman who is sexually active should discuss her risk factors with a health care provider who can then determine if more frequent screening is necessary.
Does Azithromycin Also Cure Chlamydia
Azithromycin was the first choice antibiotic to treat chlamydia until February 2019 when BASHH guidance was issued recommending a 7-day course of doxycycline as the first choice treatment based on recent data. Azithromycin is now recommended only for pregnant women and those with an allergy to doxycycline.
Also Check: What Gets Rid Of Chlamydia
Your Partner Didn’t Get Treated
If you have a consistent sexual partner, it’s important to tell them about your infection so they can get treatment, too. Once you’ve both gotten treated, you have to wait until the treatment has had time to work before you start having sex again .
Without taking these important steps, it is possible for the two of you to end up passing the STD back and forth.
What Complications Can Result From Chlamydial Infection
The initial damage that chlamydia causes often goes unnoticed. However, chlamydial infections can lead to serious health problems with both short- and long-term consequences.
In women, untreated chlamydia can spread into the uterus or fallopian tubes and cause pelvic inflammatory disease . Symptomatic PID occurs in about 10 to 15 percent of women with untreated chlamydia.30,31 However, chlamydia can also cause subclinical inflammation of the upper genital tract . Both acute and subclinical PID can cause permanent damage to the fallopian tubes, uterus, and surrounding tissues. The damage can lead to chronic pelvic pain, tubal factor infertility, and potentially fatal ectopic pregnancy.32,33
Some patients with chlamydial PID develop perihepatitis, or Fitz-Hugh-Curtis Syndrome, an inflammation of the liver capsule and surrounding peritoneum, which is associated with right upper quadrant pain.
In pregnant women, untreated chlamydia has been associated with pre-term delivery,34 as well as ophthalmia neonatorum and pneumonia in the newborn.
Reactive arthritis can occur in men and women following symptomatic or asymptomatic chlamydial infection, sometimes as part of a triad of symptoms formerly referred to as Reiters Syndrome.35
Recommended Reading: How Does One Contract Chlamydia
How Do You Treat A Chlamydia Infection During Pregnancy
If a chlamydia infection occurs during pregnancy, the treatment options are more limited, as many antibiotics must not be given during pregnancy. However, therapy should be carried out before birth, as otherwise transmission to the child may occur at birth. In the child, the infection manifests itself in an inflammation of the eyes, and in some cases also of the middle ear.
The standard doxycycline used for chlamydial infections must not be used from the 2nd trimester onwards, as the teeth of the still unborn child can turn yellow if it is taken. Doxycycline may also reduce bone growth and increase susceptibility to caries. Therefore, azytrhromycin is usually prescribed to pregnant women to treat a chlamydia infection. Erythromycin can also be used as an alternative. Preventive screening for chlamydia in pregnant women is carried out in Germany in order to avert possible consequences for mother and child through early therapy.
What Happens If You Get Chlamydia Multiple Times
PID can cause permanent damage to your reproductive system. This can lead to long-term pelvic pain, infertility, and ectopic pregnancy. Women who have had chlamydia infections more than once are at higher risk of serious reproductive health complications. Men often dont have health problems from chlamydia.
You May Like: How To Get Rid Of Chlamydia In The Mouth
What Is The Treatment For Chlamydia
Chlamydia can be easily cured with antibiotics. HIV-positive persons with chlamydia should receive the same treatment as those who are HIV-negative.
Persons with chlamydia should abstain from sexual activity for 7 days after single dose antibiotics or until completion of a 7-day course of antibiotics, to prevent spreading the infection to partners. It is important to take all of the medication prescribed to cure chlamydia. Medication for chlamydia should not be shared with anyone. Although medication will stop the infection, it will not repair any permanent damage done by the disease. If a persons symptoms continue for more than a few days after receiving treatment, he or she should return to a health care provider to be reevaluated.
Repeat infection with chlamydia is common. Women whose sex partners have not been appropriately treated are at high risk for re-infection. Having multiple chlamydial infections increases a womans risk of serious reproductive health complications, including pelvic inflammatory disease and ectopic pregnancy. Women and men with chlamydia should be retested about three months after treatment of an initial infection, regardless of whether they believe that their sex partners were successfully treated.
Infants infected with chlamydia may develop ophthalmia neonatorum and/or pneumonia. Chlamydial infection in infants can be treated with antibiotics.
Can A Treated Std Come Back

Monique Rainford, MD, is board-certified in obstetrics-gynecology, and currently serves as an Assistant Clinical Professor at Yale Medicine. She is the former chief of obstetrics-gynecology at Yale Health.
Chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, and trichomoniasis can all be treated, and often cured, with antibiotics. While it’s important that you find treatment for your STD, having your STD treated is not a guarantee that it will never come back. You have to use your medication as directed, and you also have to be careful about prevention so you won’t get re-infected.
Don’t Miss: Do I Have Chlamydia Male
What Are The Symptoms
Many people have no symptoms, so they can pass gonorrhea to their sex partners without knowing it.
If there are symptoms, they may include:
- Pain when you urinate.
- Abnormal discharge from the penis or vagina.
Gonorrhea infection in the throat may cause a sore throat, but it usually does not cause symptoms.
Symptoms in men usually are easier to notice than symptoms in women. But some men have mild or no symptoms.
In women, the early symptoms may be so mild that they are mistaken for a bladder infection or a vaginal infection. When an untreated infection moves into a woman’s pelvic organs, symptoms can include lower belly pain, pain during sex, vaginal bleeding, and a fever.
The time from exposure to gonorrhea until symptoms begin usually is 2 to 5 days. But it may take as long as 30 days before symptoms start.
You can spread gonorrhea even if you don’t have symptoms. You are contagious until you have been treated.
How Long Should I Avoid Sex If I Have Chlamydia
Because chlamydia is a sexually transmitted disease, it’s important to avoid sex until you’ve completed treatment for the infection. Treatment involves seeing a doctor and finishing any and all medications – antibiotics like azithromycin, doxycycline, or erythromycin – that are prescribed to you. Medications may be given in one dose, or as a week’s worth of pills. Usually, the infection is cleared up within a week or two, and you can resume having safe sex at that point. Any partners who’ve had sexual contact with an infected person should also avoid sexual contact and should be treated for chlamydia so partners avoid re-infecting one another.
Important: This content reflects information from various individuals and organizations and may offer alternative or opposing points of view. It should not be used for medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. As always, you should consult with your healthcare provider about your specific health needs.
Read Also: Do They Test For Chlamydia When Donating Plasma
How Long Does It Take For Chlamydia To Go Away
How long does it take for Chlamydia to clear up? Can you have Chlamydia for years and not know it? These are questions that give headache to a lot of women at some point in their lives.
Chlamydia is a bacterial infection with the Chlamydia infectious agent, which is transmitted through sexual contact. It`s among the most common STDs in the world. Chlamydia infects the urethra in men and the cervix, urethra and superior reproductive organs in women. Chlamydia can also infect the rectum, eye surface and eyelids.
An infected mother can transmit the infection to her baby during childbirth. Between 50% and 70% of infants are born from infected mothers. They acquire the infection in the eyes, rectum, vagina and the back of the throat. Between 30% and 40% of these infected neonates develop complications, like conjunctivitis or pneumonia.
Chlamydia increases the risk of human immunodeficiency virus infection, in case of exposure.
When Can I Expect For Chlamydia Signs To Show Up
Chlamydia is a serious issue for both women and men. The majority of the infected experience no signs, which is why 70% of the women infected, and most men have no clue they carry it.
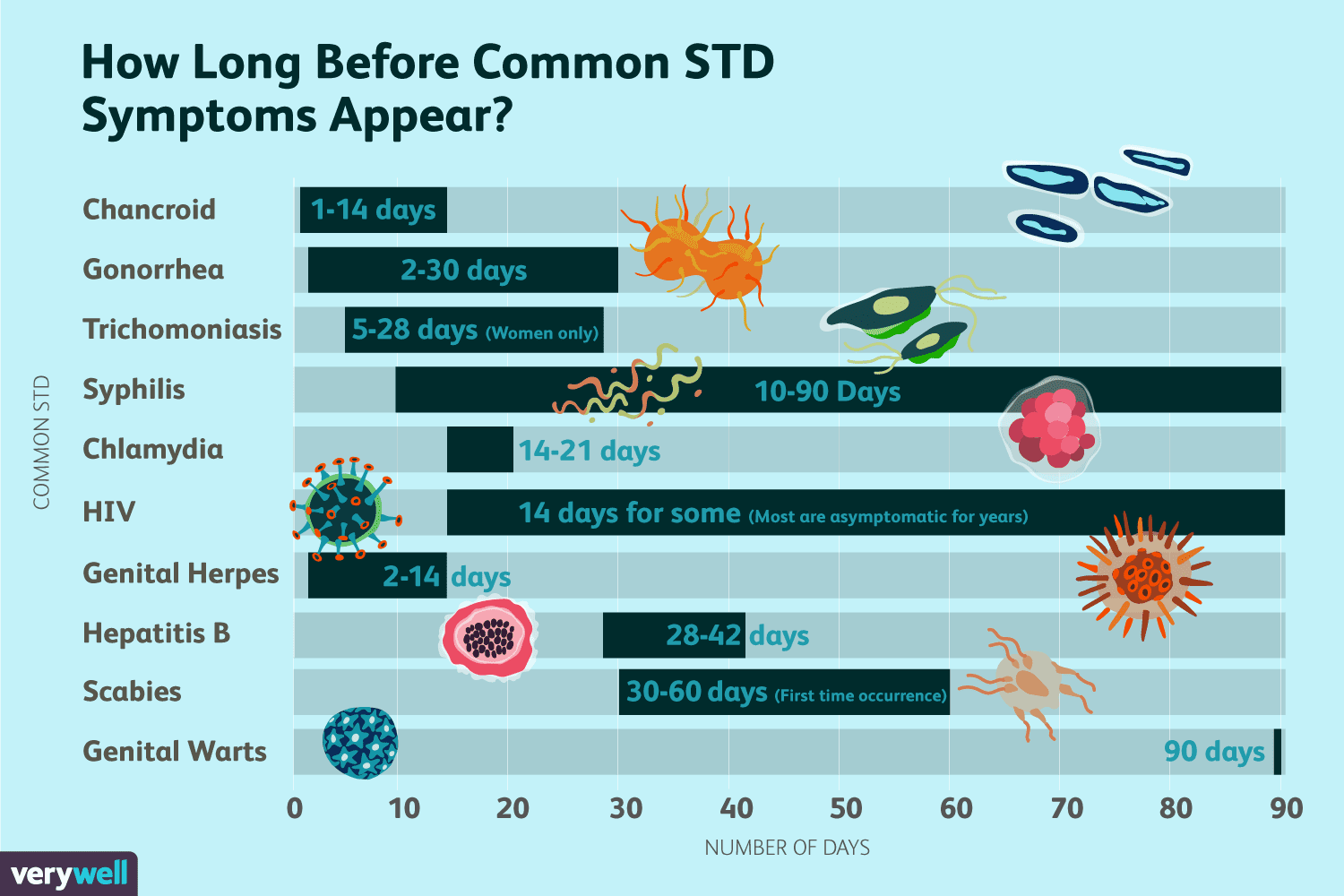
If the signs do show up, it will take 1 to 3 weeks after the patient has been exposed to the infection for the bacteria to manifest and produce symptoms. What most people dont know about is that every bacteria has an incubation period, chlamydia has one as well.
This period can vary for every individual. For example, for some individuals, the incubation period can last for a couple of days, so the first signs of the infection will start to develop just days after they have been exposed to the bacteria.
For others, it can take months for any signs to show, which means the incubation period lasts much longer, and the only way to know if that individual is infected with chlamydia is to get tested. But, on average, it takes 1 to 3 weeks after the person has been infected for any signs to show.
Recommended Reading: What Type Of Antibiotics Treat Chlamydia
What If I’m Pregnant
During delivery, the infection can spread to the newborn from the birth canal. It can cause eye infection or pneumonia. There may also be an association with preterm labour and low birth weight. Screening and treatment of chlamydia during pregnancy can prevent these complications. This is not part of the routine NHS antenatal screening. Doxycycline cannot be taken during pregnancy, but azithromycin is safe and effective.
How Long Does Chlamydia Pneumoniae Last
Thecan lastChlamydia pneumoniaeapneumoniathe
How do you know if you have chlamydia in your mouth? Symptoms of Oral Chlamydia Painless sores in the mouth. Lesions similar to cold sores around the mouth. Tonsillitis. Redness with white spots resembling strep throat. Scratchy, dry throat.
Can chlamydia make you tired? Fatigue is a symptom of a late-stage chlamydial or gonorrheal infection. It can also be caused by Hepatitis A, B, and C. When experiencing fatigue, it’s easy to chalk it up to a late night out, but it could be an indication of something much more serious.
Is chlamydia a bacteria or virus? Chlamydial diseases are sexually transmitted and caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis. However, this bacterium acts more like a virus. Chlamydia infections can affect the vagina, cervix, and rectum, among other areas. Fortunately, chlamydia is a largely preventable infection.
Can you get chlamydia from kissing? You can’t transmit chlamydia through kissing, sharing drinking glasses, or hugging, but you can spread the disease: through unprotected vaginal, oral, or anal sex with someone who has the disease. to your baby through childbirth if you’re pregnant and infected.
Also Check: Signs And Symptoms Of Chlamydia
How Contagious Is Chlamydia
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
If I Have Chlamydia Am I At Risk Of Other Sexually Transmitted Infections
Yes. By definition, having unprotected sex means risk of STI. As well as chlamydia, there are also genital warts, genital herpes, gonorrhoea, HIV, pubic lice, and syphilis. Like with chlamydia, gonorrhoea may well cause no symptoms, so being tested is the only way to really know. This can be done at your local sexual health clinic.
Also Check: Can Chlamydia Feel Like A Uti
Why Is Treatment Of Chlamydia Important
When treated early, chlamydia does not cause any long-term complications. Left untreated, serious and permanent damage can occur.
It may lead to pelvic inflammatory disease . This is when female reproductive organs, found in your pelvis, become inflamed. PID may cause ectopic pregnancies , infertility or chronic pelvic pain.
If not treated, chlamydia can spread to testicles, leading to pain and swelling. Chlamydia may occasionally cause infertility in men. Sometimes chlamydia may trigger a condition called Reiter’s disease which causes inflammation of your eyes, skin and joints.
Chlamydia can be passed from mother to baby during birth. The baby may subsequently develop eye and/or ear infections or pneumonia.