How Do You Get Chlamydia
Chlamydia is usually passed on through unprotected vaginal, anal or oral sex.
Chlamydia can be passed on through genital contact. This means you can get chlamydia from someone who has the infection if your genitals touch, even if you dont have sex or ejaculate .
You can also get chlamydia if you come into contact with infected semen or vaginal fluid, or get them in your eye.
Chlamydia cant be passed on through kissing, hugging, sharing towels or using the same toilet as someone with the infection.
What Are The Symptoms Of Chlamydia
Chlamydia is known as a silent infection because most infected people are asymptomatic and lack abnormal physical examination findings. Estimates of the proportion of chlamydia-infected people who develop symptoms vary by setting and study methodology two published studies that incorporated modeling techniques to address limitations of point prevalence surveys estimated that only about 10% of men and 5-30% of women with laboratory-confirmed chlamydial infection develop symptoms.21.22 The incubation period of chlamydia is poorly defined. However, given the relatively slow replication cycle of the organism, symptoms may not appear until several weeks after exposure in those persons who develop symptoms.
In women, the bacteria initially infect the cervix, where the infection may cause signs and symptoms of cervicitis , and sometimes the urethra, which may result in signs and symptoms of urethritis . Infection can spread from the cervix to the upper reproductive tract , causing pelvic inflammatory disease , which may be asymptomatic 23 or acute, with typical symptoms of abdominal and/or pelvic pain, along with signs of cervical motion tenderness, and uterine or adnexal tenderness on examination.
Men who are symptomatic typically have urethritis, with a mucoid or watery urethral discharge and dysuria. A minority of infected men develop epididymitis , presenting with unilateral testicular pain, tenderness, and swelling.24
How Common Is Chlamydia
CDC estimates that there were four million chlamydial infections in 2018.3 Chlamydia is also the most frequently reported bacterial sexually transmitted infection in the United States.4 However, a large number of cases are not reported because most people with chlamydia are asymptomatic and do not seek testing. Chlamydia is most common among young people. Two-thirds of new chlamydial infections occur among youth aged 15-24 years.3 It is estimated that 1 in 20 sexually active young women aged 14-24 years has chlamydia.5
Disparities persist among racial and ethnic minority groups. In 2019, reported chlamydia rates for African Americans/Blacks were nearly six times that of Whites.4 Chlamydia is also common among gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men . Among MSM screened for rectal chlamydial infection, positivity has ranged from 3.0% to 10.5%.6,7 Among MSM screened for pharyngeal chlamydial infection, positivity has ranged from 0.5% to 2.3%.7.8
Read Also: Can Chlamydia Cause Prostate Cancer
Who Is At Risk For Chlamydia
Any sexually active person can be infected with chlamydia. It is a very common STD, especially among young people.3 It is estimated that 1 in 20 sexually active young women aged 14-24 years has chlamydia.5
Sexually active young people are at high risk of acquiring chlamydia for a combination of behavioral, biological, and cultural reasons. Some young people dont use condoms consistently.15 Some adolescents may move from one monogamous relationship to the next more rapidly than the likely infectivity period of chlamydia, thus increasing risk of transmission.16 Teenage girls and young women may have cervical ectopy .17 Cervical ectopy may increase susceptibility to chlamydial infection. The higher prevalence of chlamydia among young people also may reflect multiple barriers to accessing STD prevention services, such as lack of transportation, cost, and perceived stigma.16-20
Men who have sex with men are also at risk for chlamydial infection since chlamydia can be transmitted by oral or anal sex. Among MSM screened for rectal chlamydial infection, positivity has ranged from 3.0% to 10.5%.6.7 Among MSM screened for pharyngeal chlamydial infection, positivity has ranged from 0.5% to 2.3%.7.8
How Is It Possible To Get Chlamydia In Mouth Or Nose
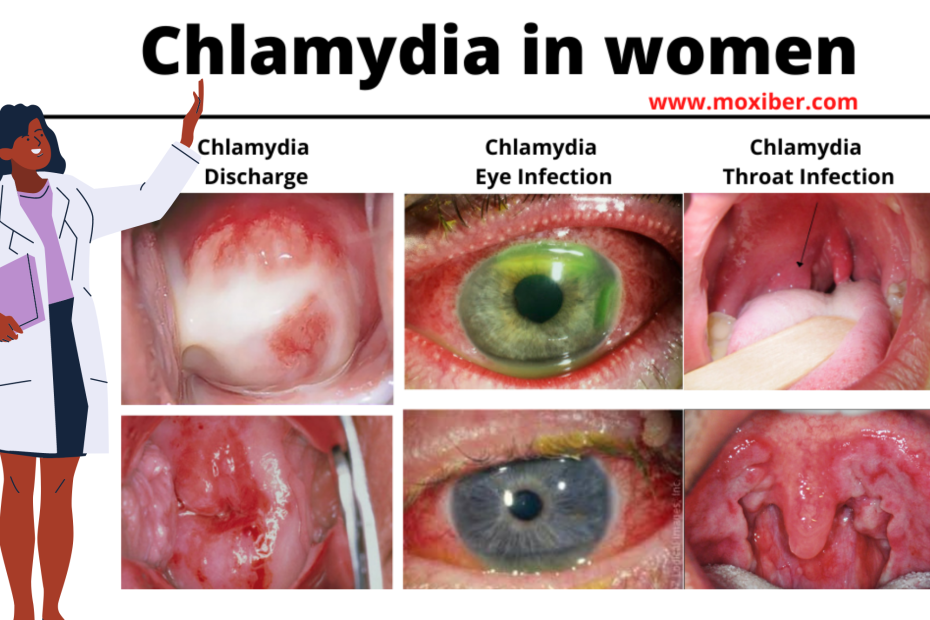
When a person is involved in oral sex with a person, who is already suffering from chlamydia, the risk of disease transmission increases. Note that, oral sex includes using lips, mouth, or tongue to cause stimulation of vagina, penis, and anus of another partner. Studies reveal that the risk of getting STD via oral sex usually depend upon the type of sexual activity performed, and on the type of infection, the person is already infected with. Generally, oral chlamydia transmission can happen if:
The strange fact is that the opposite is also true. The genital chlamydia can also occur from a person who is already suffering from oral chlamydia symptoms.
The cases include:
Don’t Miss: How Do Guys Get Tested For Chlamydia
Questions For Your Doctor About Test Results
It can be helpful to bring questions to your doctor to learn more about your chlamydia test results. Helpful questions may include:
- What is my chlamydia test result?
- Did my test check for any other STDs?
- Do I need any treatment based on my results?
- How can I talk to my sexual partners about chlamydia?
- When should I be tested for STDs and how often?
Chlamydia Treatment And Prevention
Milly DawsonSanjai Sinha, MDShutterstock
Chlamydia is easy to cure. If you test positive for chlamydia, basically you take an antibiotic, says Jill Rabin, MD, cochief in the division of ambulatory care for women’s health programs and prenatal care assistance program services for Northwell Health in New Hyde Park, New York.
Your partner must take an antibiotic, too, to keep them from reinfecting you, she says.
You have to have your partner treated, and if you have more than one partner, they should all be treated, says Dr. Rabin, regardless of your partners genders.
Even if you dont have chlamydia now, its wise to learn how to protect yourself so you wont develop this common infection in the first place. In women, chlamydia can create serious health problems, including infertility. Besides, no one ever wants to have a sexually transmitted disease and then have to tell other people about it.
Read Also: Can Chlamydia Test Be Wrong
How To Get Tested
Chlamydia testing is usually ordered by a doctor. In people without symptoms, a doctor can evaluate their risk and suggest an appropriate screening schedule. If a patient has symptoms of this infection, a doctor will order testing to diagnose or rule out chlamydia.
Testing for chlamydia can be conducted at a hospital, doctors office, health clinic, or community health program.
What Happens If Chlamydia Is Left Untreated For Too Long
When left untreated, chlamydia can increase your risk for other serious health problems, including HIV/AIDs and infertility.
Chlamydia can weaken your immune system to make you more vulnerable to other infections and diseases, including other STDs. According to the NIH, n females, untreated chlamydia can cause pelvic inflammatory disease, ectopic pregnancy, and infertility. In males, it may lead to infertility and infection of the epididymis. Untreated chlamydia may also cause arthritis, reports the NIH.
You May Like: How To Test For Oral Chlamydia
How Do You Prevent Chlamydia
Using a new male or female condom or dental dam every time you have sex is the best way to protect against chlamydia.
Chlamydia can be passed on by sharing sex toys. Always cover sex toys with a new condom and wash them after use to reduce your risk of getting chlamydia and other STIs.
Its important to regularly test for chlamydia, even if you dont have any symptoms, especially if youve had multiple sexual partners.
The contraceptive pill and other types of contraception wont prevent you getting chlamydia, and neither will PrEP.
How Do You Avoid Getting Mouth Chlamydia
How to avoid getting infected the only guaranteed way to avoid chlamydia is not having sex, but this is not a suitable options for most people. To reduce your chance of getting chlamydia you can try the following:
- Choose sexual partners carefully however difficult, you should try to discuss any previous sexual history with a new partner before you first have sex
- Get tested before the start of a new relationship and do not have unprotected sex until you know your test results and your partners an extended STI test kit which tests for chlamydia, gonorrhoea, HIV and syphilis is recommended
- Use barrier contraception such as the male condom carefully and correctly always apply the condom before any sexual contact, including oral sex
- If you are diagnosed with chlamydia, always follow the advice about treatment very carefully try to make sure, if you have had chlamydia once, you dont get it again and keep getting tested regularly
- Use condoms at the same time as other contraceptives other contraceptives dont protect against STIs and using condoms alone as a method of contraception has a high failure rate. Women are advised to use a reliable contraceptive method to avoid an unplanned pregnancy, but to use condoms as well, to reduce the chance of acquiring an STI
Who is it at a higher risk of STIs like oral chlamydia? risk factors for chlamydia include:
- Young age
- Multiple partners/frequent change of partner/overlapping partners
- Gay/bisexual men
Don’t Miss: Can Strep Throat Antibiotics Cure Chlamydia
How Common Is Mouth Chlamydia
It is difficult to be sure how commonly chlamydia is found in the throat, as study results are varied. In fact, most people with oral chlamydia do not have a sore throat and are unaware of the infection unless they test positive.
Its not always tested for the throat is not routinely sampled for chlamydia when you go for an STI screen. This is because current chlamydia tests may produce false positive results and cause anxiety. In addition, the chance of having oral chlamydia is extremely low .
When are people at risk? in a clinic, you may be offered a throat swab for chlamydia if there are other risk factors such as:
Signs And Symptoms Of Oral And Nose Chlamydia
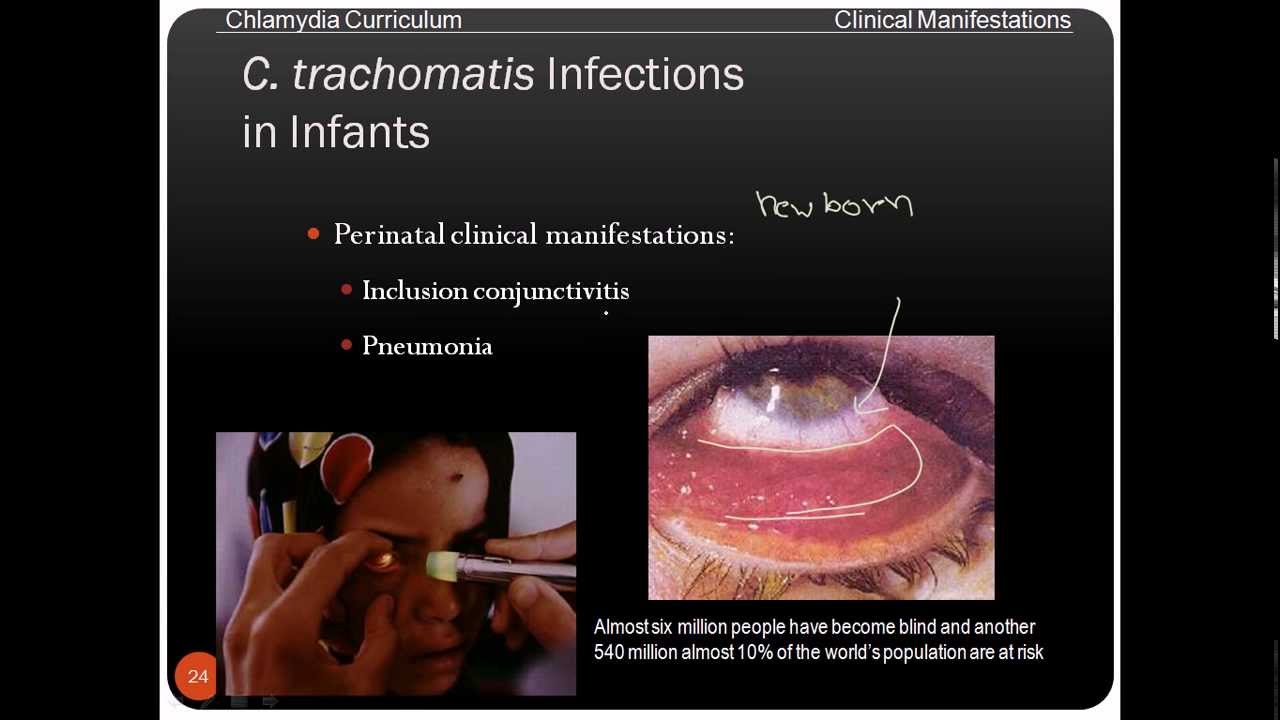
Most medical health reports reveal that Chlamydia lives like a silent infection in most people. In fact, around 50% of men and 75% of women do not show any specific symptom of this disease. However, in other cases, the person may show signs even within one to three weeks after getting infected. Males and females generally have similar kind of symptoms for oral and nose chlamydia, but few gender-specific symptoms can be observed as well.
The major impact of oral chlamydia is seen on cell lining and throat area. Most patients report a sore throat or pharyngitis, and it may last for several days. The level of discomfort may vary person to person when it has a major impact on the throat, a person usually face difficulty in swallowing. A sore throat is generally accompanied by low-grade fever, and people may also have swollen lymph nodes on the neck area. But in general, most people infected with oral chlamydia do not show any recognizable symptom however, nose chlamydia may have few.
Some of the most common symptoms associated with oral and nose chlamydia are listed below:
Read Also: Can I Get Tested For Chlamydia A Week After Treatment
How Can You Avoid Getting Oral Chlamydia
Practice safe sex consistentlyâsuch as using condoms during sex, including oral sexâto help lower your odds of contracting STIs like chlamydia from a sex partner. Making sure you regularly test for STIs is also important, especially if you may have been involved with an infected person. Though it might not directly prevent you from getting oral chlamydia, routine STI testing can be a powerful way to detect a chlamydial infection early onâbefore itâs been passed on to others or seriously affected your health. Because untreated chlamydia increases one’s risk of long-term health complications, be sure to speak with your healthcare provider as soon as possible if you think you might be infected or if you test positive.
To easily check for 6 common STIs , consider our at-home STD Test for women or men.
References
1. Chan PA, Robinette A, Montgomery M, et al. Extragenital Infections Caused by Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae: A Review of the Literature. Infect Dis Obstet Gynecol. 2016 2016:5758387. doi:10.1155/2016/5758387
2. Vonck RA, Darville T, O’Connell CM, Jerse AE. Chlamydial infection increases gonococcal colonization in a novel murine coinfection model. Infect Immun. 2011 79:1566-1577. doi:10.1128/IAI.01155-10
3. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease – CDC Fact Sheet. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. URL. Accessed January 31, 2020.
What Is The Treatment For Chlamydia
Chlamydia can be easily cured with antibiotics. HIV-positive persons with chlamydia should receive the same treatment as those who are HIV-negative.
Persons with chlamydia should abstain from sexual activity for 7 days after single dose antibiotics or until completion of a 7-day course of antibiotics, to prevent spreading the infection to partners. It is important to take all of the medication prescribed to cure chlamydia. Medication for chlamydia should not be shared with anyone. Although medication will stop the infection, it will not repair any permanent damage done by the disease. If a persons symptoms continue for more than a few days after receiving treatment, he or she should return to a health care provider to be reevaluated.
Repeat infection with chlamydia is common. Women whose sex partners have not been appropriately treated are at high risk for re-infection. Having multiple chlamydial infections increases a womans risk of serious reproductive health complications, including pelvic inflammatory disease and ectopic pregnancy. Women and men with chlamydia should be retested about three months after treatment of an initial infection, regardless of whether they believe that their sex partners were successfully treated.
Infants infected with chlamydia may develop ophthalmia neonatorum and/or pneumonia. Chlamydial infection in infants can be treated with antibiotics.
Don’t Miss: How To Get Rid Of Chlamydia Without A Doctor
More About Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
For women, one of the most serious complications from untreated chlamydia is pelvic inflammatory disease .
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, between 1020% of women with untreated chlamydia and gonorrhea infections may develop PID. And 1 in 8 women with a history of PID experience difficulties getting pregnant. PID can also cause ectopic pregnancy and chronic pelvic pain.
Like chlamydia, it is possible for a woman to have PID and not have any symptoms, or have symptoms too mild to notice, for an unknown period of time. If symptoms do occur, they could include:
- Dull pain or tenderness in the lower abdomen
- Burning or pain when you urinate
- Nausea and vomiting
- Increased or changed vaginal discharge
- Pain during sex
How Is Chlamydia Diagnosed
There are a number of diagnostic tests for chlamydia, including nucleic acid amplification tests , cell culture, and others. NAATs are the most sensitive tests, and can be performed on easily obtainable specimens such as vaginal swabs or urine.43
Vaginal swabs, either patient- or clinician-collected, are the optimal specimen to screen for genital chlamydia using NAATs in women urine is the specimen of choice for men, and is an effective alternative specimen type for women.43 Self-collected vaginal swab specimens perform at least as well as other approved specimens using NAATs.44 In addition, patients may prefer self-collected vaginal swabs or urine-based screening to the more invasive endocervical or urethral swab specimens.45 Adolescent girls may be particularly good candidates for self-collected vaginal swab- or urine-based screening because pelvic exams are not indicated if they are asymptomatic.
NAATs have demonstrated improved sensitivity and specificity compared with culture for the detection of C. trachomatis at rectal and oropharyngeal sites.40 Certain NAAT test platforms have been cleared by FDA for these non-genital sites and data indicate NAAT performance on self-collected rectal swabs is comparable to clinician-collected rectal swabs. 40
Don’t Miss: I Got A Shot For Chlamydia
Sex Partners Need Treatment Too
If you are diagnosed with chlamydia, you will need to tell all of your sexual partners, because they will need the same treatment you are receiving.
In most states, a doctor or other healthcare provider can give you the medicine that your partner or partners will need to take. Then you can deliver it to those partners. This practice is called expedited partner therapy or patient delivered partner therapy.
These options can help a lot if your partner doesnt have a healthcare provider or feels embarrassed about seeking care, says Dr. Dombrowski.
Its natural to feel nervous or upset about having to tell your partner or partners about having an STD. Your healthcare provider can help with this problem. They may even rehearse the conversation with you, says Dombrowksi.
Learning about chlamydia and seeking advice from a healthcare provider about how to discuss it with your partner can help you handle the conversation with less anxiety and more confidence.
Remember, chlamydia is not just common: It is the most common infection reported to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . You are being helpful, mature, and responsible by telling your partners.