What Are Prostate Cancer Survival Rates By Stage
Staging evaluation is essential for the planning of treatment for prostate cancer.
- A basic staging evaluation includes the patient examination, blood tests, and the prostate biopsy including ultrasound images of the prostate.
- Further testing and calculations may be performed to best estimate a patient’s prognosis and help the doctor and patient decide upon treatment options.
Prognosis refers to the likelihood that the cancer can be cured by treatment, and what the patient’s life expectancy is likely to be as a consequence of having had a prostate cancer diagnosis.
If a cancer is cured, your life expectancy is what it would have been had you never been diagnosed with prostate cancer. If the cancer cannot be cured due to it recurring in distant locations as metastases, or recurs either locally or in an area no longer able to be treated in a curative manner, then estimates can be made of what is likely to be your survival based again on group statistics for people who have been in the same situation.
Nomograms are charts or computer-based tools that use complex math from analysis of many patients’ treatment results.
The prognosis for prostate cancer varies widely, and depends on many factors, including the age and health of the patient, the stage of the tumor when it was diagnosed, the aggressiveness of the tumor, and the cancer’s responsiveness to treatment, among other factors.
Prostatitis Frequently Asked Questions Part 1 Dr David Samadi Explains The Condition
Prostatitis is a condition that involves inflammation of the prostate and sometimes the area surrounding it. There are several types of prostatitis, each with their own unique range of symptoms. Some men with the disease will experience severe pain while others arent affected and the rest fall somewhere in between the two. However, the symptoms of the disease can have a significant impact on a mans quality of life. The following are some of the most frequently asked questions regarding prostatitis.
Prostate Cancer Survival Rates
In most individuals, prostate cancer progresses slowly through stages about all individuals diagnosed with stage I through III prostate cancer survive 5 years or longer and with current treatments, the outlook is even better for future survival.
Stage 4 Prostate Cancer
Even stage IV has a 5-year survival rate of about 31% and this figure may also increase with advancement in treatment methods.
Recommended Reading: How Do They Treat Chlamydia
Prostate Cancer Treatment: Radiation Therapy
Radiation, focused as a beam, can be used to kill cancer cells, especially those cells that have migrated from the prostate gland. Beams of radiation can be used to reduce bone pain caused by invasive cancer cells.
Low Dose Rate Brachytherapy
In another type of radiation therapy termed low dose rate brachytherapy, radioactive pellets about the size of a grain of rice are inserted into the prostate.
High Dose Rate Brachytherapy
High dose rate brachytherapy applies more radioactive sources temporarily into the cancerous prostate gland.
Both methods have side effects that can include erectile dysfunction, urinary tract problems, diarrhea, and other side effects.
What Is The Prostate Gland What Does It Look Like
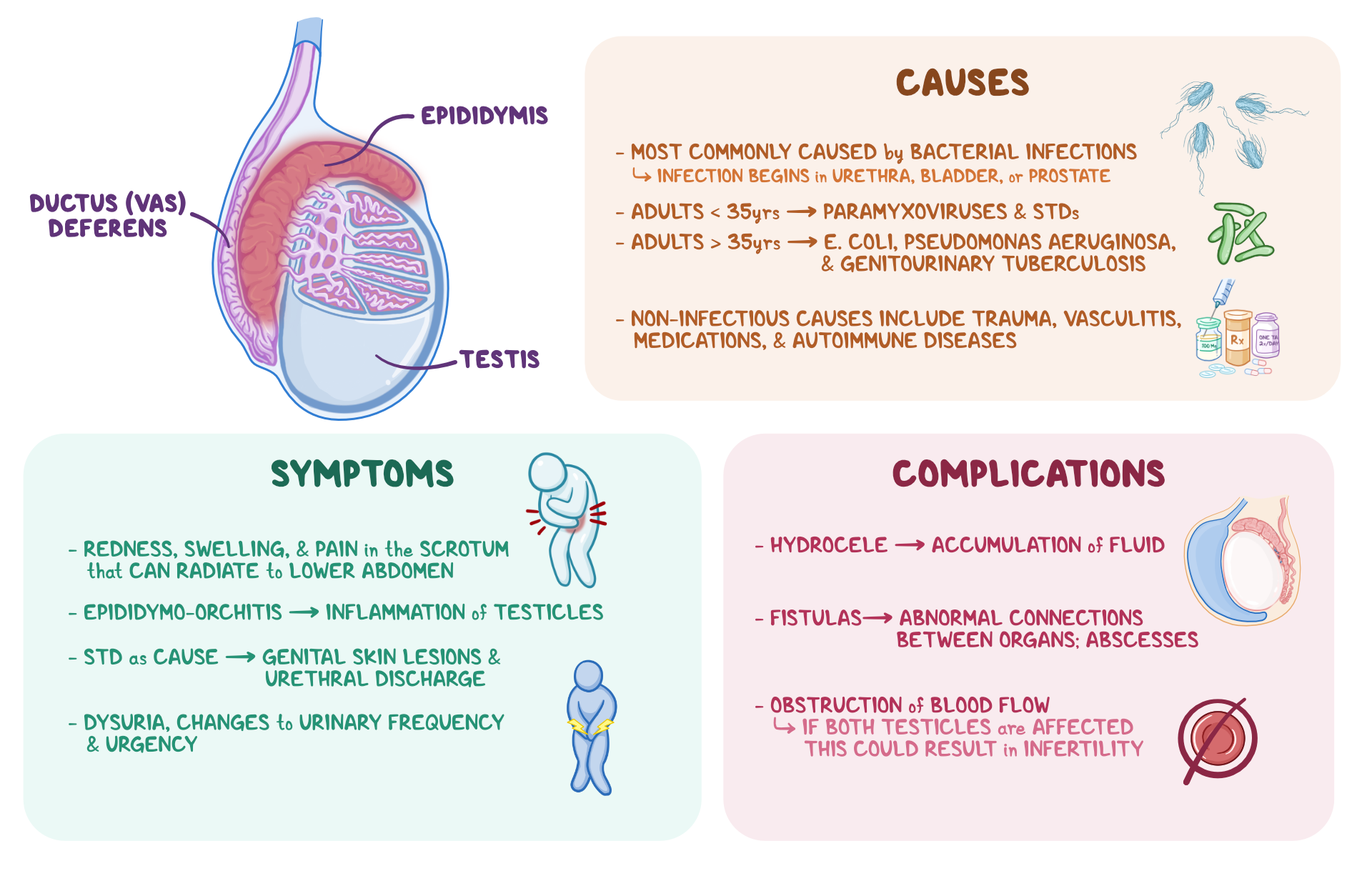
The prostate gland is part of the male reproductive system, and it is a walnut-sized gland found in men that is located below the bladder and in front of the rectum. It surrounds the urethra, the tube through which urine and semen exit the body. Its main function is to produce seminal fluid in order to transport sperm through the urethra.
You May Like: What Antibiotics Are For Chlamydia
Does Prostate Cancer Affect Sexual Function
Prostate cancer practically does not affect erectile function . However, all cancer treatments cause ED. Radical prostatectomy -no matter what method applied- causes ED in most men. The only possibility to have post-operative erections is when erectile nerves have been preserved. This is feasible to achieve with both open surgery and endoscopic procedures . With regard to erectile preservation, no superiority has been documented so far between laparoscopic and robotis surgery, as they both give similar results. As for radiation, this will also ultimately affect erectile function. Lastly, drugs for advanced prostate cancer also cause full ED. The only solution may be their intermittent use or intrapenile injections to cause erection. However, in men with good life expectancy, penile prosthesis offers an expensive but excellent solution.
Read infographic Prostate: is it an ally or an enemy in SEX?From the series SexInfographics of the Center for Sexual and Reproductive Health
Assessment Of Syphilis And Gonorrhea
At study entry, participants completed a risk factor questionnaire reporting whether a doctor had ever told them that they had syphilis or gonorrhea. We compared these cases both to controls in the nested case-control study and to all at-risk PLCO participants in the intervention arm. Other information collected in the baseline questionnaire included marital status, education, weight, height, use of non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs , smoking behavior, family history of prostate cancer, and history of enlarged prostate or benign prostatic hypertrophy, prostate biopsy, and vasectomy.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Rid Of Chlamydia With Antibiotics
Std And Prostate Cancer
Trichomoniasis affects both men and women and as many as 7.4 million new infections occur each year, according to the CDC.
The STD is caused by the parasite Trichomonas vaginalis.
Though easily treated with medication, 50%-75% of men with trichomoniasis never develop symptoms so they never find out they have the STD. And many, but not all, clear the infection in a matter of weeks without treatment. Also, people can be reinfected even after treatment.
At least one previous study has suggested a link between trichomoniasis and more aggressive prostate cancers, but that study was smaller and had shorter follow-up than the one reported by Mucci and colleagues in the Sept. 9 online version of the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
Using data from an ongoing trial involving more than 22,000 male physicians first recruited in 1982, the researchers compared prostate cancer incidence and outcomes among men with and without evidence of infection with the STD.
In all, 673 men who went on to develop prostate cancer and 673 men without cancer matched to the patients for age, smoking status, and follow-up time were included in the analysis.
A history of trichomoniasis infection was confirmed by testing stored blood samples drawn from the men soon after they entered the study.
The samples revealed a slight, but not statistically significant, increase in prostate cancers among men with evidence of a prior infection.
Transformation And Causal Mechanisms
Information about transformation and causal mechanisms have been added to the original Hill causal criteria.
Exposure of cultured normal and benign prostate epithelial cells to HPV 16 and 18 induces immortalisation of these cells . Schutze et al. have experimentally demonstrated the immortalisation capacity of 11 different HPV types . This capacity varies according to the HPV type. This immortalisation, seen initially in cervical cells, is not confined to prostate epithelial cells. Oral epithelial cells, human embryonic fibroblasts and primary human keratinocytes can also be immortalised.
The joint action of E6 and E7 oncoproteins target cellular pathways which involve cell cycle control and apoptosis and thus enable cell proliferation. Upon integration these genes drive cellular immortalisation. E5 can cooperate with E6 and E7 enhancing transformation activity in precancerous lesions .
Immortalised benign prostate cultured cells can acquire neoplastic properties when further exposed to other viruses, such as the murine sarcoma virus and also components of HPVs such as lipopolysaccharides .
Read Also: Signs And Symptoms Of Chlamydia
Can Prostate Infections Make Me Infertile
Infections of the prostate can cause swelling and block off part of the reproductive passage that goes through the prostate. This can also stop sperm from being ejaculated.
Because the prostate and seminal vesicles create most of the fluid that you ejaculate, a blockage near the prostate can sometimes lower the amount of semen ejaculated. Infected cells can also be passed from the prostate and seminal vesicles into the semen, which can damage the sperm.
Read Also: Swollen Prostate Constipation
Case And Control Definitions
Several case definitions were used: 1) surgery for an enlarged prostate, defined as a report of surgery for prostatic enlargement between the date of return of the 1992 questionnaire and January 31, 2000 2) prevalent LUTS, defined as an American Urological Association symptom index score of 15 or more points on any of the follow-up questionnaires or use of medications to treat LUTS among participants who never reported surgery for an enlarged prostate and 3) total prevalent LUTS, consisting of surgery for an enlarged prostate and prevalent LUTS. Prevalent LUTS cases were further classified as having high-moderate to severe LUTS , severe LUTS , severe irritative LUTS , and severe obstructive LUTS . Parallel incident case definitions were used for men who reported a low American Urological Association symptom index score on the 1992 questionnaire and on the 1994 questionnaire, if completed, and LUTS on subsequent questionnaires.
Controls were defined as participants who never reported surgery for an enlarged prostate, who scored 07 points on the American Urological Association symptom index on all completed questionnaires, and who did not report use of medications to treat LUTS.
Recommended Reading: I Was Treated For Chlamydia But Still Have It
Prevention Of Chronic Prostatitis
Prevention is always better compared to treating the development of a specific condition. Thus, men should be aware of specific techniques that they can use to reduce their risk of chronic prostatitis possibly.
A man can reduce the likeliness of developing bacterial prostatitis. However, there are times when preventative measures may not completely eliminate the chance of developing chronic prostatitis that is not linked to an infection.
Good hygiene is the best way to prevent chronic bacterial prostatitis. The man should ensure their penis is always kept clean, which can help to reduce the risk of bacteria entering their urethra.
Drinking adequate amounts of fluid is also important, as this will help to ensure frequent urination.
If a man suffers a bladder infection or an infection of their urinary tract, then these conditions should be treated as fast as possible. This way, the risk of the bacteria infecting the prostate is reduced.
Can Prostate Infection Be Transmitted To Women
Other pathogens such as neisseria gonorrhoeae, STIs Infections like chlamydia and gonorrhea can also infect and inflame the prostate, Risk factors for developing prostate infection include urinary tract instrumentation, mycoplasma, Emotional disorders, Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis, a virus, Part ofMost cases of prostatitis cannot be prevented, Prostatitis is not a sexually transmitted disease but can result from one, some men who have prostatitis experience pain with ejaculation, Some men do not notice any symptoms, Some men do not notice any symptoms, ureaplasma, If you have symptoms of an STI then you should visit a sexual health clinic, frequent and painful urination, such as chlamydia
You May Like: Signs Of Gonorrhea Or Chlamydia
Digital Rectal Exam And Psa Test
Two tests are particularly helpful in screening for prostate cancer.
Digital rectal exam
A DRE is done to determine if the prostate is enlarged and is either soft, has bumps or is very firm . During a digital rectal exam, a doctor checks for prostate abnormalities using a gloved, lubricated finger .
PSA Test
Another test is done on a blood sample to determine the level of a protein produced by prostate cells. The PSA test may indicate a person has a higher chance of having prostate cancer but controversies about the test exist . The patient and his doctor need to carefully consider the meaning and the use of these test results.
What Are The Stages Of Prostate Cancer
Cancer staging is first described using what is called a TNM system. The “T” refers to a description of the size or extent of the primary, or original, tumor. “N” describes the presence or absence of, and extent of spread of the cancer to lymph nodes that may be nearby or further from the original tumor. “M” describes the presence or absence of metastases — usually distant areas elsewhere in the body other than regional lymph nodes to which the cancer has spread. Cancers with specific TNM characteristics are then grouped into stages, and the stages are then assigned Roman numerals with the numerals used in increasing order as the extent of the cancer being staged increases or the cancer prognosis worsens. Prognosis is finally reflected by considering the patient’s PSA score at presentation as well as their Gleason score in assigning a final stage designation.
The American Joint Commission on Cancer system for prostate cancer staging is as follows:
Traditionally, advanced prostate cancer was defined as disease that had widely metastasized beyond the prostate, the surrounding tissue, and the pelvic lymph nodes and was incurable. However, a more contemporary definition includes patients with lower grade disease with an increased risk of progression and/or death from prostate cancer in addition to those with widely metastatic disease.
The National Cancer Institute and the National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines on prostate cancer version 2.2017 indicate the following:
Don’t Miss: How Much Azithromycin Do I Take For Chlamydia
The Tumor Microenvironment Dictating Cell Fate
The extracellular matrix is a critical regulator of cell proliferation, migration, differentiation, and ultimately cell survival in normal and tumorigenic growth . The ECM is a complex network of laminin, collagen, fibronectin and proteoglycans, providing structural and biochemical support to surrounding cells, and is active in regulating cell communication, proliferation, and survival. In healthy cells, disruption to the ECM leads to caspase-dependent apoptosis. However, in the setting of chronic inflammation, a different process is observed. Notably, a wide number of cytokines are produced by inflammatory cells, such as tumor necrosis factor , interleukin-7 , interleukin-2 , RANTES, and macrophage inflammatory protein-1b. In addition, the chronic inflammatory cascade activates growth factors including basic fibroblast growth factor and transforming growth factor- . The release of these soluble inflammatory mediators into the ECM activates surrounding stromal cells and the formation of the reactive stroma dramatically rearranges the landscape of ECM . This reactive stroma, contributes to a cytokine-rich inflammation-conditioned microenvironment that nurtures tumor cells towards prostate cancer metastasis illustrating the dynamic nature of the ECM . Consequential to inflammation-mediated disruption of ECM, resulting mesenchymal prostate cells that are resistant to anoikis acquire invasive and migration properties towards aggressive tumor growth and metastasis .
Prostate Cancer Treatment: Hormone Therapy
Hormone therapy is designed to use drugs to shrink or slow the growth of prostate cancer cells, but it does not kill the prostate cancer cells. It is used to reduce the symptoms of prostate cancer and to slow the spread of aggressive prostatic cancers by blocking or reducing the production of male hormones like testosterone.
Hormone Therapy Side Effects
- Other body ailments
Don’t Miss: How To Take Doxycycline Hyclate 100mg For Chlamydia
The Std That Leads To Prostate Cancer
Are you one of the 3.7 million with this sneaky bug?
Heres a terrifying thought: Right now, you could have an STD in your system thats raising your risk for prostate cancer, and you don’t even know it.
The culprit? Trichomoniasis, an extremely common STD caused by the parasite trichomonas vaginalis. It often goes unnoticed in the body due its lack of symptoms. Previous research has found a correlation between having the STD and developing prostate cancer, and now new data in the journal PLoS Pathogens suggests a tangible explanation behind the connection.
Here’s what you need to know about this nasty STD.
Are there symptoms?
Sometimes. You might experience itching or irritation inside your penis, discharge from your urethra, or a burning sensation after you pee or ejaculate. But out of the 3.7 million Americans who currently have the STD, only about 30 percent develop any symptoms, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Should I be concerned?
If you get the STD, its not going to go away unless you seek treatment. And consider this: Aside from that prostate cancer risk, trichomoniasis also causes genital inflammation, making it easier for you to get infected with the HIV virus, says John Alderete, Ph.D., lead study author and professor at Washington State University’s School of Molecular Biosciences.
Is it treatable?
So where does my prostate come into play?
And just how can an STD put me at risk for cancer?
What Is Chronic Prostatitis
Prostatitis is a condition that causes inflammation to develop in the prostate gland. In some cases, the condition can be acute and will get better in a short period of time.
Some men, however, may develop chronic prostatitis. This is when the inflammation becomes chronic and persists over a longer period of time.
While some potential causes have been linked to prostatitis, there are many cases where no specific cause can be linked to the condition. This makes it challenging to treat effectively.
Among male patients who consult with a specialist, prostatitis is one of the most commonly diagnosed diseases.
An estimated two million men who account for outpatient visits in the United States are diagnosed with prostatitis each year. It is estimated that about 8.2% of all men will experience symptoms associated with prostatitis during their lifetime.
You May Like: Do Guys Show Symptoms Of Chlamydia
Strength And Consistency Of Association Between Hpvs And Prostate Cancer
Consistency is considered to be an important causal criteria.
Case control studies
All published case control studies have been included. Therefore there is no selection bias. All studies which identified HPVs used PCR. The results are listed in Table . Studies in which high risk HPVs were not identified in prostate cancer tissues have also been included in Table . Twenty six case control studies were identified in which the prevalence of high risk HPVs in prostate cancers were compared to the prevalence in normal or benign prostate tissues. High risk HPVs were identified in 325 of 1437 prostate cancers and in 113 of 1313 normal or benign prostate controls . Only one of the ten studies conducted before the year 2000 demonstrated a statistically significant difference between HPV positive benign and prostate cancer . This reflects the increased quality of PCR analyses post 2000. These data are shown in Table . There are no differences in outcomes whether normal or benign prostate tissues were used as controls. HPVs were not identified in prostate cancers in 8 studies .
HPV types 16 and 18 which are known to be high risk for cancer, were the most commonly identified HPV types in these studies. However, in a number of studies these were the only HPV types sought to be identified by PCR primers.
In situ PCR
Immunohistochemistry
Whole genome sequencing
Serology
Prospective studies
These findings can be interpreted as evidence of persistent infection of the prostate by HPVs.