Is There Anything Else I Need To Know About A Chlamydia Test
Chlamydia testing enables diagnosis and treatment of the infection before it can cause serious health problems. If you are at risk for chlamydia due to your age and/or lifestyle, talk to your health care provider about getting tested.
You can also take steps to prevent getting infected with chlamydia The best way to prevent chlamydia or any sexually transmitted disease is to not have vaginal, anal or oral sex. If you are sexually active, you can reduce your risk of infection by:
- Being in a long-term relationship with one partner who has tested negative for STDs
- Using condoms correctly every time you have sex
How Long Does It Take To Show Up On A Test
There are several tests that you doctor might use to diagnose chlamydia:
- Urine test. Youll pee in a cup thats sent off to a laboratory testing facility to see if any chlamydia bacteria are present in your urine.
- Blood test. Your doctor will use a sterile needle to draw some of your blood and send it to a lab to see if antibodies to the chlamydia bacteria are present in your bloodstream.
- Swab. Your doctor will use a cotton round or stick to take a small sample of tissue or fluid that carries the infection, which is then sent to a lab to be cultured so that lab technicians can see what bacteria grows from the sample.
How long it takes for the results to show up depends on the test and on your specific health insurance plan.
- Urine tests take about 2 to 5 days to show a positive or negative result.
- Blood tests can come back with results in a few minutes if the blood is analyzed on site. But they can take a week or more if sent to an off-site lab.
- Swab results take about 2 to 3 days to show a positive or negative.
1 to 3 weeks to show up in people with vulvas.
Symptoms may take up a few months to show up. This is because bacteria are living creatures and have an incubation period that affects how long it takes them to cluster together and become infectious.
This incubation period is dependent on a variety of factors, including:
How Soon Should I Test For Stds After Exposure
Use the table below to determine when you should get tested following exposure to an STD. The first column lists some of the most common types of STDs. The second column has the earliest time that tests offered by myLAB Box could be positive after a potential exposure. Some of the times listed are estimates due to limited data in other cases the window period is simply unknown. The third column tells you how long it could take following initial exposure to test positive for an STD.
For example, say you have been potentially exposed to genital herpes. If you look at the second column, it says you should take your first test 2 weeks from the date of exposure. This is the earliest that genital herpes will be detectable in your system. But according to the third column, it could take as long as 4 months, or 16 weeks, for genital herpes to become detectable in your system. In other words, the incubation period for genital herpes could be anywhere from 2 to 16 weeks following exposure.
This means if your results are negative when you get tested two weeks following exposure, you should get retested after 16 weeks. This way, you can confirm that it was not a false negative caused by testing before the STD was detectable.
- Birth defects
- Organ damage
Also Check: How To Get Rid Of Chlamydia Pain
If Your Partner Did Not Get Treated
Itâs important to understand that the antibiotics used to treat chlamydia donât work like a vaccine. They eliminate the existing chlamydia infection, but antibiotics donât make you immune to the disease. That means that you can get reinfected by a sexual partner who has chlamydia.
If you are in a committed monogamous relationship, itâs important that your sex partner also gets tested and treated for chlamydia as soon as you receive your diagnosis. Without proper diagnosis and treatment, you and your partner may end up just passing the infection back and forth through unprotected sex until you both receive treatment.
Easily check for chlamydia from the comfort and privacy of home with the at-home chlamydia test, or try the at-home STD Test to check for 6 common sexually transmitted infections with a single test kit.
If you are not in a committed monogamous relationship, talk to any recent sexual partners to make sure that they also get tested to prevent the potential spread of the disease. You and your sex partner should also get tested again about three to four months following treatment to ensure that the chlamydia infection is no longer in your system.
Symptoms In The Throat
Chlamydia symptoms can sometimes appear in the throat, although this is uncommon. When it does occur, the time frame is likely to be similar to that of chlamydia infections of the genitals.
In people who experience symptoms, the main one is a persistent sore throat. A doctor may refer to a chlamydia infection in the throat as pharyngeal chlamydia.
Testing for chlamydia in the throat is not a common practice in STI testing, as it does not have approval from the Food and Drug Administration . However, if a person suspects that they have pharyngeal chlamydia, a doctor may take a swab from the throat.
A person can undergo testing for chlamydia at their:
- doctors office
- local health department
- local planned parenthood center
A person can also order a chlamydia test online, take it at home, and then send it off for testing.
If people are at high risk of chlamydia, they may need screening for all types of chlamydia every 36 months.
At risk groups include people who have:
- multiple or unknown sexual partners
- sex in combination with illegal drug use
- sexual partners who use illegal drugs or have multiple partners
7 days .
People should avoid having sex until their treatment is complete. If a person is experiencing symptoms even after the treatment, they should see a doctor.
People who menstruate should notice that their periods return to normal or that bleeding between periods stops by their next period.
You May Like: Can Your Body Fight Chlamydia On Its Own
When To Get Tested For Chlamydia
Now is the right time to get tested if you are sexually active, havent been tested recently, have a new sex partner, or believe you are at risk. The CDC recommends the following guidelines:
Sexually active women under 25 should test for chlamydia every year. Women who are older than 25 with new or multiple sex partners should also test yearly.
Anyone who has a sex partner who has an STD should be tested.
Pregnant women who are at risk should be tested for chlamydia early in the pregnancy and again at the third trimester. Plus, they need tests for gonorrhea, syphilis, HIV, and hepatitis B.
Men who have sex with men should get tested once a year, or more frequently if they have multiple partners.
Men who are exposed to an infected partner should be tested.
If you believe youve been exposed, chlamydia testing can take place within 1-5 days from exposure, but is most accurate after five.
How often to get tested for chlamydia: The CDC recommends that men and women at increased risk be tested every 3-6 months, and that sexually active women under 25 years be screened for chlamydia annually . Clinicians also test for the infection during initial pregnancy screenings and again in the third trimester.
For general STD testing, see our page about when to get tested for each one.
Can A Treated Std Come Back
Monique Rainford, MD, is board-certified in obstetrics-gynecology, and currently serves as an Assistant Clinical Professor at Yale Medicine. She is the former chief of obstetrics-gynecology at Yale Health.
Chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, and trichomoniasis can all be treated, and often cured, with antibiotics. While it’s important that you find treatment for your STD, having your STD treated is not a guarantee that it will never come back. You have to use your medication as directed, and you also have to be careful about prevention so you won’t get re-infected.
Don’t Miss: Will 250 Mg Of Azithromycin Cure Chlamydia
When Should I Get Tested For Stds
To help stay as safe as possible, the CDC recommends that you get tested for STDs after having an unprotected sexual encounter with a person outside of a monogamous sexual relationship. However, beyond this general principle, there are specific windows of time during which you should get tested for each STD. Its important to be aware of these time windows because if you get tested before the window begins, you could have a false negative STD test, according to the CDC. This means that you could get a negative result when you actually do have the STI. It can be agonizing to waitbut its definitely worth it to get tested during the appropriate time window. Another important thing to keep in mind is that you should refrain from any sexual activity until you are sure you do not have an STI.
When To See A Doctor
If a person has symptoms of chlamydia after testing and treatment or thinks that they have come into contact with chlamydia again, they should see their doctor.
Females are less likely than males to have symptoms of chlamydia, so testing is especially important for them.
The recommend chlamydia testing every year for the following groups of people:
- sexually active females under the age of 25 years
- females over the age of 25 years who have new or multiple sexual partners
- anyone with a sexual partner who has an STI
- sexually active gay and bisexual males
Pregnant women should have a chlamydia test early on in their pregnancy.
Don’t Miss: How To Get Treated For Chlamydia Without Insurance
Almost Everyone Needs Tested
If youre sexually active and not in a long-term relationship, you should be tested for STDs on a regular basis. The federal Centers for Disease Control and Prevention offers this general testing guide:
- Everyone 13 to 64: At least once for HIV.
- Sexually active women under 25: Yearly for chlamydia and gonorrhea.
- All pregnant women: Tested for syphilis, HIV and hepatitis B
- All women in at-risk pregnancies: Tested for chlamydia and gonorrhea.
- Those having unprotected sex or sharing needles: Yearly for HIV.
Also, sexually active bisexual or gay men should get frequent tests for HIV, up to every 3-6 months, and yearly tests for syphilis, chlamydia, and gonorrhea.
Does Chlamydia Cause Cervical Cancer
No, chlamydia doesn’t cause cervical cancer.
It’s possible to get a sexually transmitted infection by having sex with someone who has an STI, even if they have no symptoms.
The following measures will help protect you from most STIs including chlamydia, gonorrhoea and HIV.
If you have an STI, they’ll also help prevent you from passing it on to someone:
- Use condoms every time you have vaginal or anal sex.
- If you have oral sex , use a condom to cover the penis, or a dam to cover the vulva or anus.
- Avoid sharing sex toys. If you do share them, wash them or cover them with a new condom before anyone else uses them.
Recommended Reading: How Long Should You Wait After Chlamydia Treatment
How To Help Partners Get Treatment
If you are not sure whether your sexual partner will seek treatment, ask your doctor for extra chlamydia medication . You can give it to them so they can be treated as soon as possible.
This is known as patient delivered partner therapy for chlamydia. Talk to your doctor to see if PDPT is right for you and your sexual partner.
Taking The Incorrect Medication
Keep in mind that your treatment can fail if you’re taking the wrong medication. You might be prescribed the wrong drugs due to syndromatic treatment, an efficient, but sometimes inaccurate treatment method in which patients are prescribed STD treatment based on symptoms, rather than testing. This is sometimes done in STD clinics when there is a concern that the patient might not come back for their test results.
And you could be taking the wrong medication if you’ve acquired it on your own and chose the wrong onessuch as taking medication that was prescribed for a past STD you had, or for your partner, or for a friend.
Not all STDs are caused by the same pathogens . Different illnesses require different treatments.
That’s why it’s so important for your healthcare provider to correctly identify what’s causing your infection. That’s also why you can’t just take any random antibiotic and hope it’s going to work.
Recommended Reading: Can You Not Get Chlamydia From Someone That Has It
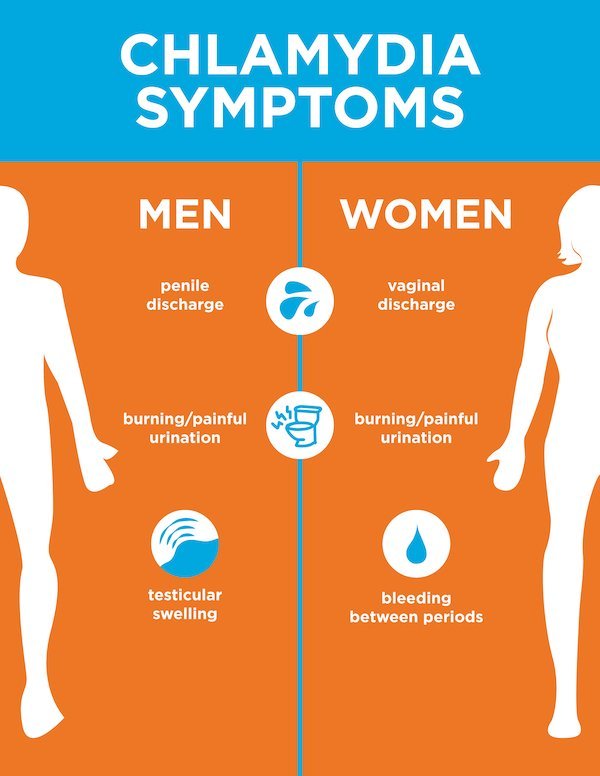
What Are The Symptoms Of Chlamydia
Chlamydia doesn’t usually cause any symptoms. So you may not realize that you have it. People with chlamydia who have no symptoms can still pass the disease to others. If you do have symptoms, they may not appear until several weeks after you have sex with an infected partner.
Symptoms in women include
If the infection spreads, you might get lower abdominal pain, pain during sex, nausea, or fever.
Symptoms in men include
- A burning sensation when urinating
- Burning or itching around the opening of your penis
- Pain and swelling in one or both testicles
If the chlamydia infects the rectum , it can cause rectal pain, discharge, and/or bleeding.
Randomization Specimen Collection And Testing Procedures
Patients with a positive urogenital CT nucleic acid amplification test were randomized for chlamydia retesting, either 8, 16, or 26 weeks after they received treatment, advised on partner notification, and counselled. The randomization procedure was automated within the electronic patient file, and the moment of clicking a button determined the randomization category, which switched invisibly every 2 seconds. After clicking, the randomization category appeared on the screen, and the patient was informed by the nurse when to expect an invitation for retesting. Patients were free to choose between 2 retest options: either collect a self-sample at home with a home collection kit , or return to the clinic for an on-site self-collected sample. Those who chose home collection received an email 7 days before the scheduled time of retest, informing them they would receive a self-collection kit within the next week, with a preaddressed return envelope. To those who chose to return to the clinic, an email with an open invitation was sent 7 days before the scheduled time of retest. Regardless of the chosen option, email and/or SMS reminders were sent 7 and 14 days after the scheduled retest time to all patients who failed to provide a retest sample at the planned date.
You May Like: Why Wont My Chlamydia Go Away
When Will The Signs And Symptoms Go Away
You should notice an improvement quite quickly after having treatment.
- Discharge or pain when you urinate should improve within a week.
- Bleeding between periods or heavier periods should improve by your next period.
- Pelvic pain and pain in the testicles should start to improve quickly but may take up to two weeks to go away.
If you have pelvic pain or painful sex that doesnt improve, see your doctor or nurse as it may be necessary to have some further treatment or investigate other possible causes of the pain.
What Happens If Chlamydia Isn’t Treated
Only some people who have chlamydia will have complications. If chlamydia is treated early, its unlikely to cause any long-term problems. But, without proper treatment, the infection can spread to other parts of the body. The more times you have chlamydia the more likely you are to get complications.
- If you have a vulva, chlamydia can spread to other reproductive organs causing pelvic inflammatory disease . This can lead to long-term pelvic pain, blocked fallopian tubes, infertility and ectopic pregnancy .
- In people with a vulva, chlamydia can also cause pain and inflammation around the liver, though this is rare. This usually gets better with the correct antibiotic treatment.
- If you have a penis, chlamydia can lead to infection in the testicles. If this isnt treated, theres a possibility it could affect your fertility but more research is needed to understand how likely this is.
- Rarely, chlamydia can lead to inflammation of the joints. This is known as Sexually Acquired Reactive Arthritis and is sometimes accompanied by inflammation of the urethra and the eye. This is more likely to occur in people with a penis than people with a vulva.
Don’t Miss: My Partner Has Chlamydia But I Don T
How Accurate Are The Tests
The accuracy of a chlamydia test depends on the kind of test used and the type of sample thats collected. The recommended tests are over 95% accurate in picking up chlamydia. As no test is 100% accurate theres a small chance that the test will give a negative result when you do have chlamydia. This is known as a false negative result. This can sometimes explain why you might get a different result from another test or why you and a partner might get a different test result.
Its possible for the test to be positive if you havent got chlamydia, but this is rare.
Treating Chlamydia During Pregnancy
If a pregnant woman is infected with chlamydia, it is important to treat it due to complications it can cause during pregnancy. According to the CDC, chlamydia has been associated with preterm delivery.4 You can give chlamydia to your baby during childbirth, which can cause the baby to be born with pneumonia and conjunctivitis.
Talk to your prescribing physician about antibiotics you can take while pregnant.
Should You Retest After Treatment?
If you have been recently treated and want to retest to be sure the treatment worked, wait at least 3-4 weeks after completing your treatment. The CDC recommends retesting three months after treatment, preferably along with your partner, so that you can be sure that all of you are chlamydia free.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Early Signs Of Chlamydia