Urogenital Infection In Women
In women, chlamydial infection of the lower genital tract occurs in the endocervix. It can cause an odorless, mucoid vaginal discharge, typically with no external pruritus, although many women have minimal or no symptoms.2 An ascending infection can result in pelvic inflammatory disease .
Physical findings of urogenital chlamydial infection in women include cervicitis with a yellow or cloudy mucoid discharge from the os. The cervix tends to bleed easily when rubbed with a polyester swab or scraped with a spatula. Chlamydial infection cannot be distinguished from other urogenital infections by symptoms alone. Clinical microscopy and the amine test can be used to help differentiate chlamydial infection from other lower genital tract infections such as urinary tract infection, bacterial vaginosis, and trichomoniasis.3 In addition, chlamydial infection in the lower genital tract does not cause vaginitis thus, if vaginal findings are present, they usually indicate a different diagnosis or a coinfection.
Some women with C. trachomatis infection develop urethritis symptoms may consist of dysuria without frequency or urgency. A urethral discharge can be elicited by compressing the urethra during the pelvic examination. Urinalysis usually will show more than five white blood cells per high-powered field, but urethral cultures generally are negative.
How Do I Test For Chlamydia
You can get tested for chlamydia even if you dont have any symptoms.
Getting tested for chlamydia is easy and doesnt hurt. A healthcare professional will ask for a urine sample and/or take a swab from the area that might be infected. This is usually the lower part of the womb or the vagina for women, and the tip of the penis for men. If youve had anal or oral sex, you may have a swab taken from your anus or throat.
In some countries you can get a self-testing kit to do at home.
If you test positive for chlamydia, its important to tell any recent sexual partner/s so they can also get tested, and treated if necessary. If you need advice about how to do this, speak to your healthcare professional. You should also test for other STIs.
Is There A Home Test For Trichomoniasis
Home trichomoniasis tests allow people to take a vaginal fluid or urine sample which is then sent to a lab for testing. These tests can be purchased as trichomoniasis-only tests or as multiple-STD tests. Results will take two to four days to receive. The cost of the lab test is usually included in the cost of the kit.
Read Also: What Are The Signs Of Having Chlamydia
What Increases Your Risk
Behaviors that will increase your risk of getting trichomoniasis include:
- Not using condoms when having sex with a new partner or a partner who may have been exposed to a sexually transmitted infection . It is possible for a partner to transmit the trich parasite without having any symptoms of the infection.
- Having many sex partners, which increases your risk of being exposed to someone who has trich. Teenagers and young adults are at higher risk for getting trich and other STIs, because their sex partners often have had other recent partners who may carry an STI.
You can get other STIs, such as gonorrhea, chlamydia, HIV, and syphilis, at the same time you get a trich infection. If one STI is diagnosed, testing for other STIs should be done so that all infections can be treated at the same time.
Some infections that can be spread through sexual contact, such as the human immunodeficiency virus infection, are life-threatening. Studies show that trich infection may increase the risk of transmitting HIV infection.footnote 2 Health professionals around the world are concerned about the increased risk of trichomoniasis and HIV.
Women who have trich may also be at risk for other vaginal infections such as yeast infections or bacterial vaginosis.
Barriers And Challenges To Diagnosis
The medical system does not fully meet the needs of some populations, including young people and men who have sex with men, regarding their sexual and reproductive health.
Ongoing barriers among young people include reluctance to use available health services, limited access to STI testing, worries about confidentiality, and the shame and stigma associated with STIs.
Men who have sex with men have a higher incidence of STIs than other groups. Since STIs are associated with a higher risk of human immunodeficiency virus infection, it is important to detect, diagnose, and manage STIs in this groupand in all high-risk groups. Rectal STIs are an independent risk factor for incident HIV infection. In addition, many men who have sex with men face challenges navigating the emotional, physical, and cognitive aspects of adolescence, a voyage further complicated by mental health issues, unprotected sexual encounters, and substance abuse in many, especially among minority youth. These same factors also impair their ability to access resources for preventing and treating HIV and other STIs.
You May Like: Why Is Penicillin Ineffective Against Chlamydia
Antibiotics For The Most Common Stds
Sexual activity is starting at a younger age today and many experiment without thinking about the repercussions. They may not be aware or educated about the many problems that can arise with sexually activity. This always leaves a concern of STD’s due to unsafe safe practices.
Do you think that you’re suffering from an STD? Find out more about the signs, symptoms and treatment of common STD’s below.
There are several common Sexually Transmitted Diseases or the newer term Sexually Transmitted Infections that are seen more often that others in the United States today. Chlamydia, Gonorrhea and Trichomonas are the most prevalent STD’s in the U.S. With appropriate antibiotic treatment these infections are curable.
The person may present with no symptoms, or have some overlapping of symptoms. Common symptoms include increased vaginal or penis discharge, painful urination and irritation or itching. There is a hallmark symptom that may help distinguish Trichomonas from Chlamydia or Gonorrhea. Malodorous frothy better described as bubbly, yellow, green discharge is characteristic of trich.
These sexually transmitted infections may be diagnosed clinically, but usually lab testing is done in order to verify the results. Testing is recommended for those who have had sexually activity, specifically risky behaviors such as: no protection or multiple partners. Common testing for STD’s includes a NAAT test, gram stain or urine test.
How Can I Prevent Contracting Trichomoniasis
Being sexually active puts people at risk for contracting an STI. Using condoms during every sex act can greatly reduce the risk of contracting trichomoniasis . Condoms should be used not just during ejaculation, but before any genital or sexual contact starts.
Ask all partners whether theyâve been tested recently for STIs before starting sexual contact. If a partner has sex with multiple people, ask about their STI status and encourage them to also get tested. Limiting the number of sexual partners you are exposed to will also decrease your risk of contracting trichomoniasis and other STIs.
If unprotected sex has occurred, or if symptoms of a trichomoniasis infection are present, visit your healthcare provider or local STI clinic for screening tests.
In addition, practices like douching should be avoided, as this may actually increase chances of contracting an STI .
Don’t Miss: How Do You Know If You Have Chlamydia Male
Trichomoniasis In Pregnant Women
Trichomoniasis during pregnancy raises the risk of prelabor rupture of membranes and preterm delivery. Treating the infection may not always reduce this risk, but it can relieve symptoms and prevent infection in the newborn. If you are pregnant and have trichomoniasis, talk to your doctor about the pros and cons of treatment.
Vaginal suppositories and creams aren’t effective in curing trich, but they may reduce discomfort and swelling in the genital area.
Cdc Updates Guidelines On Treatment Of Sexually Transmitted Infections
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has updated its guidelines for the treatment of people who have or are at risk for sexually transmitted infection .
Key changes were made to treatment recommendations for Neisseriagonorrhoeae, Chlamydiatrachomatis, Trichomonasvaginalis, pelvic inflammatory disease and
Mycoplasma genitalium.
Along with the AAP Red Book, the guidelines are a source of clinical guidance for the diagnosis, management and treatment of STIs based on current evidence.
Adolescent screening recommendations
Reported rates of STI, including chlamydia and gonorrhea, continue to rise across the U.S. Prevalence rates of certain STIs are highest among adolescents and young adults .
The CDC continues to recommend routine laboratory screening for common STIs for all sexually active AYA.
It also suggests providers consider opt-out screening for chlamydia and gonorrhea for AYA females regardless of reported sexual activity as part of a clinical visit. Cost-effectiveness analyses indicate that opt-out chlamydia screening among AYA females could increase screening significantly, save costs and identify STIs among youths who do not disclose their sexual behavior.
Chlamydia
Chlamydia continues to be the most commonly reported notifiable infectious disease in the U.S., and prevalence rates are highest among sexually active females ages 15-24.
Gonorrhea
If chlamydial co-infection cannot be excluded, doxycycline 100 mg orally twice daily for seven days should be added.
Read Also: What Are The Chances Of Getting Chlamydia
Summary Of Chlamydia Vs Trichomonas Infection
- Chlamydiacauses either a pneumonia infection or an STD depending on the species of bacterium that s involved.
- Trichomonas is a parasite that causes an STD infection in men and women.
- Chlamydia is caused by a bacterium that invades the cells of the host and lives inside these cells.
- Trichomonas is caused by a flagellated protozoan parasite that lives outside the cells of the host.
- Having many sexual partners increases the risk of catching C. trachomatis and T. vaginalis.
Strategies For Treatment And Control
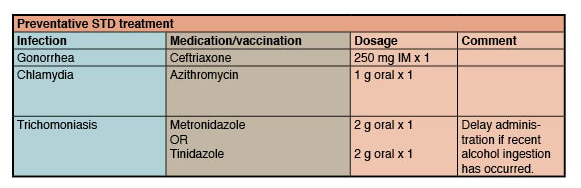
Historically, people treated for gonorrhea have been treated for chlamydia at the same time, as these diseases tend to go together. This can be with a single intramuscular dose of ceftriaxone for the gonorrhea plus a single oral dose of azithromycin for the chlamydia. For patients who have only gonorrhea, this double regimen may help prevent the development of resistant gonorrhea strains.
Chlamydia treatment is also detailed in .
Treatment recommendations for common sexually transmitted infections
All the patients sexual partners in the previous 60 days should be tested and treated, and expedited partner therapy should be offered if possible. Patients should be advised to have no sexual contact until they complete the treatment, or 7 days after single-dose treatment. Testing should be repeated 3 months after treatment.
Also Check: What Antibiotic Treat Chlamydia And Trichomoniasis
Can I Get Trichomoniasis More Than Once
Its possible to get trich multiple times. Approximately one in five people who are treated for trich become infected again within three months. To prevent reinfection, you and your sexual partners should take anti-infective medications at the same time. After finishing treatment, you should wait a week before having sex to give the medication time to work and for symptoms to go away.
Transmission Questions: Can A Man Give A Woman Trichomoniasis

One of the most common search terms for trich is can a man give a woman trichomoniasis? The short answer is, yes. Absolutely.Trichaffects both men and women. The infection can be spread through sexual intercourse as well as skin-to-skin contact. However, it is not spread by shaking hands, kissing, or other types of touching.
The CDC estimates that nearly three million people in the United States are infected with trich. If symptoms do present themselves, they may appear from anywhere between a few days and several months after the infection begins. If you do not have any symptoms, you can still infect others. Women are more likely to experience symptoms than men. The reasons for this are varied. In many cases, it is suspected that trich and semen dont quite mix. Prostatic fluid, which is a secretion from the prostate, is one of the components that make up semen. It is possible that this fluid can damage the parasite. Thats good news for men, but its not exactly comforting for women. It can still be passed between partners, no matter what.
You May Like: How Many Mg Of Azithromycin To Treat Chlamydia
What Are The Symptoms
Many women and most men do not have any symptoms of trich. But when you do have symptoms, they usually start within 1 week after you were infected.
In women, symptoms include:
- Changes in your vaginal discharge. You may notice a color or odor that isn’t normal.
- Vaginal itching.
- Pain during urination or sex.
In men, symptoms include:
- An abnormal discharge from the penis.
- Irritation of the tip of the penis.
- A burning feeling when you urinate.
The time from contact with the trich parasite until you get symptoms can range from 5 to 28 days.footnote 1 This is called the incubation period. You can spread trich to others during this time and until you finish the prescribed medicine. You should avoid all sexual contact until you finish taking your medicine and the symptoms are gone.
Possible Though Unlikely Sources Of Trich:
There are a few ways that trich can be spread without having sexual relations:
- Public Pools: If the water in a community swimming pool is not properly cleaned and filtered, it is possible for the parasite to survive and infect others.
- Sharing damp clothing, towels or swimsuits: Much like the pool, if clothes are not properly washed, it is technically possible for the infection to spread from wearer to wearer.
Of course, please remember that sexual activity is by far the most common source of infection. While these potential sources can be comforting to a worried partner, they are quite unlikely to actually be the cause. Compared to skin-to-skin contact, the reports of trich being spread through these means are few and far between.
Recommended Reading: Can Boric Acid Cure Chlamydia
What Are The Potential Complications Of Trichomoniasis
In pregnant people, untreated trichomoniasis infections can result in preterm delivery and low birth weight babies . If you are pregnant and suspect your have trichomoniasis or are at risk of contracting the infection, speak to your healthcare provider about testing.
Having an STI, like trichomoniasis, can also increase your chances of contracting HIV if exposed to it, or spreading HIV if already infected . Also, people with trichomoniasis infections are at greater risk of developing pelvic inflammatory disease if they are HIV positive .
If you think you have trichomoniasis, or any STI, it is important for you to seek help from your healthcare provider or an STI clinic. Many clinics provide free or low-cost STI testing. This will all help keep you, your sexual partners, and your community healthy.
to track sex, discharge, and your period.
Let’s support one another.
How Do You Prevent Chlamydia
Using a new male or female condom or dental dam every time you have sex is the best way to protect against chlamydia.
Chlamydia can be passed on by sharing sex toys. Always cover sex toys with a new condom and wash them after use to reduce your risk of getting chlamydia and other STIs.
Its important to regularly test for chlamydia, even if you dont have any symptoms, especially if youve had multiple sexual partners.
The contraceptive pill and other types of contraception wont prevent you getting chlamydia, and neither will PrEP.
Don’t Miss: How Soon Can You Feel Symptoms Of Chlamydia
Diagnosis And Treatment Of Chlamydia Trachomatis Infection
KARL E. MILLER, M.D., University of Tennessee College of Medicine, Chattanooga, Tennessee
Am Fam Physician. 2006 Apr 15 73:1411-1416.
Chlamydia trachomatis infection most commonly affects the urogenital tract. In men, the infection usually is symptomatic, with dysuria and a discharge from the penis. Untreated chlamydial infection in men can spread to the epididymis. Most women with chlamydial infection have minimal or no symptoms, but some develop pelvic inflammatory disease. Chlamydial infection in newborns can cause ophthalmia neonatorum. Chlamydial pneumonia can occur at one to three months of age, manifesting as a protracted onset of staccato cough, usually without wheezing or fever. Treatment options for uncomplicated urogenital infections include a single 1-g dose of azithromycin orally, or doxycycline at a dosage of 100 mg orally twice per day for seven days. The recommended treatment during pregnancy is erythromycin base or amoxicillin. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommend screening for chlamydial infection in women at increased risk of infection and in all women younger than 25 years.
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
Azithromycin or doxycycline is recommended for the treatment of uncomplicated genitourinary chlamydial infection.
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
Azithromycin or doxycycline is recommended for the treatment of uncomplicated genitourinary chlamydial infection.
What Is The Best Medication For Trichomoniasis
The drugs of choice for trichomoniasis are the nitroimidazole antibiotics metronidazole and tinidazole. The optimal choice will depend on the patients allergies to these drugs, the organisms drug resistance, the presence of HIV infection, and the persistence of the infection.
| Best Medications for Trichomoniasis | |
|---|---|
| Four 500 mg tablets taken in a single dose taken with food | Metallic taste in the mouth, nausea, fatigue |
Many of the standard dosages above are from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and the National Institutes of Health. Dosage is determined by your doctor based on your medical condition, response to treatment, age, and weight. Other possible side effects exist. This is not a complete list.
Also Check: Can I Get Tested For Chlamydia A Week After Treatment
How Do You Get Chlamydia
Chlamydia is usually passed on through unprotected vaginal, anal or oral sex.
Chlamydia can be passed on through genital contact. This means you can get chlamydia from someone who has the infection if your genitals touch, even if you dont have sex or ejaculate .
You can also get chlamydia if you come into contact with infected semen or vaginal fluid, or get them in your eye.
Chlamydia cant be passed on through kissing, hugging, sharing towels or using the same toilet as someone with the infection.