How Is Chlamydia Spread
You can get chlamydia by having vaginal, anal, or oral sex with someone who has chlamydia.
If your sex partner is male you can still get chlamydia even if he does not ejaculate .
If youve had chlamydia and were treated in the past, you can still get infected again. This can happen if you have unprotected sex with someone who has chlamydia.
What Happens If Chlamydia Goes Untreated
If a person is not treated for chlamydia, complications may occur. Women frequently develop pelvic inflammatory disease . PID can cause infertility , chronic pelvic pain, tubal pregnancies, and the continued spread of the disease. In men, untreated chlamydia can cause urethral infection and complications such as swollen and tender testicles. Chlamydia infection during pregnancy may result in premature rupture of membranes, preterm delivery and possible tubal pregnancy in a small percent of women. In addition, chlamydia can cause conjunctival and pneumonic infection in the newborn. Persons with a chlamydia infection have an increased chance of getting other infections such as gonorrhea or HIV.
Essential Facts About Chlamydia
Chlamydia often causes no symptoms in the short term, but it can have serious health consequences if it goes untreated.
If youre sexually active, you should know about chlamydia, a common sexually transmitted bacterial infection. These 10 facts will bring you up to speed on whos at risk, why regular screening is so important, and how to avoid getting chlamydia and other sexually transmitted infections .
You May Like: How To Take Chlamydia Medication
Chlamydia In The Rectum Throat Or Eyes
Chlamydia can also infect:
- the rectum if you have unprotected anal sex this can cause discomfort and discharge from your rectum
- the throat if you have unprotected oral sex this is uncommon and usually causes no symptoms
- the eyes if they come into contact with infected semen or vaginal fluid this can cause eye redness, pain and discharge
Chlamydia Can Lead To Infertility

A lot of us don’t realize that some sexually transmitted diseases can cause no symptoms, meaning you could have an STD and not know it. And some STDs can silently lead to infertility, ectopic pregnancy, or chronic pelvic pain.
Chlamydia is one of those diseases. CDC estimates that more than 2.8 million people are infected each year.
Chlamydia is most common in sexually active young adults. More than half of all infections involve people ages 18 to 24. You can get chlamydia during oral, vaginal, or anal sexual contact with an infected partner. The disease can cause penile discharge in men and infertility in women. It can also cause serious health problems in newborn babies of infected mothers.
Many women, and some men, are infected with chlamydia but don’t know it. Even without symptoms, the disease can cause complications, particularly infertility. The longer the infection is untreated, the more damage that can be done.
If symptoms do show up, they usually occur within weeks of exposure. Men and women may face painful urination, an abnormal discharge from the urethra, or both. Women also may have abdominal pain, bleeding, and an abnormal discharge from the vagina. Symptoms usually appear within one to three weeks after being infected and may be very mild.
In pregnant women, chlamydia can cause premature delivery, the CDC says. A child born to an infected woman can develop an infection in their eyes and respiratory tracts.
Recommended Reading: I Got Treated For Chlamydia
Why Early Detection Is Necessary
When symptoms reach a stage that patients end up in the emergency room, those with undiagnosed STIs are often misdiagnosed. In fact, studies show that almost two thirds of them are diagnosed with and treated for a UTI. This will not clear up chlamydia, since its a short course of antibiotics that are typically used.
Because its left undiagnosed and untreated, chlamydia often involves serious complications that are life altering. Because it resides in the mucusy parts of the body, chlamydia can affect not just the sexual organs but also the anus, the eyelids, and the throat. One of the most common complications of untreated chlamydia is pelvic inflammatory disease, or PID, which has its own set of concerns, including complications during pregnancy. Other problems include:
- Pain and inflammation in the sexual organs, as well as in the prostate in men
- Damage to the tear ducts and the cornea
- Infertility in both men and women
How Do I Know If I Have Chlamydia
Most people who have chlamydia have no symptoms. If you do have symptoms, they may not appear until several weeks after you have sex with an infected partner. Even when chlamydia causes no symptoms, it can damage your reproductive system.
Women with symptoms may notice
- An abnormal vaginal discharge
- A burning sensation when urinating.
Symptoms in men can include
- A discharge from their penis
- A burning sensation when urinating
- Pain and swelling in one or both testicles .
Men and women can also get infected with chlamydia in their rectum. This happens either by having receptive anal sex, or by spread from another infected site . While these infections often cause no symptoms, they can cause
- Rectal pain
- Discharge
- Bleeding.
You should be examined by your doctor if you notice any of these symptoms or if your partner has an STD or symptoms of an STD. STD symptoms can include an unusual sore, a smelly discharge, burning when urinating, or bleeding between periods.
You May Like: Can You Give Someone Chlamydia After Being Treated
If I Have Chlamydia Once Am I Immune To It
- If you have chlamydia, don’t have sex until your symptoms clear up and you get the okay from your doctor
- Use condoms when having sex to protect you from STD transmission
- Get tested for STDs regularly
- Get tested for STDs when beginning a new intimate relationship. Ask your partner to get tested, too, for good measure.
Does Your Partner Need To Get Treated Too
If you have a sexual partner, or if youve recently had sex with someone, talk with them about your chlamydia diagnosis. Theyll need to get tested and treated, too.
If your sexual partner doesnt seek treatment, theres a risk that they can transmit it back to you, even after your infection has been cured.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Test For Oral Chlamydia
How To Help Partners Get Treatment
If you are not sure whether your sexual partner will seek treatment, ask your doctor for extra chlamydia medication . You can give it to them so they can be treated as soon as possible.
This is known as patient delivered partner therapy for chlamydia. Talk to your doctor to see if PDPT is right for you and your sexual partner.
What Happens If I Dont Get Treated
The initial damage that chlamydia causes often goes unnoticed. However, chlamydia can lead to serious health problems.
If you are a woman, untreated chlamydia can spread to your uterus and fallopian tubes . This can cause pelvic inflammatory disease . PID often has no symptoms, however some women may have abdominal and pelvic pain. Even if it doesnt cause symptoms initially, PID can cause permanent damage to your reproductive system. PID can lead to long-term pelvic pain, inability to get pregnant, and potentially deadly ectopic pregnancy .
Men rarely have health problems linked to chlamydia. Infection sometimes spreads to the tube that carries sperm from the testicles, causing pain and fever. Rarely, chlamydia can prevent a man from being able to have children.
Also Check: How Long Does Chlamydia Last Without Treatment
What Exactly Causes Chlamydia
A type of bacterium called Chlamydia trachomatis causes chlamydia. This bacterium can take hold in the tissues of your genitals, anus, eyes, or throat.
Its usually transmitted from one person to another during penetrative vaginal or anal sex or oral sex, although sex without penetration can also transmit it.
Chlamydia can also be transmitted to a baby during vaginal delivery if the person giving birth has an untreated chlamydia infection.
Who Is At Risk For Chlamydia
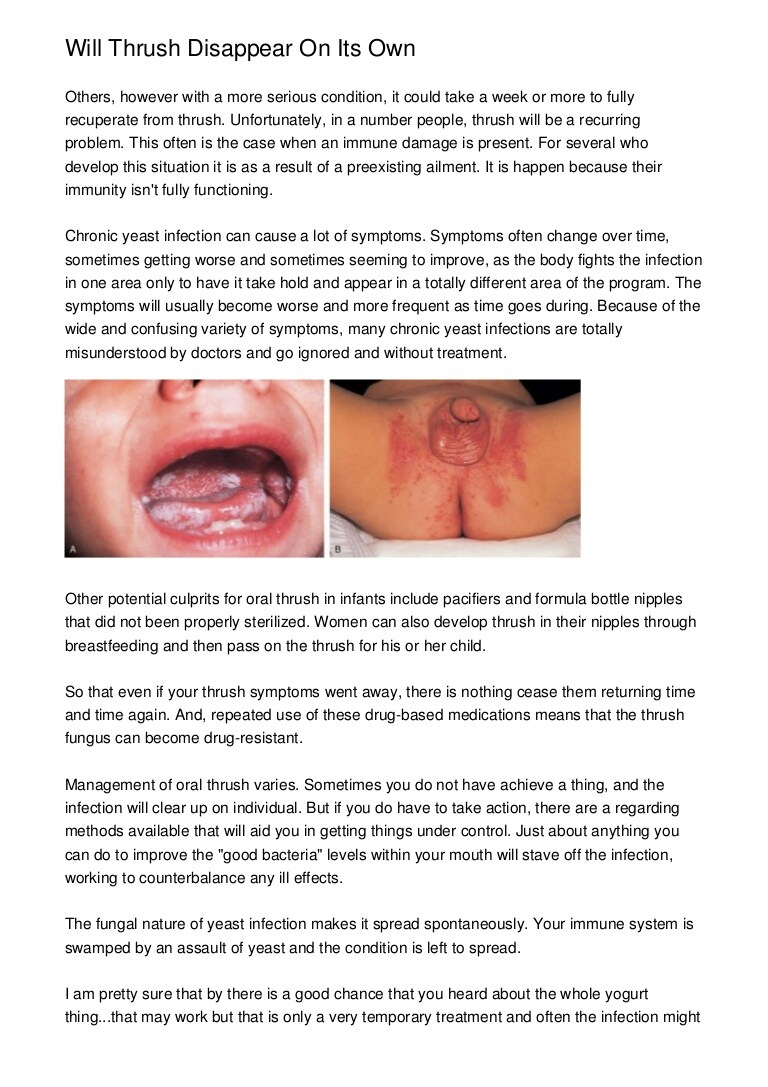
Any sexually active person can be infected with chlamydia. It is a very common STD, especially among young people.3 It is estimated that 1 in 20 sexually active young women aged 14-24 years has chlamydia.5
Sexually active young people are at high risk of acquiring chlamydia for a combination of behavioral, biological, and cultural reasons. Some young people dont use condoms consistently.15 Some adolescents may move from one monogamous relationship to the next more rapidly than the likely infectivity period of chlamydia, thus increasing risk of transmission.16 Teenage girls and young women may have cervical ectopy .17 Cervical ectopy may increase susceptibility to chlamydial infection. The higher prevalence of chlamydia among young people also may reflect multiple barriers to accessing STD prevention services, such as lack of transportation, cost, and perceived stigma.16-20
Men who have sex with men are also at risk for chlamydial infection since chlamydia can be transmitted by oral or anal sex. Among MSM screened for rectal chlamydial infection, positivity has ranged from 3.0% to 10.5%.6.7 Among MSM screened for pharyngeal chlamydial infection, positivity has ranged from 0.5% to 2.3%.7.8
Recommended Reading: How Long Does Chlamydia Last
How Long Can You Have Chlamydia Before It Causes Damage
If left untreated, chlamydia can cause a number of complications. Its difficult to determine how long it takes for the infection to cause damage because every person and body is different.
Some people have strong immune systems that can keep the infection at bay for longer, while others will struggle.
If the bacteria move from the vaginal canal into the uterus, the infection will develop into PID and cause damage. Chlamydia bacteria can also inflame the lining of the uterus, causing scarring. When scar tissue develops, it can make it difficult for a fertilized egg to implant in the uterine lining.
The trouble with chlamydia is that most people dont realize they have it until its already caused some damage. In fact, people dont have symptoms 70% of the time.
One in five women with chlamydia will develop PID.
How Long Does Gonorrhea Last Untreated?
Gonorrhea affects each person differently. The effects of the STI will depend on the strength of the immune system and whether the strain of gonorrhea is resistant to antibiotics.
But what happens if the infection goes untreated? Gonorrhea is often asymptomatic, meaning most people dont experience any symptoms. To make matters worse, the symptoms may come and go, leading you to believe that the infection cleared on its own.
In most cases, gonorrhea does not clear up on its own nor will chlamydia.
If thats not possible, get tested after sex with a new partner, whether it was protected or unprotected sex.
Risk Factors And Demographic Factors For Chlamydia Trachomatis Infection
The most common demographic correlate of infection with chlamydial infection in women is young age . This could be explained by the anatomic differences in the cervix of the younger women, wherein the squamo-columnar junction, a primary host target for C. trachomatis, is everted and thus more exposed. Other factors associated with chlamydial infection include unmarried status, nulliparity, black race and poor socio-economic condition. A large number of sexual partners, a new sexual partner, lack of use of barrier contraceptive devices and concurrent gonococcal infection are also known to be associated with chlamydial infection. Cervical chlamydial infections are also found to be associated with the use of oral contraceptives.
You May Like: Does Garlic Get Rid Of Chlamydia
How Long Can You Have Chlamydia Without Knowing Years Or Months
How long can you have chlamydia without knowing is a common question after an unprotected sexual contact.
What is chlamydia infection?
Chlamydia infection, caused by Chlamydia trachomatis, is a common sexually transmitted infection that affects both men and women. In the united stated, more than 1.4 million new cases of chlamydia are detected yearly.
Chlamydia can affect the eyes , the joints, the vagina, anus and the penis. It may sometimes cause infertility if left untreated in men and women.
In women, chlamydia infection can ascend up the genital tracts resulting to pelvic inflammatory disease with symptoms like fever, abdomen pain and difficulty conceiving.
Chlamydia trachomatis infection is transmitted through
- Unprotected anal intercourse
If youve had intercourse with these symptoms, then its likely you have chlamydia. You should inform your doctor ASAP or get a chlamydia test kit to detect chlamydia.
Chlamydia Trachomatis And Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Twenty per cent of the women with chlamydial lower genital tract infection will develop PID and 4 per cent will develop chronic pelvic pain. The clinical spectrum of chlamydial PID ranges from subclinical endometritis to frank salpingitis, tubo-ovarian masses, pelvic peritonitis, periappendicitis and perihepatitis. However, symptomatic chlamydial infections represent only the tip of the iceberg of all chlamydial infections as majority of genital chlamydial infections are asymptomatic.
You May Like: How Many Mg Of Azithromycin To Treat Chlamydia
Can Chlamydia Go Away And Come Back
If youve had unprotected intercourse, its likely you may not have chlamydia if your partner is not infected. If treated chlamydia can go away and not come back if you abstain or ensure protected sex.
However, dont assume chlamydia will go away without taking medications. You may not have symptoms immediately and may still have chlamydia long-term problems.
How Can You Get Rid Of Chlamydia
If your chlamydia test comes back positive, you may be wondering how to get chlamydia treated. Itâs important to discuss treatment options with your healthcare provider. Most likely, you will be treated for chlamydia with oral antibiotics. With treatment, infections often clear up in one to two weeks.
Even if your symptoms resolve sooner, however, itâs very important to complete your healthcare providerâs entire course of prescribed antibiotics. Otherwise, the infection may not be completely eliminated and you could be at risk for reinfection. You could also still pass chlamydia to a partner if you donât complete the recommended course of antibiotics.
Finally, as part of your treatment for chlamydia, connect with any sexual partners you may have unintentionally exposed to this infection. Your healthcare provider may also recommend antibiotics for your partner. This is a key part of chlamydia treatment, since it can help prevent reinfection when you resume sexual intercourse.
Chlamydia is a potentially harmful infection, but fortunately, itâs easy to test for. Itâs also simple to treat when you have a confirmed diagnosis. The important thing is stay informed and know your statusâsomething you can do from the privacy and comfort of home with our STD Test for women.
References
1. Overview: Chlamydia. National Health Service. URL. Accessed March 27, 2020.
2. Chlamydia – CDC Fact Sheet. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. URL. Accessed March 27, 2020.
Also Check: Pills To Take For Chlamydia
How Much Does The Test Cost
The cost of chlamydia testing varies based on many factors. Chlamydia testing may be paid for by health insurance when ordered by a doctor. Because health plans vary, its important for patients to discuss the cost of testing, including any copays or deductibles, with their health plan.
For patients without health insurance coverage, the cost of testing may include the cost of the office visit and sample collection as well as technician fees. Testing may also be available for free or at low cost through community-based organizations and local health departments.
What Happens If You Dont Seek Treatment
If you take your antibiotics as directed, chlamydia is likely to go away. But if its left untreated, it can cause a few complications.
For example, if you have a vulva, you could develop pelvic inflammatory disease . PID is a painful infection that could damage your uterus, cervix, and ovaries.
Untreated chlamydia can also lead to scarred fallopian tubes, which can cause infertility.
If youre pregnant, untreated chlamydia can be transmitted to the baby during vaginal delivery. Chlamydia can cause eye infections and pneumonia in newborns.
Untreated chlamydia can lead to epididymitis, which is when the epididymis becomes inflamed, causing pain.
Chlamydia can also spread to the prostate gland, which can lead to painful sex, lower back pain, and a fever.
Fortunately, treatment for chlamydia is relatively straightforward. And if its treated quickly, youre unlikely to experience any long-term complications.
Don’t Miss: Can You Treat Chlamydia Naturally
How Common Is Chlamydia
CDC estimates that there were four million chlamydial infections in 2018.3 Chlamydia is also the most frequently reported bacterial sexually transmitted infection in the United States.4 However, a large number of cases are not reported because most people with chlamydia are asymptomatic and do not seek testing. Chlamydia is most common among young people. Two-thirds of new chlamydial infections occur among youth aged 15-24 years.3 It is estimated that 1 in 20 sexually active young women aged 14-24 years has chlamydia.5
Disparities persist among racial and ethnic minority groups. In 2019, reported chlamydia rates for African Americans/Blacks were nearly six times that of Whites.4 Chlamydia is also common among gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men . Among MSM screened for rectal chlamydial infection, positivity has ranged from 3.0% to 10.5%.6,7 Among MSM screened for pharyngeal chlamydial infection, positivity has ranged from 0.5% to 2.3%.7.8
How Is Chlamydia Treated
If detected early, chlamydia can be treated with a single dose of antibiotic.
If complications from chlamydia infection are present such as pelvic inflammatory disease in women a longer course of antibiotics will be required.
Do not have sex for 7 days after you and your current partner have completed treatment. This includes all kinds of sex with or without a condom.
You can get reinfected with chlamydia if you have sex within the 7 days.
After you have completed treatment, have another test for chlamydia in 3 months time to make sure you have not been re-infected.
Recommended Reading: The Difference Between Gonorrhea And Chlamydia