How Common Is It
Oral chlamydia is not as common as genital chlamydia. Research shows that approximately 10% of people who visited a sexually transmitted disease clinic had genital chlamydia, but only 1.5% also had an infection in the throat.
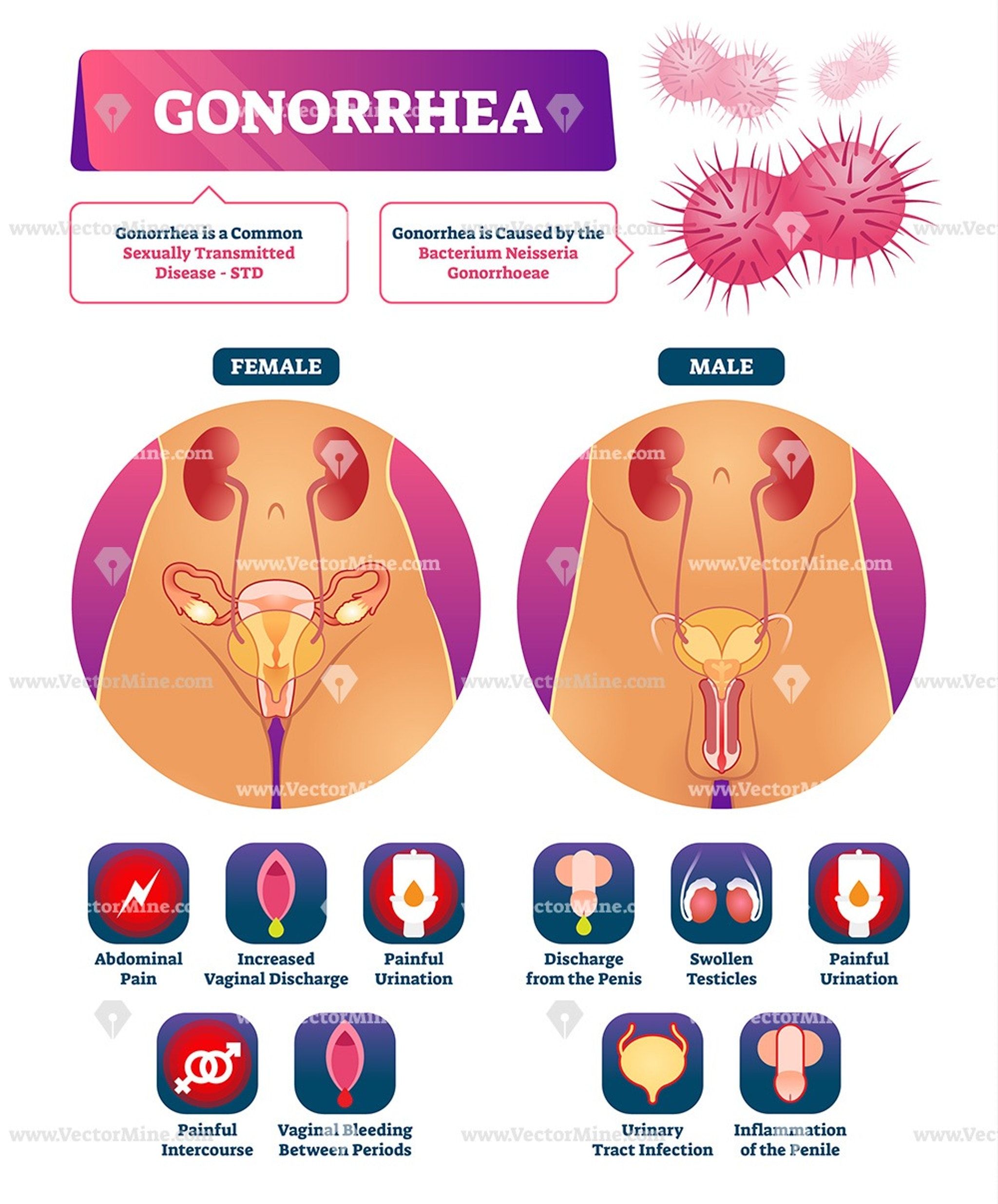
Genital gonorrhea is not as common as genital chlamydia, but oral gonorrhea is more common than oral chlamydia.
Chlamydia And Gonorrhea Symptoms
The symptoms of chlamydia and gonorrhea overlap, so it can be difficult to differentiate between the two unless you visit your healthcare provider or take a test for chlamydia or gonorrhea.
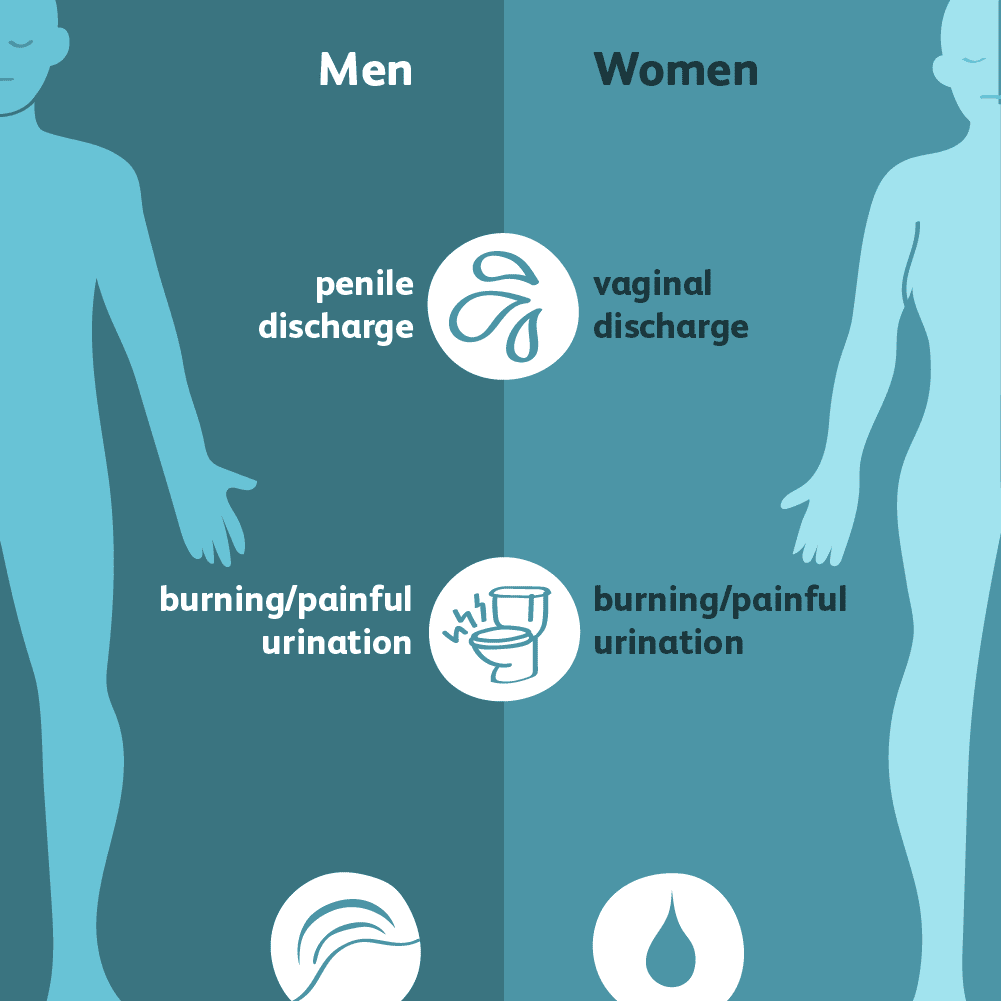
The overlapping symptoms for chlamydia and gonorrhea in men and women include:
- A burning sensation during urination
- Abnormal genital or rectal discharge
- Pain in the rectum
- Sore throat
With both chlamydia or gonococcal infections , men might also experience swelling and pain in the testicles and/or scrotum.
In women, both a gonorrhea and chlamydia infection might be mistaken for a yeast infection. Women may also experience painful periods, bleeding between periods, pain during sex, or abdominal pain.
Although the symptoms overlap, the discharge caused by chlamydia vs. gonorrhea can vary slightly. For a chlamydia infection, a womanâs vaginal discharge might have a strong odor and yellowish tint. Men might have a cloudy or clear discharge. With gonorrhea, both women and men may experience green, yellow, or white discharge.
If you’re a woman experiencing abnormal vaginal discharge or a man with abnormal penile discharge, be sure to consult your healthcare provider as soon as possible as this is a common sign of an infection.
Can Chlamydia Be Cured
Yes, chlamydia can be cured with the right treatment. It is important that you take all of the medication your doctor prescribes to cure your infection. When taken properly it will stop the infection and could decrease your chances of having complications later on. You should not share medication for chlamydia with anyone.
Repeat infection with chlamydia is common. You should be tested again about three months after you are treated, even if your sex partner was treated.
Read Also: Can Chlamydia Develop On Its Own
How Can I Reduce My Risk Of Getting Chlamydia
The only way to avoid STDs is to not have vaginal, anal, or oral sex.
If you are sexually active, you can do the following things to lower your chances of getting chlamydia:
- Be in a long-term mutually monogamous relationship with a partner who has been tested and has negative STD test results
- Use latex condoms the right way every time you have sex.
How Can I Prevent Getting Chlamydia And Gonorrhea
Get some information about their sexual history. Get some information about any recently treated diseases. Have safe sex with right utilization of a condom. Utilize a condom each time you have vaginal, oral, or butt-centric sex. Get tried for explicitly sent diseases in the event that you or your partner are not mono
gamous
Be abstinent
Read Also: Is Chlamydia Detected In A Blood Test
What Is Chlamydia And Gonorrhea
Both gonorrhea and chlamydia are common sexually transmitted infections occurring in men and women. So how do you get gonorrhea and chlamydia? They are transmitted through vaginal, anal, or oral sex with someone whoâs infected.
Both infections are caused by bacteriaâChlamydia trachomatis in cases of chlamydia and Neisseria gonorrhoeae in cases of gonorrhea.
Although gonorrhea is a common sexually transmitted infection, chlamydia has a higher prevalenceâwith over 1.7 million cases of chlamydia reported in the United States in 2017.
Risk factors for getting gonorrhea and chlamydia are often identical and include:
- Having multiple sex partners. You’re more likely to be exposed to someone with a sexually transmitted infection if you have multiple sex partners.
- Unprotected sex. Condom usage during sex substantially reduces the risk of getting a sexually transmitted infection, so your risk is higher if you have unprotected sex.
- Having other STIs: If you already have a sexually transmitted infection, you can be at a greater risk of getting another STI. For example, if you contract chlamydia, you could be more likely to contract gonorrhea.
Always Practice Safe Sex
Notice how this is under a section titled How can you reduce your risk. Reduce being the operative word. Even if you always wear a condom or a dental dam, theres a risk of infection. This is because some diseases are spread from skin to skin contact, from bodily fluids touching a part of your body, or from defective prophylactics.
This includes vaginal, anal, and oral sex. So if youre in high school and think that by going down on someone youre safe, hopefully youre reading this before going to that party.
Recommended Reading: Signs You May Have Chlamydia
How Is Chlamydia Spread
You can get chlamydia by having vaginal, anal, or oral sex with someone who has chlamydia.
If your sex partner is male you can still get chlamydia even if he does not ejaculate .
If youve had chlamydia and were treated in the past, you can still get infected again. This can happen if you have unprotected sex with someone who has chlamydia.
What Are Chlamydia And Gonorrhea
Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted disease, affecting both men and women all over the world. It is a bacterial infection, transferred when having unprotected sex: anal, vaginal and oral. It affects all ages and can be easily passed from an infected person to another. The only way to prevent it is by not having sex. Other preventive measures include using a latex condom, consistently, every time you have sex limiting the number of sex partners, getting checked regularly and avoiding douching. Gonorrhea, also, is a bacterial infection considered to be a sexually transmitted disease. It is normally spread through unprotected sex with an infected person, whether its oral, vaginal, or anal.
Chlamydia symptoms, very similar to the gonorrheas, can be numerous, ranging from an abnormal vaginal discharge, and itching as well as burning sensation in the vaginal area, to having bleeding between periods and feeling pain during sex and urination. For men, symptoms are different and consist of a cloudy discharge, burning and itching at the tip of the penis, as well as feeling some pain and swelling around the area of the testicles. While the symptoms of both STDs are similar, the treatment plan is different.
Also Check: Is Chlamydia Medication Over The Counter
How Do You Know If You Have Chlamydia In Your Throat
Many people with chlamydia in the throat have no symptoms. The only way to know for certain if you have this sexually transmitted infection in the throat is to get tested by a healthcare provider. Possible signs that you may have oral chlamydia include a sore throat that doesnât go away, along with a low-grade fever swollen lymph nodes oral canker sores or white spots in the back of the throat.
In some cases, one might confuse these chlamydia symptoms with strep throat or some other kind of throat infection. That’s why testing for STDs is so important, so consult with your healthcare provider if you suspect you may have been infected with an oral sexually transmitted disease.
How Do People Get Chlamydia
Chlamydia is transmitted through sexual contact with the penis, vagina, mouth, or anus of an infected partner. Ejaculation does not have to occur for chlamydia to be transmitted or acquired. Chlamydia can also be spread perinatally from an untreated mother to her baby during childbirth, resulting in ophthalmia neonatorum or pneumonia in some exposed infants. In published prospective studies, chlamydial conjunctivitis has been identified in 18-44% and chlamydial pneumonia in 3-16% of infants born to women with untreated chlamydial cervical infection at the time of delivery.9-12 While rectal or genital chlamydial infection has been shown to persist one year or longer in infants infected at birth,13 the possibility of sexual abuse should be considered in prepubertal children beyond the neonatal period with vaginal, urethral, or rectal chlamydial infection.
People who have had chlamydia and have been treated may get infected again if they have sexual contact with a person infected with chlamydia.14
Also Check: How Long Do You Have Chlamydia
What Are The Signs Of Chlamydia Or Gonorrhea
Many people who have chlamydia or gonorrhea dont have any signs or symptoms. When there are symptoms, chlamydia and gonorrhea cause very similar things.
Women with symptoms may have:
- Abnormal discharge from the vagina
- Burning when they urinate
- Bleeding between periods
Men with symptoms may have:
- Abnormal discharge from the penis
- Burning when they urinate
- Painful or swollen testicles
Am I At Risk For Gonorrhea
Any sexually active person can get gonorrhea through unprotected vaginal, anal, or oral sex.
If you are sexually active, have an honest and open talk with your health care provider and ask whether you should be tested for gonorrhea or other STDs. If you are a sexually active man who is gay, bisexual, or who has sex with men, you should be tested for gonorrhea every year. If you are a sexually active woman younger than 25 years or an older woman with risk factors such as new or multiple sex partners, or a sex partner who has a sexually transmitted infection, you should be tested for gonorrhea every year.
Read Also: How To Make Chlamydia Go Away
What Are The Treatments For Gonorrhea Can Gonorrhea Be Cured
In the past, the treatment of uncomplicated gonorrhea was fairly simple. A single injection of penicillin cured almost every infected person. Unfortunately, there are new strains of gonorrhea that have become resistant to various antibiotics, including penicillins, and are therefore more difficult to treat. Fortunately, gonorrhea can still be treated by other injectable or oral medications.
Uncomplicated gonococcal infections of the cervix, urethra, and rectum, are usually treated by a single injection of ceftriaxone intramuscularly or by cefixime in a single oral dose. For uncomplicated gonococcal infections of the pharynx, the recommended treatment is ceftriaxone in a single IM dose.
Alternative regimens for uncomplicated gonococcal infections of the cervix, urethra, and rectum is spectinomycin in nonpregnant women in a single IM dose or single doses of cephalosporins , or cefotaxime).
It is important to note that doxycycline, one of the recommended drugs for treatment of PID, is not recommended for use in pregnant women.
Gonorrhea is one of the easier STIs to prevent because the bacterium that causes the infection can survive only under certain conditions. The use of condoms protects against gonorrhea infection. Since the organism can live in the throat, condoms should be used during oral-genital contact as well.
Is There A Cure For Chlamydia And Gonorrhea
Yes. Chlamydia and gonorrhea can both be cured with the right treatment. If these STDs arent treated, they can cause serious health problems, like making it difficult or impossible for a woman to get pregnant.
If you have an STD, its important to get treatment right away. Its also important to tell anyone youve had sex with that you have an STD so they can get treated, too. This can help protect you from getting infected again.
You May Like: How Much Is Chlamydia Medicine
How To Get Tested
A person can meet with a doctor to get a diagnosis for either of these infections.
The doctor will collect bodily fluids to test for the infection. The test can use either a urine sample or a sample from the vagina or penis, which a doctor will collect with a cotton swab.
Most health insurance plans, including Medicare, cover sexually transmitted infection testing completely. If a person does not have health insurance, they can go to a free clinic, their local health departments STI clinic, a student health center, or an urgent care clinic.
Because both chlamydia and gonorrhea can present with no symptoms, it is important that people who are sexually active get tested regularly.
After a doctor has determined which infection a person has contracted, they will prescribe an antibiotic.
People should take the full course of antibiotics and wait an additional 7 days before having sex again. This helps prevent a person from spreading the infection to another person and possibly reinfecting themselves later.
A person can contract both chlamydia and gonorrhea again, even if they have already experienced and treated the STI before.
Gonorrhea Chlamydia And Syphilis: Causes Symptoms And Treatment Options
When it comes to freaking out worthy events, being diagnosed with a sexually transmitted disease comes pretty close to the top.
What will happen to your nether regions ? Do they have a cure? How are you going to share this information with future sex partners? Youve got questions, weve got answers.
Don’t Miss: How Long Does Chlamydia Last Without Treatment
Can Chlamydia Be Prevented
The only sure way to prevent chlamydia is to not have vaginal, anal, or oral sex.
Correct usage of latex condoms greatly reduces, but does not eliminate, the risk of catching or spreading chlamydia. If your or your partner is allergic to latex, you can use polyurethane condoms.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Chlamydia And Gonorrhea
There is a wide range of sexually-transmitted diseases that every sexually active adult should be aware of, but two of the best-known and most common are chlamydia and gonorrhea. While both gonorrhea and chlamydia can be cured with proper medical treatment, recognizing the signs early is critical in obtaining timely care. While regular STD testing is one of the only no-fail methods for detecting STDs, being aware of the typical symptoms can be very helpful as well.
Here is a useful guide to the most common symptoms of chlamydia and gonorrhea, giving you a handy resource for supporting optimal sexual health. If you notice one or more of the symptoms below, its important to seek proper testing and treatment immediately.
Don’t Miss: How Soon Can I Test For Chlamydia
How Common Is Chlamydia
CDC estimates that there were four million chlamydial infections in 2018.3 Chlamydia is also the most frequently reported bacterial sexually transmitted infection in the United States.4 However, a large number of cases are not reported because most people with chlamydia are asymptomatic and do not seek testing. Chlamydia is most common among young people. Two-thirds of new chlamydial infections occur among youth aged 15-24 years.3 It is estimated that 1 in 20 sexually active young women aged 14-24 years has chlamydia.5
Disparities persist among racial and ethnic minority groups. In 2019, reported chlamydia rates for African Americans/Blacks were nearly six times that of Whites.4 Chlamydia is also common among gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men . Among MSM screened for rectal chlamydial infection, positivity has ranged from 3.0% to 10.5%.6,7 Among MSM screened for pharyngeal chlamydial infection, positivity has ranged from 0.5% to 2.3%.7.8
When To See A Healthcare Provider
It’s important to talk to your healthcare provider if you have any signs or symptoms of chlamydia, any other symptoms that concern you, or if you know or think you’ve been exposed to the infection.
According to the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, women 25 and under and those who are sexually active should be screened for chlamydia every year, as should older women who have an increased risk of infection.
Screening for other STIs/STDs is important as well, as the risk factors for chlamydia also increase the likelihood of contracting these other infections. If you are treated for chlamydia, be sure to tell your healthcare provider if any symptoms persist.
You May Like: Signs And Symptoms Of Chlamydia In Females
Im Pregnant How Does Chlamydia Affect My Baby
If you are pregnant and have chlamydia, you can pass the infection to your baby during delivery. This could cause an eye infection or pneumonia in your newborn. Having chlamydia may also make it more likely to deliver your baby too early.
If you are pregnant, you should get tested for chlamydia at your first prenatal visit. Testing and treatment are the best ways to prevent health problems.
Complications Of Oral Chlamydia
Chlamydia of the throat does not lead to complications in that area. The biggest concern with oral chlamydia is that people without symptoms are more likely to continue having sex and spreading the infection to other people.
Long-standing chlamydia infection most commonly leads to pelvic inflammatory disease , an infection and inflammation of the uterus and fallopian tubes. People with PID often have difficulties getting pregnant or are at risk of ectopic pregnancy.
Chlamydia infection can also cause an inflammatory reaction throughout the body that causes joint pain or conjunctivitis, an inflammation or infection in the eye.
Recommended Reading: How To Get A Chlamydia Prescription
In Both Males And Females
Complications that may be seen in anyone include:
- Other STIs. Chlamydia and gonorrhea both make you more susceptible to other STIs, including human immunodeficiency virus . Having chlamydia can also increase your risk of developing gonorrhea, and vice versa.
- Reactive arthritis . Also called Reiters syndrome, this condition results from an infection in your urinary tract or intestines. Symptoms of this condition cause pain, swelling, or tightness in your joints and eyes, and a variety of other symptoms.
- Infertility. Damage to reproductive organs or to sperm can make it more challenging or, in some cases, impossible to become pregnant or to impregnate your partner.
Danger Factors For Getting Gonorrhea And Chlamydia Are Frequently Indistinguishable And Include:
- Having numerous sex partners. Youre bound to be presented to somebody with an explicitly sent contamination if you have numerous sex partners.
- Unprotected sex. Condom utilization during sex generously decreases the danger of getting a sexually transmitted infection, so your danger is higher if you have unprotected sex.
- Having different STIs: If you as of now have a sexually transmitted infection, you can be at a more serious danger of getting another STI. For instance, if you contract chlamydia, you could be bound to contract gonorrhea.
Don’t Miss: Can You Pass Chlamydia Without Having It