Whats The Treatment For Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is usually super easy to get rid of. Your nurse or doctor will prescribe antibiotics to treat the infection. Some strains of gonorrhea resist the antibiotics and are hard to treat, so your doctor may give you two antibiotics, in shot and pill form. Sometimes you only have to take one pill. Other gonorrhea pill treatments are taken for 7 days. Your doctor will help you figure out which treatment is best for you.
If youre treated for gonorrhea, its really important for your sexual partners to get treated also. Otherwise, you may pass the infection back and forth, or to other people. Sometimes your doctor will give you medicine for both you and your partner.
Why Is It Important To Take Antibiotics Such As Amoxicillin For Chlamydia And Gonorrhea
Its important to treat any STDespecially chlamydia or gonorrheaas quickly as possible. If left untreated, both of these STDs can lead to serious health complications, including:
- Pelvic inflammatory disease
- Life-threatening pregnancy
- Vaginal, rectal, and/or oral infections
The only way to avoid these complications is to seek medical attention immediately after finding out you have tested positive.
In Both Males And Females
Complications that may be seen in anyone include:
- Other STIs. Chlamydia and gonorrhea both make you more susceptible to other STIs, including human immunodeficiency virus . Having chlamydia can also increase your risk of developing gonorrhea, and vice versa.
- Reactive arthritis . Also called Reiters syndrome, this condition results from an infection in your urinary tract or intestines. Symptoms of this condition cause pain, swelling, or tightness in your joints and eyes, and a variety of other symptoms.
- Infertility. Damage to reproductive organs or to sperm can make it more challenging or, in some cases, impossible to become pregnant or to impregnate your partner.
Read Also: What Happens If Chlamydia Is Left Untreated
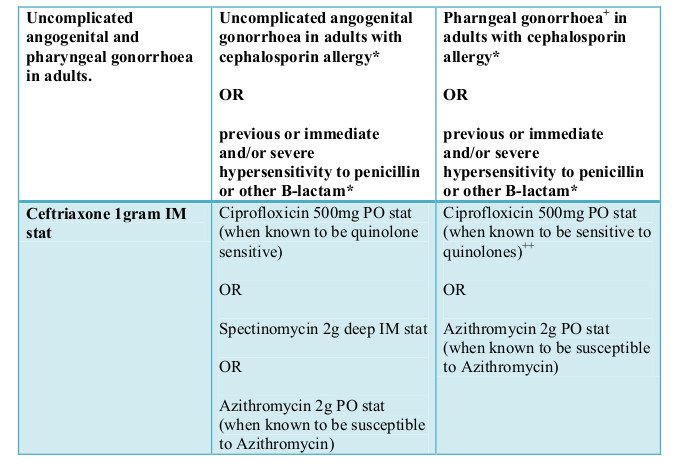
What Are The Best Antibiotics For Gonorrhea
The choice of best antibiotics for gonorrhea can depend on several factors. These include an individuals previous response to first line medications and the type of gonorrhea that is present. It also matters if individuals are simultaneously infected with chlamydia, which is not particularly uncommon. In these cases, more than one antibiotic may need to be tried.
As of 2007, the US Centers for Disease Control published clear guides on how to choose the best antibiotics for gonorrhea. Shortly before this publication, studies indicated that one common group of antibacterial medicines, called floroquinolones, had begun to be ineffective and strains of the sexually transmitted disease were showing resistance to it. As it turns out, gonorrhea has behaved this way in the past with other antibiotics. It normally wont respond to treatment with drugs like penicillin or tetracycline either.
Who New Treatment Guidelines For Gonorrhea Chlamydia And Syphilis
The World Health Organization on 30th Aug released new therapy guidelines for 3 sexually transmitted infections , stating the updates respond to an urgent need in light of improving antimicrobial resistance.
Ian Askew, director of reproductive health and research at WHO said,
Chlamydia, gonorrhoea and syphilis are main public health issues globally, impacting large numbers of peoples quality lifestyle, causing severe illness and often death. The new WHO guidelines strengthen the need to treat these STIs with the appropriate antibiotic, at the appropriate dose, and the right time to decrease their spread and enhance sexual and reproductive health.
With respect to WHO, the 3 bacteria cause over 200 million infections every year, and increasing resistance has made them more complicated or impossible to treat with current antibiotics. Of the 3 infections, WHO states that, gonorrhea is the very challenging to treat, with some strains now resistant to all accessible antibiotics.
When drawing the guidelines, WHO states it looked for therapies that provided high efficacy and quality while paying attention to cost, toxicity, route of administration, along with the likelihood for resistance to the therapies developing.
Furthermore to revamping its therapy recommendations, WHO says that individual health systems should boost surveillance for the infections, and urges nations to quickly follow the new guidelines.
You May Like: Can You Detect Chlamydia In Urine
How Do You Get Chlamydia And Gonorrhea
- Engaging with multiple sexual partners in one year The more partners who engage with, the more likely you will be exposed to an infected person and contract an STD.
- Having unprotected sex Condoms can reduce the likelihood of you contracting an STD however, condoms are never 100% effective. If you are concerned you may have an STD, you should get tested regardless of whether you used a condom in your last sexual encounter.
- Younger than 24 Individuals younger than 24 tend to practice unprotected sex more often than other age groups and are less likely to be tested.
- Previous diagnosis of an STD Having already contracted an STD increases your bodys susceptibility to contracting another STD. It can be common for those who have contracted chlamydia to be at risk for contracting gonorrhea or HIV. If you contract gonorrhea, you are at a greater risk of contracting HIV.
Amoxicillin For Chlamydia: Is It Effective
Amoxicillin is not the preferred treatment option for gonorrhea, but is it an effective way to treat chlamydia? The CDC reports that chlamydia can be easily treated with a course of antibiotics. But this does not mean that amoxicillin is effective simply because it is an antibiotic.
The CDC recommends that healthcare providers prescribe either azithromycin or doxycycline to treat chlamydia. The CDC also suggests several alternative antibiotics that can be used to treat chlamydia, including erythromycin, levofloxacin, or ofloxacin.
Amoxicillin is not on the list of antibiotics that the CDC recommends for the general treatment of chlamydia. However, it is on the list of antibiotics that the CDC recommends for the treatment of chlamydia in pregnant women. So if you are pregnant, your doctor may prescribe amoxicillin to treat chlamydia.
Recommended Reading: How Do Guys Test For Chlamydia
What Causes Gonorrhea And Chlamydia
Chlamydia and gonorrhea are sexually transmitted diseases that affect both women and men. They are transmitted by having oral, anal, or vaginal sex with a person who already has the disease.
Both STDs are caused by a bacterial infection that affects the mucous membranes, which are moist, soft tissues not covered by our outer layer of skin.
- Chlamydia is caused by the bacteria, chlamydia trachomatis, and can be found in the vagina, cervix, urethra, and rectum as well as the throat or eyes .
- Gonorrhea, also called the clap or the drip, is caused by the bacteria, Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
Like chlamydia, gonorrhea bacteria can grow and infect women in the cervix, uterus, or fallopian tubes and in men, in the urethra. It can also infect the anus, mouth, and throat.
The infection is spread through semen and vaginal fluids, but the transmission of the disease is not dependent on ejaculation. While the infection comes from these fluids, it can infect the eyes and throat in addition to the vagina, cervix, penis, urethra, and anus.
However, since these fluids are required to transmit the bacteria, you cannot get either STD through casual contact. For example, it is not possible to get chlamydia or gonorrhea from holding hands, hugging, sneezing, sitting on a toilet, or sharing food. It is very unlikely to get chlamydia or gonorrhea from kissing, even kissing someone with the infection in their throat.
Read: Why is Gonorrhea Called the Clap?
How To Treat Gonorrhea And Chlamydia At Home: Get Tested
Taking antibiotics is the only way to treat gonorrhea and chlamydia, and these antibiotics must be prescribed by a physician. This means you cannot treat these STDs at home. But there is something you can do at home: get tested. The results of this at-home test will determine whether or not you need to contact a medical professional to discuss treatment options.
Also Check: How Do I Get Chlamydia Medication
Will Penicillin Cure Chlamydia
Penicillin is not used in the treatment of chlamydia. However a range of other antibiotics can effectively cure chlamydia, in some cases only requiring a single dose.
Chlamydia is a bacterial infection and is treated with antibiotic medications. They kill the bacteria and prevent their growth.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends a range of antibiotics for its treatment, in particular azithromycin and doxycycline . These are not forms of penicillin.
Occasionally, doctors may recommend that pregnant women take amoxicillin, which is a specific type of penicillin. Some of the brand names for amoxicillin include Amoxil, Trimox and Moxilin. However it will only be prescribed to women who are unable to use azithromycin, which is generally a more effective medication.
Is Treatment Different For Pregnant Women With Gonorrhea
The medications used for pregnant women with gonorrhea are essentially the same as the medications used for non-pregnant women.
Treatment is necessary to prevent disease transmission to, or complications for, the baby.
Gonorrhea in babies often manifests as conjunctivitis, or pink eye. Some states require that all newborns are given antibiotic eye drops, such as erythromycin, as a preventive measure against the disease.
Pregnant women who are diagnosed with gonorrhea should be tested for other STIs as well.
Recommended Reading: When You Get Treated For Chlamydia
Which Stds Are Causing The Most Concern
Gonorrhea is far and away the most pressing concern. Currently, thereâs only one CDC-recommended treatment for it: a combination of two powerful antibiotics, azithromycin and ceftriaxone.
Syphilis and chlamydia have also begun to show resistance to antibiotics in some parts of the world, though Klausner says there are several treatment options for both.
STDs, which donât always have symptoms, can cause serious complications if left untreated:
- Gonorrhea can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease , which causes inflammation of the ovaries, the fallopian tubes, and the uterus, which can ultimately lead to infertility. In men, it can cause infection of the testes and sterility. In rare cases, gonorrhea can spread to your blood or joints, which can be life-threatening. Untreated gonorrhea may increase your risk of HIV.
- Chlamydia can also cause PID in women, which may result in permanent damage. Though men seldom have long-term complications from untreated chlamydia, it can lead to sterility in rare cases.
- Syphilis, in its early stages, can cause chancre sores, rashes, fever, swollen lymph glands, and other symptoms. If left untreated for years, it can eventually damage the brain, heart, liver, and other organs, causing paralysis, numbness, blindness, dementia, and death.
Pregnant women with untreated STDs have a higher chance of stillbirth and newborn death, according to the World Health Organization. STDs can also affect babies during delivery.
Common Stds Becoming Untreatable: How Worried Should We Be
In United States, drug-resistant gonorrhea is a public health problem of national concern. But untreatable gonorrhea isnt the only STD that has health officials worried.
Earlier this week, the World Health Organization released new treatment guidelines for three common sexually transmitted diseases chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis in response to increasing antibiotic resistance.
Gonorrhea has developed the strongest resistance to drugs, but the worries about untreatable syphilis and chlamydia come at a time when rates for the three STDs are rising rapidly in the U.S, especially among young people ages 20 to 24. According to data published by the CDC in 2014, the most recent year available: cases of chlamydia have increased 2.5 percent gonorrhea 5.1 percent and syphilis 15.1 percent. This is the first increase in the United States since 2006.
How worried should we be?
STDs are hidden epidemics of enormous health and economic consequence in the United States, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
In the US, STDs are most frequent among college-age women, the highest prevalence being among women, ages 20 to 24.
According to the CDC, there are about 820,000 new gonorrhea infections each year in the United States. In fact, gonorrhea is the second most commonly reported infectious disease, after chlamydia.
How do the superbugs spread through STDs?
Also Check: How To Tell If A Male Has Chlamydia
Who Should Take An At
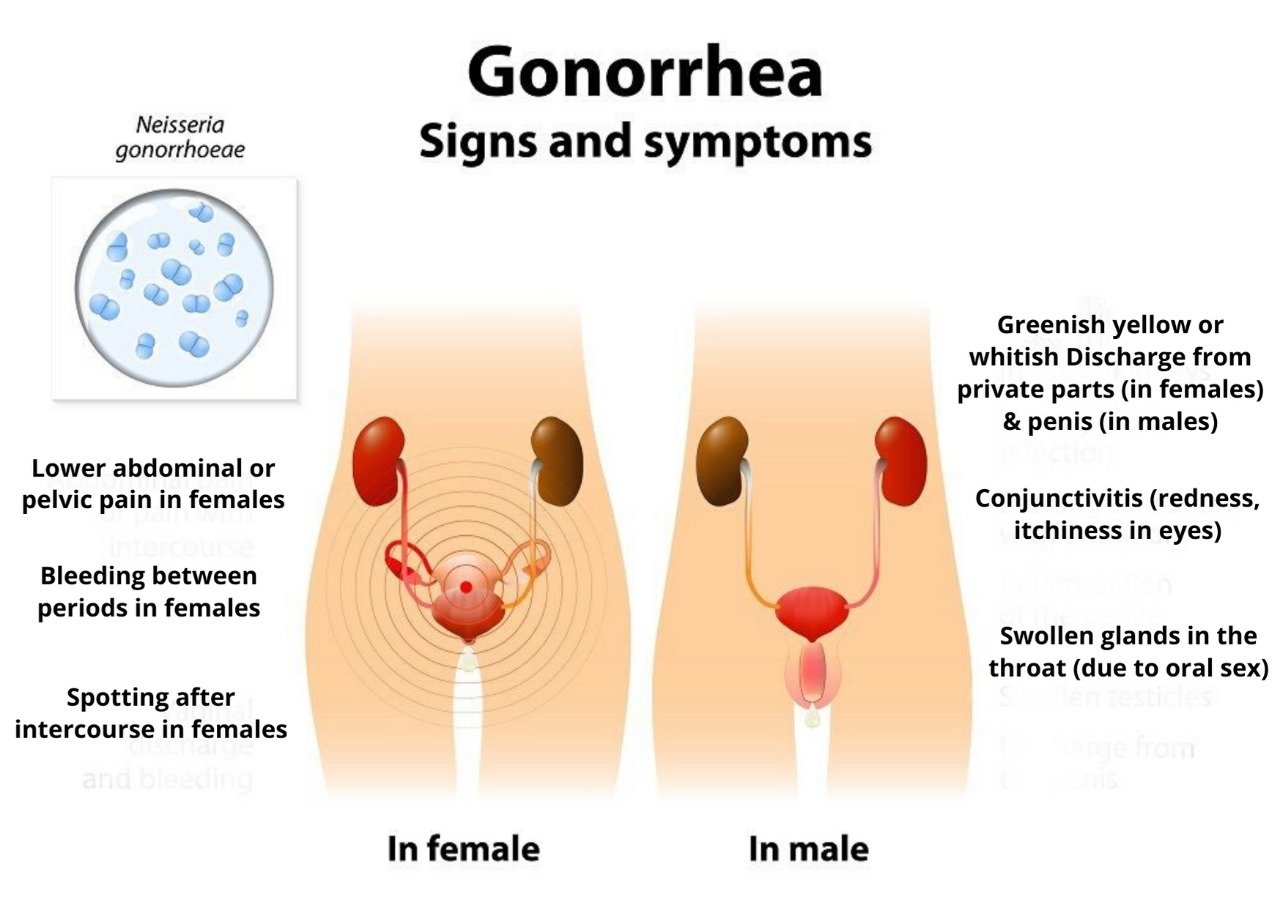
Before you start worrying about amoxicillin, you should first get a proper diagnosis. For cases in which chlamydia orgonorrhea symptoms are present, these are the signs to watch out for:
- More frequent urination or the urge to urinate
- Painful sensation when urinating
- Red and swollen penis near the urinary meatus
- Abnormal discharge or fluid from the penis or vaginal area
- Sore throat that wont go away
- Fever
- Testicular pain and swelling in men
- Lower abdominal pain in women
- Heavier period or excessive spotting in women
If you notice any of these symptoms, its in your best interest to purchase an at-home STD kit to test for gonorrhea and chlamydia right away.
Dont assume that you dont need to get tested simply because you arent experiencing any symptoms. In many cases, gonorrhea and chlamydia may not show any visible signs of infection at all. For this reason, every sexually active person should be tested regularly for all common sexually transmitted infections.
In general, the CDC recommends that every sexually active adult get tested for chlamydia and gonorrhea at least once a year.But if you engage in certain sexual activities, you may need to get tested more frequently.This is especially true for people who meet one or more of the following conditions:
Treatments For Gonorrhea And Chlamydia
Since both STDs are caused by a bacterial infection, the treatment is a regimen of oral antibiotics.
Some strains of gonorrhea in the US have become antibiotic resistant, sometimes called super gonorrhea. Therefore, a medical physician will decide on the best course of antibiotics.
The most commonly recommended antibiotics for both chlamydia and gonorrhea are:
The infection should clear after one to two weeks.
You should never stop taking antibiotics until the recommended course is finished, even if you think the infection cleared or you are feeling better.
If you do not finish the antibiotics, the infection can come back and be resistant to the antibiotics you were taking.
Additionally, since antibiotic resistant strains of bacteria are already more common, if your symptoms continue after a few days of taking antibiotics, consult your doctor. They may switch you to a different strain of antibiotics.
Some people report home remedies for chlamydia and gonorrhea easing their symptoms, but the only effective treatment for both STDs are antibiotics.
Gonorrhea and chlamydia are curable by taking the appropriate medication as directed however, repeat infections are common.
You and your sexual partner should always be tested after three months of completing treatment, especially if you are unsure whether your partner received treatment.
Read Also: How Soon Can I Test For Chlamydia
Does Amoxicillin Treat Std Infections Such As Gonorrhea
Now its time to discuss how to treat STDs with amoxicillin. Each STD is unique, so the treatment options will vary depending on the type of STD you have.
On the whole, gonorrhea tends to be treatable with common drugs such as penicillin, ampicillin, tetracycline and doxycycline. With several doses of amoxicillin or a similar drug, gonorrhea can be cured in a few days.
Antibiotics such as amoxicillin have been prescribed by doctors to treat gonorrhea in the past. Of course, even though Amoxicillin is one of the most well-known drugs, that doesnt mean that it is the primary drug of choice for treatment of gonorrhea. In fact, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that uncomplicated gonorrhea be treated only with the antibiotic ceftriaxone given as an injection in combination with either azithromycin or doxycycline two antibiotics that are taken orally.
According to the CDC, this combination of prescription medications will successfully treat gonorrhea, but it will not repair permanent damage caused by this STD. For this reason, its important to seek medical treatment right away to ensure you can get rid of this infection before it causes permanent damage.
Can Chlamydia Turn Into Gonorrhea
No, chlamydia on its own cannot turn into gonorrhea as they are caused by two different bacteria.
It does happen that people contract and carry both chlamydia and gonorrhea bacteria, so you can have them at the same time. Also, having one increases your likelihood of contracting another thus, it is always important to be treated for both.
Also Check: Things Not To Do When You Have Chlamydia
What Should You Do If You Test Positive For Chlamydia Or Gonorrhea
Testing positive for gonorrhea or chlamydia is a nerve-wracking experience, but its important to stay calm. If you test positive for either STD, seek medical treatment right away. If your symptoms do not improve after taking the prescribed antibiotics, make sure to contact your doctor to discuss other treatment options so you can avoid these serious complications.
Be sure to get tested again once you have completed the full course of antibiotics. Taking another test will help you confirm that the treatment was successful. If you are still testing positive for either gonorrhea or chlamydia after completing your treatment, contact your doctor to discuss your next steps.
You will also need to reach out to your sexual partners as soon as possible after testing positive for chlamydia or gonorrhea. Share your test results with your sexual partners and encourage them to get tested right away. This may be an uncomfortable conversation, but you shouldnt put it off. Telling your sexual partners about your test results right away is the only way to stop the spread of chlamydia and gonorrhea.