Symptoms Of Gonorrhea In Women
Many women donât have noticeable gonorrhea symptoms. If they do, the symptoms can be mild or mimic the symptoms of other infections. Symptoms of gonorrhea in women can resemble yeast infections, other bacterial infections, or urinary tract infectionsâwhich is why itâs important to regularly test for STIs like gonorrhea.
Gonorrhea symptoms in women can include abnormal vaginal dischargeâparticularly a watery, creamy, or slightly green discharge. Women with gonorrhea may also experience frequent urination alone with pain or a burning sensation while urinating. Women can also have spotting between periods or experience heavier-than-usual periods. You might also feel pain during sex or feel sharp pains in the lower abdomen. Gonorrhea in women can also cause a fever or sore throat. Symptoms can also include an itchy or sore anus as well as discharge, bleeding, and painful bowel movements.
If a woman isnât treated for gonorrhea, the infection can damage the reproductive system and increase the risk of getting or transmitting HIV. It can also lead to pelvic inflammatory disease or infertility. In some rare cases, gonorrhea can spread to the bloodstream and joints, which is known as disseminated gonorrhea.
How Is It Treated
Antibiotics are used to treat gonorrhea. It’s important to take all of the medicine as directed. Otherwise the medicine may not work. Both sex partners need treatment to keep from passing the infection back and forth.
Getting treatment as soon as possible helps prevent the spread of the infection and lowers your risk for other problems, such as pelvic inflammatory disease.
Many people who have gonorrhea also have chlamydia, another STI. If you have gonorrhea and chlamydia, you will get medicine that treats both infections.
Avoid all sexual contact while you are being treated for an STI. If your treatment is a single dose of medicine, you should not have any sexual contact for 7 days after treatment so the medicine will have time to work.
Having a gonorrhea infection that was cured does not protect you from getting it again. If you are treated and your sex partner is not, you probably will get it again.
Finding out that you have an STI may make you feel bad about yourself or about sex. Counselling or a support group may help you feel better.
Infection In The Rectum Throat Or Eyes
Both men and women can develop an infection in the rectum, throat or eyes by having unprotected anal or oral sex.
If infected semen or vaginal fluid comes into contact with the eyes, you can also develop conjunctivitis.
Infection in the rectum can cause discomfort, pain or discharge. Infection in the eyes can cause irritation, pain, swelling and discharge, and infection in the throat usually causes no symptoms.
Recommended Reading: Does Chlamydia Make You Poop A Lot
Always Practice Safe Sex
Notice how this is under a section titled How can you reduce your risk. Reduce being the operative word. Even if you always wear a condom or a dental dam, theres a risk of infection. This is because some diseases are spread from skin to skin contact, from bodily fluids touching a part of your body, or from defective prophylactics.
This includes vaginal, anal, and oral sex. So if youre in high school and think that by going down on someone youre safe, hopefully youre reading this before going to that party.
What Happens During A Gonorrhea Test
If you are a woman, a sample may be taken from your cervix. For this procedure, you will lie on your back on an exam table, with your knees bent. You will rest your feet in supports called stirrups. Your health care provider will use a plastic or metal instrument called a speculum to open the vagina, so the cervix can be seen. Your provider will then use a soft brush or plastic spatula to collect the sample.
If you are a man, your provider may take a swab from the opening of your urethra.
For both men and women, a sample may be taken from a suspected area of infection, such as the mouth or rectum. Urine tests are also used for both men and women.
Some gonorrhea tests can be done with an at-home STD test kit. If your health care provider recommends at-home testing, be sure to follow all directions carefully.
Your health care provider may order tests for other STDs when you get a gonorrhea test. These may include tests for chlamydia, syphilis, and/or HIV.
Read Also: How Easy Is It To Get Rid Of Chlamydia
Chlamydia And Gonorrhea Symptoms
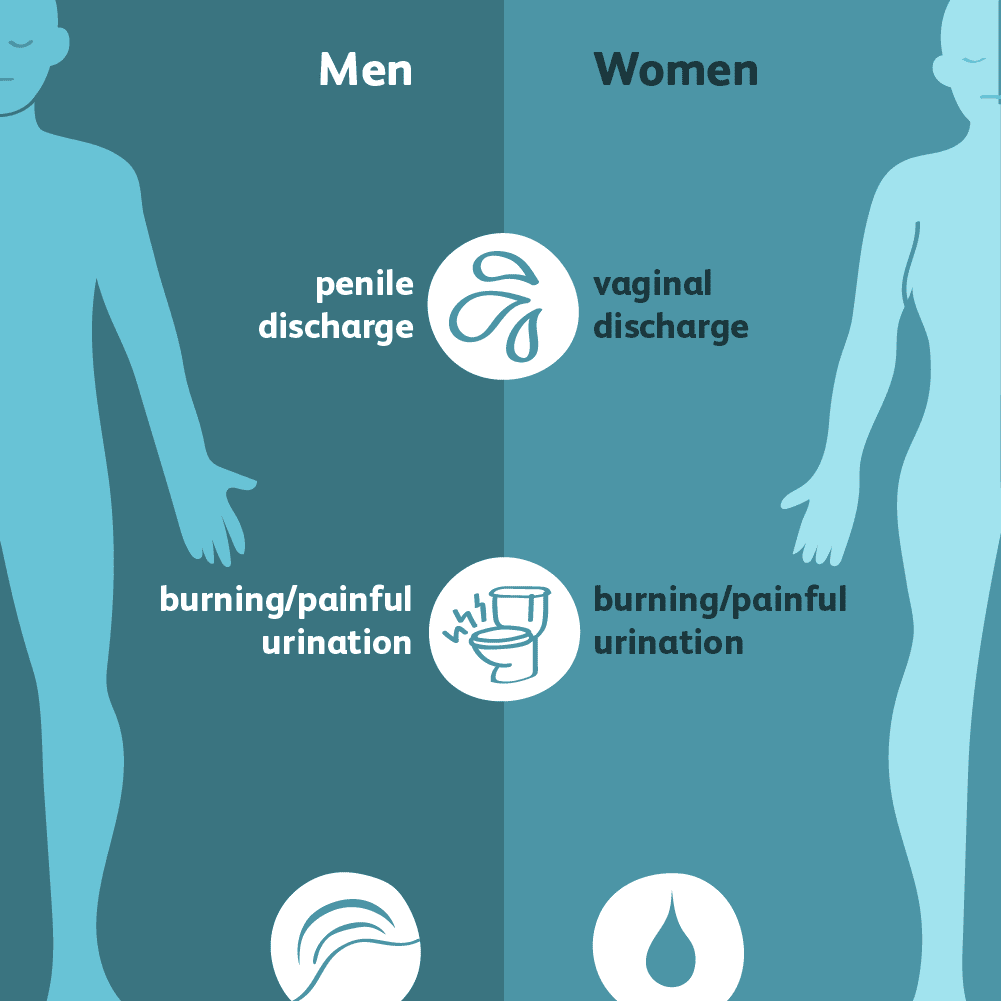
The symptoms of chlamydia and gonorrhea overlap, so it can be difficult to differentiate between the two unless you visit your healthcare provider or take a test for chlamydia or gonorrhea.
The overlapping symptoms for chlamydia and gonorrhea in men and women include:
- A burning sensation during urination
- Abnormal genital or rectal discharge
- Pain in the rectum
- Sore throat
With both chlamydia or gonococcal infections , men might also experience swelling and pain in the testicles and/or scrotum.
In women, both a gonorrhea and chlamydia infection might be mistaken for a yeast infection. Women may also experience painful periods, bleeding between periods, pain during sex, or abdominal pain.
Although the symptoms overlap, the discharge caused by chlamydia vs. gonorrhea can vary slightly. For a chlamydia infection, a womanâs vaginal discharge might have a strong odor and yellowish tint. Men might have a cloudy or clear discharge. With gonorrhea, both women and men may experience green, yellow, or white discharge.
If you’re a woman experiencing abnormal vaginal discharge or a man with abnormal penile discharge, be sure to consult your healthcare provider as soon as possible as this is a common sign of an infection.
In Men Untreated Chlamydia Can Lead To:
- Epididymitis painful inflammation of the inner structures of the testicles, which may cause reduced fertility or sterility. A rare complication of Epididymitisis reactive arthritis, which causes pain in the inflamed joints that can be disabling
- Prostatitis
- Occasionally, Reiters syndrome
- Urethritis inflammation of the urethra with a yellow discharge appearing at the tip of the penis. Untreated urethritis results in narrowing of the urethra which leads to painful urinating and can cause kidney problems
Also Check: How Long Before Signs Of Chlamydia
How Long Does It Take To Show Signs Of Chlamydia
Chlamydia is the most prevalent bacteria on the planet. Based on 2018 statistics, around 2.86 million are infected annually, and more than two-thirds of those infected are young teenagers and adults between the ages of 15 and 24. Every sexually active individual is exposed to chlamydia and can get infected no matter how many or how few partners theyve changed.
Here, we will help you answer some of the most common questions you might have about this infection. We will talk about when you can expect the infection to turn up, how to recognize it, and why you need to get tested.
How Is Chlamydia Diagnosed
You should see your doctor if you experience any of the above symptoms. During your clinic visits, some test will be carried out.
Urine sample are not reliable in women. Cervix swab and urethral swabs are used for testing. Some chlamydia tests include
- Polymerase chain reaction
- Culture of specimen. This test has a can detect the infection but it is expensive.
- Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests .
In addition, you should inform your partner to get tested and treated. Reinfection can occur if you have sexual intercourse with an infected partner again. Also, contact tracing should be done. This is to inform people youve had unprotected intercourse with to get tested as well.
You May Like: Over The Counter Chlamydia Treatment Walgreens
What Is Chlamydia And Gonorrhea
Both gonorrhea and chlamydia are common sexually transmitted infections occurring in men and women. So how do you get gonorrhea and chlamydia? They are transmitted through vaginal, anal, or oral sex with someone whoâs infected.
Both infections are caused by bacteriaâChlamydia trachomatis in cases of chlamydia and Neisseria gonorrhoeae in cases of gonorrhea.
Although gonorrhea is a common sexually transmitted infection, chlamydia has a higher prevalenceâwith over 1.7 million cases of chlamydia reported in the United States in 2017.
Risk factors for getting gonorrhea and chlamydia are often identical and include:
- Having multiple sex partners. You’re more likely to be exposed to someone with a sexually transmitted infection if you have multiple sex partners.
- Unprotected sex. Condom usage during sex substantially reduces the risk of getting a sexually transmitted infection, so your risk is higher if you have unprotected sex.
- Having other STIs: If you already have a sexually transmitted infection, you can be at a greater risk of getting another STI. For example, if you contract chlamydia, you could be more likely to contract gonorrhea.
How To Get Tested
A person can meet with a doctor to get a diagnosis for either of these infections.
The doctor will collect bodily fluids to test for the infection. The test can use either a urine sample or a sample from the vagina or penis, which a doctor will collect with a cotton swab.
Most health insurance plans, including Medicare, cover sexually transmitted infection testing completely. If a person does not have health insurance, they can go to a free clinic, their local health departments STI clinic, a student health center, or an urgent care clinic.
Because both chlamydia and gonorrhea can present with no symptoms, it is important that people who are sexually active get tested regularly.
After a doctor has determined which infection a person has contracted, they will prescribe an antibiotic.
People should take the full course of antibiotics and wait an additional 7 days before having sex again. This helps prevent a person from spreading the infection to another person and possibly reinfecting themselves later.
A person can contract both chlamydia and gonorrhea again, even if they have already experienced and treated the STI before.
Recommended Reading: How To Get Rid Of Chlamydia And Gonorrhea
Toxicity And Side Effect Management
In neonates being treated for chlamydial infection, both azithromycin and erythromycin are associated with a risk of infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. This is particularly a concern for infants two weeks old or younger. Parents and physicians should observe infants closely for any signs of intestinal obstruction.
Frequently Asked Questionsexpand All

- What is a sexually transmitted infection ?
A sexually transmitted infection is an infection spread by sexual contact. There are many STIs. This FAQ focuses on chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis. These STIs can cause long-term health problems and problems during pregnancy. Having an STI also increases the risk of getting human immunodeficiency virus if you are exposed to it.
- What is chlamydia?
Chlamydia is the most commonly reported STI in the United States. Chlamydia is caused by a type of bacteria, which can be passed from person to person during vaginal sex, oral sex, or anal sex. Infections can occur in the mouth, reproductive organs, urethra, and rectum. In women, the most common place for infection is the cervix .
- What are the risk factors for chlamydia?
The following factors increase the risk of getting chlamydia:
-
Having a new sex partner
-
Having more than one sex partner
-
Having a sex partner who has more than one sex partner
-
Having sex with someone who has an STI
-
Having an STI now or in the past
-
Not using condoms consistently when not in a mutually monogamous relationship
-
Exchanging sex for money or drugs
Chlamydia usually does not cause symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they may show up between a few days and several weeks after infection. They may be very mild and can be mistaken for a urinary tract or vaginal infection. The most common symptoms in women include
yellow discharge from the vagina or urethra
yellow vaginal discharge
Recommended Reading: What Type Of Antibiotics Treat Chlamydia
What Causes Gonorrhea And Chlamydia
Chlamydia and gonorrhea are sexually transmitted diseases that affect both women and men. They are transmitted by having oral, anal, or vaginal sex with a person who already has the disease.
Both STDs are caused by a bacterial infection that affects the mucous membranes, which are moist, soft tissues not covered by our outer layer of skin.
- Chlamydia is caused by the bacteria, chlamydia trachomatis, and can be found in the vagina, cervix, urethra, and rectum as well as the throat or eyes .
- Gonorrhea, also called the clap or the drip, is caused by the bacteria, Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
Like chlamydia, gonorrhea bacteria can grow and infect women in the cervix, uterus, or fallopian tubes and in men, in the urethra. It can also infect the anus, mouth, and throat.
The infection is spread through semen and vaginal fluids, but the transmission of the disease is not dependent on ejaculation. While the infection comes from these fluids, it can infect the eyes and throat in addition to the vagina, cervix, penis, urethra, and anus.
However, since these fluids are required to transmit the bacteria, you cannot get either STD through casual contact. For example, it is not possible to get chlamydia or gonorrhea from holding hands, hugging, sneezing, sitting on a toilet, or sharing food. It is very unlikely to get chlamydia or gonorrhea from kissing, even kissing someone with the infection in their throat.
Read: Why is Gonorrhea Called the Clap?
How Do I Test For Chlamydia
You can get tested for chlamydia even if you dont have any symptoms.
Getting tested for chlamydia is easy and doesnt hurt. A healthcare professional will ask for a urine sample and/or take a swab from the area that might be infected. This is usually the lower part of the womb or the vagina for women, and the tip of the penis for men. If youve had anal or oral sex, you may have a swab taken from your anus or throat.
In some countries you can get a self-testing kit to do at home.
If you test positive for chlamydia, its important to tell any recent sexual partner/s so they can also get tested, and treated if necessary. If you need advice about how to do this, speak to your healthcare professional. You should also test for other STIs.
Also Check: How Long Can You Leave Chlamydia Untreated
If The Clap Not Treated
Gonorrhea infection can spread through the bloodstream to other parts of the body, causing damage & serious problems.
In women, it can cause:
- life-threatening complications such as ectopic pregnancy
- blocked fallopian tubes , which can result in reduced fertility or infertility
- long-term pelvic pain
In men, it can lead to:
- painful inflammation of the testicles, which may result in reduced fertility or sterility
Gonorrhea Compared To Similar Conditions: Uti Chlamydia And Bv
In this chapter, we compare gonorrhea to other common medical conditions. This will help you understand the most important differences from a doctorâs viewpoint.
Often, different conditions have similar symptoms and signs. Any experienced doctor keeps in mind other conditions that look and present similarly. Itâs called making a differential diagnosis.
The differences between similar conditions can be subtle. So, all signs and symptoms should be analyzed carefully:
- Whatâs the timing of the symptoms?
- How did the symptoms begin?
- How are the symptoms evolving over time?
- What do statistics tell us about the prevalence in the relevant geographic area of the conditions youâre considering?
- Other relevant questions
In this section, weâll help you distinguish the gonorrhea infection from other similar conditions: UTI, chlamydia, and BV.
We present side-by-side comparisons in tables so it will be easier to see the similarities of and differences between those conditions and gonorrhea.
After the tables youâll see frequently asked questions from real patients and an expert physicianâs answers.
Letâs proceed!
You May Like: How Long Does It Take To Get Symptoms Of Chlamydia
Chlamydia Cdc Fact Sheet
Chlamydia is a common sexually transmitted disease that can be easily cured. If left untreated, chlamydia can make it difficult for a woman to get pregnant.
Basic Fact Sheet | Detailed Version
Basic fact sheets are presented in plain language for individuals with general questions about sexually transmitted diseases. The content here can be syndicated .
How Is Gonorrhea Contracted
Gonorrhea spreads through semen or vaginal fluids during unprotected sexual contact, heterosexual or homosexual, with an infected partner:
- vaginal or anal sex with an infected partner
- oral sex, although this is less common
- sharing sex toys
- touching parts of the body with fingers
- any very close physical contact
- the bacteria can be passed from hand to hand
- from a mother to her baby at birth
You can NOT catch it from simple kissing, sharing baths, towels, cups, or from toilet seats.
114 days.
You May Like: How Soon Can You Get Symptoms Of Chlamydia
Std Prevention In 3 Steps
As previously mentioned, anyone who is sexually active can get an STD. And as you can see from the information provided above, some of these diseases dont show any signs or symptoms.
It is for these reasons that you should do the following if you want to reduce your risk of contracting any sexually transmitted disease:
Common Signs Of Chlamydia

Like gonorrhea, chlamydia often displays few symptoms and can easily go unnoticed for a considerable amount of time. Men and women infected with chlamydia may notice one or more of the following symptoms:
- Abnormal vaginal discharge or penile discharge
- Painful, burning urination
- In women, bleeding between periods
- In men, swollen or sore testicles
- Rectal pain, bleeding, or discharge
- Lower abdominal pain
Read Also: How Many Mg Of Azithromycin To Treat Chlamydia
How Do You Get Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is a STD, meaning it is transmitted by having oral, anal, or vaginal sex with a person who already has Gonorrhea. The infection is spread through semen and vaginal fluids, but the transmission of the disease is not dependent on ejaculation. While the infection comes from these fluids, it can infect the eyes, mouth, and throat in addition to the genitals, urethra, and anus. Anyone can get Gonorrhea, even if they have been diagnosed and treated for Gonorrhea before. Additionally, women who are pregnant can pass Gonorrhea onto their child during birth. This can result in the baby having joint, eye, or blood infections.
Since semen and vaginal fluids are required to transmit the bacteria that causes Gonorrhea, you cannot get gonorrhea through casual contact. For example, it is not possible to get Gonorrhea from kissing, holding hands, hugging, sneezing, sitting on a toilet, or sharing food.
Certain traits do increase your likelihood of contracting gonorrhea: