What Is The Treatment For Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea can be cured with the right treatment. CDC recommends a single dose of 500 mg of intramuscular ceftriaxone. Alternative regimens are available when ceftriaxone cannot be used to treat urogenital or rectal gonorrhea. Although medication will stop the infection, it will not repair any permanent damage done by the disease. Antimicrobial resistance in gonorrhea is of increasing concern, and successful treatment of gonorrhea is becoming more difficult. A test-of-cure follow-up testing to be sure the infection was treated successfully is not needed for genital and rectal infections however, if a persons symptoms continue for more than a few days after receiving treatment, he or she should return to a health care provider to be reevaluated. A test-of-cure is needed 7-14 days after treatment for people who are treated for a throat infection. Because re-infection is common, men and women with gonorrhea should be retested three months after treatment of the initial infection, regardless of whether they believe that their sex partners were successfully treated.
Who Should Take An At
Before you start worrying about amoxicillin, you should first get a proper diagnosis. For cases in which chlamydia orgonorrhea symptoms are present, these are the signs to watch out for:
- More frequent urination or the urge to urinate
- Painful sensation when urinating
- Red and swollen penis near the urinary meatus
- Abnormal discharge or fluid from the penis or vaginal area
- Sore throat that wont go away
- Fever
- Testicular pain and swelling in men
- Lower abdominal pain in women
- Heavier period or excessive spotting in women
If you notice any of these symptoms, its in your best interest to purchase an at-home STD kit to test for gonorrhea and chlamydia right away.
Dont assume that you dont need to get tested simply because you arent experiencing any symptoms. In many cases, gonorrhea and chlamydia may not show any visible signs of infection at all. For this reason, every sexually active person should be tested regularly for all common sexually transmitted infections.
In general, the CDC recommends that every sexually active adult get tested for chlamydia and gonorrhea at least once a year.But if you engage in certain sexual activities, you may need to get tested more frequently.This is especially true for people who meet one or more of the following conditions:
Amoxicillin For Chlamydia: Is It Effective
Amoxicillin is not the preferred treatment option for gonorrhea, but is it an effective way to treat chlamydia? The CDC reports that chlamydia can be easily treated with a course of antibiotics. But this does not mean that amoxicillin is effective simply because it is an antibiotic.
The CDC recommends that healthcare providers prescribe either azithromycin or doxycycline to treat chlamydia. The CDC also suggests several alternative antibiotics that can be used to treat chlamydia, including erythromycin, levofloxacin, or ofloxacin.
Amoxicillin is not on the list of antibiotics that the CDC recommends for the general treatment of chlamydia. However, it is on the list of antibiotics that the CDC recommends for the treatment of chlamydia in pregnant women. So if you are pregnant, your doctor may prescribe amoxicillin to treat chlamydia.
Don’t Miss: How Do Men Test For Chlamydia
What Do I Need To Know If I Get Treated For Gonorrhea
If youre getting treated for gonorrhea:
-
Take all of your medicine the way your doctor tells you to, even if your symptoms go away sooner. The infection stays in your body until you totally finish the antibiotics.
-
Your partner should also get treated for gonorrhea so you dont re-infect each other or anyone else.
-
Dont have sex for 7 days. If you only have 1 dose of medication, wait until a week after you take it to have sex. If youre taking medicine for 7 days, dont have sex until youve finished all of your pills.
-
Get tested again in 3 months to make sure your infection is gone.
-
Dont share your medicine with anyone. Your doctor may give you a separate dose of antibiotics for your partner. Make sure you both take all of the medicine you get.
-
If you still have symptoms after you finish your treatment, call your doctor.
-
Even if you finish your treatment and the gonorrhea is totally gone, its possible to get infected with gonorrhea again. Gonorrhea isnt a one-time-only deal. So use condoms and get tested regularly.
Other Approaches To Prevention

The USPSTF has issued recommendations on screening for other STIs, including hepatitis B, genital herpes, HIV, and syphilis. The USPSTF has also issued recommendations on behavioral counseling for all sexually active adolescents and for adults who are at increased risk for STIs. These recommendations are available at .
Also Check: My Partner Tested Positive For Chlamydia But I Didn T
Std Prevention In 3 Steps
As previously mentioned, anyone who is sexually active can get an STD. And as you can see from the information provided above, some of these diseases dont show any signs or symptoms.
It is for these reasons that you should do the following if you want to reduce your risk of contracting any sexually transmitted disease:
What Happens If You Dont Get Treated For Gonorrhea
Even though gonorrhea is common and doesnt always cause symptoms, it can become a big deal if its not treated.
Gonorrhea can spread to your uterus and fallopian tubes, causing pelvic inflammatory disease . PID might not have any symptoms at first, but it can cause permanent damage that may lead to chronic pain, infertility, or ectopic pregnancy. Getting tested for gonorrhea really lowers your chances of getting PID.
If you have a penis, an untreated gonorrhea infection can spread to your epididymis , and can cause pain in your testicles. Rarely, it can make you infertile.
Having gonorrhea also increases your chances of getting or spreading HIV, the virus that causes AIDS. Rarely, untreated gonorrhea may spread to your blood, skin, heart, or joints and lead to serious health problems, or even death.
If you have gonorrhea while youre pregnant and dont treat it, it can be passed to your baby when youre giving birth. This can lead to problems for the baby, including blindness, joint infections, or blood infections which can be deadly.
The best way to avoid all these problems? Get tested and treated early.
Read Also: Azithromycin 500mg Tablets For Chlamydia
Amoxicillin For Std Treatment: Does It Work
Amoxicillin is one of the first drugs people think of when they learn that they have contracted a sexually transmitted infection or disease. Many common web searches show that people searching for chlamydia treatments or information on how to treat gonorrhea at home are curious about this as a potential treatment.
At myLAB Box, we understand and appreciate our customers concerns. So we want to address the question: will amoxicillin cure gonorrhea or chlamydia? Lets take a closer look.
Chlamydia Treatment And Prevention
Milly DawsonSanjai Sinha, MDShutterstock
Chlamydia is easy to cure. If you test positive for chlamydia, basically you take an antibiotic, says Jill Rabin, MD, cochief in the division of ambulatory care for women’s health programs and prenatal care assistance program services for Northwell Health in New Hyde Park, New York.
Your partner must take an antibiotic, too, to keep them from reinfecting you, she says.
You have to have your partner treated, and if you have more than one partner, they should all be treated, says Dr. Rabin, regardless of your partners genders.
Even if you dont have chlamydia now, its wise to learn how to protect yourself so you wont develop this common infection in the first place. In women, chlamydia can create serious health problems, including infertility. Besides, no one ever wants to have a sexually transmitted disease and then have to tell other people about it.
Recommended Reading: How Are Men Tested For Chlamydia
Screening And Selecting Studies For Inclusion
For the database searches, two reviewers will independently screen the titles and abstracts using broad inclusion/exclusion criteria. Citations will be classified as include/unsure,exclude, or reference . One reviewer will review the reference group and will screen results of the supplementary searches . The full text of all studies classified as include/unsure, identified through review of the reference citations, or screened as relevant from the supplementary searches will be retrieved for full review. Two reviewers will independently assess eligibility of full texts using a standard, piloted, form that outlines the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Disagreements on final inclusion of all studies will be resolved through consensus or a third reviewer. The title/abstract screening and full-text selection processes will be conducted and documented in DistillerSR. We will contact authors via e-mail when the details necessary to decide on inclusion have not been adequately documented in the publication. The flow of literature and reasons for full text exclusions will be recorded in a PRISMA Flow Chart, and for each study in an excluded studies list.
How To Get Tested
A person can meet with a doctor to get a diagnosis for either of these infections.
The doctor will collect bodily fluids to test for the infection. The test can use either a urine sample or a sample from the vagina or penis, which a doctor will collect with a cotton swab.
Most health insurance plans, including Medicare, cover sexually transmitted infection testing completely. If a person does not have health insurance, they can go to a free clinic, their local health departments STI clinic, a student health center, or an urgent care clinic.
Because both chlamydia and gonorrhea can present with no symptoms, it is important that people who are sexually active get tested regularly.
After a doctor has determined which infection a person has contracted, they will prescribe an antibiotic.
People should take the full course of antibiotics and wait an additional 7 days before having sex again. This helps prevent a person from spreading the infection to another person and possibly reinfecting themselves later.
A person can contract both chlamydia and gonorrhea again, even if they have already experienced and treated the STI before.
You May Like: Does Chlamydia And Gonorrhea Go Away
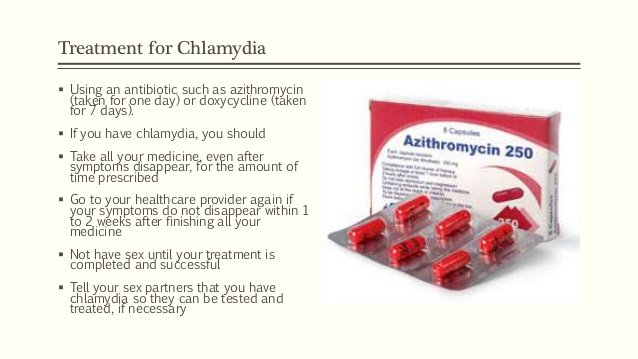
What Is The Treatment For Chlamydia
Chlamydia can be easily cured with antibiotics. HIV-positive persons with chlamydia should receive the same treatment as those who are HIV-negative.
Persons with chlamydia should abstain from sexual activity for 7 days after single dose antibiotics or until completion of a 7-day course of antibiotics, to prevent spreading the infection to partners. It is important to take all of the medication prescribed to cure chlamydia. Medication for chlamydia should not be shared with anyone. Although medication will stop the infection, it will not repair any permanent damage done by the disease. If a persons symptoms continue for more than a few days after receiving treatment, he or she should return to a health care provider to be reevaluated.
Repeat infection with chlamydia is common. Women whose sex partners have not been appropriately treated are at high risk for re-infection. Having multiple chlamydial infections increases a womans risk of serious reproductive health complications, including pelvic inflammatory disease and ectopic pregnancy. Women and men with chlamydia should be retested about three months after treatment of an initial infection, regardless of whether they believe that their sex partners were successfully treated.
Infants infected with chlamydia may develop ophthalmia neonatorum and/or pneumonia. Chlamydial infection in infants can be treated with antibiotics.
Testing And Treating Sexual Partners
If you test positive for chlamydia, it’s important that your current sexual partner and any other recent sexual partners you’ve had are also tested and treated.
A specialist sexual health adviser can help you contact your recent sexual partners, or the clinic can contact them for you if you prefer.
Either you or someone from the clinic can speak to them, or the clinic can send them a note to let them know they may have been exposed to a sexually transmitted infection .
The note will suggest that they go for a check-up. It will not have your name on it, so your confidentiality will be protected.
Page last reviewed: 01 September 2021 Next review due: 01 September 2024
Don’t Miss: What Antibiotics Are For Chlamydia
What If Symptoms Persist
Unfortunately, some types of gonorrhea bacteria dont respond to the usual antibiotic treatment. Doctors call this antibiotic resistance. Theyve been seeing a rise in these stronger bacteria for several years. If you continue to have symptoms a few days after treatment, see your doctor again. They may prescribe a longer course of different antibiotics
How To Treat Gonorrhea And Chlamydia At Home: Get Tested
Taking antibiotics is the only way to treat gonorrhea and chlamydia, and these antibiotics must be prescribed by a physician. This means you cannot treat these STDs at home. But there is something you can do at home: get tested. The results of this at-home test will determine whether or not you need to contact a medical professional to discuss treatment options.
You May Like: Can Chlamydia Cause Kidney Infection
Recommendation On Screening For Chlamydia And Gonorrhea In Primary Care For Individuals Not Known To Be At High Risk
www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.201967-f see related article at www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.210604
-
Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae are the most commonly reported sexually transmitted bacterial infections in Canada and can cause complications including pelvic inflammatory disease, chronic pelvic pain, ectopic pregnancy and infertility.
-
Opportunistic offering of screening for chlamydia in primary care may reduce pelvic inflammatory disease in females, although the evidence is uncertain.
-
Most patients likely prioritize the potential benefits of screening over harms a small proportion of those eligible for screening may experience psychosocial harms of embarrassment, anxiety or stigma.
-
The Canadian Task Force on Preventive Health Care recommends screening of sexually active individuals younger than 30 years for chlamydia and gonorrhea annually at primary care visits, as feasible .
Key messages for the public
Screening sexually active individuals for chlamydia and gonorrhea could reduce clinical complications and transmission, but should be done only if benefits from screening exceed harms, and resource use is justifiable.
Gonococcal Meningitis And Endocarditis
For people affected by gonococcal meningitis and gonococcal endocarditis, the CDC recommends an initial treatment of:
- ceftriaxone, 1-2 g given intravenously every 12-24 hours
- azithromycin , 1 g, a single dose taken orally
Parenteral therapy, otherwise known as intravenous feeding, is also recommended. Total treatment time for meningitis should last at least 10 days, while total treatment time for endocarditis should last at least 4 weeks.
Read Also: 1 Day Treatment For Chlamydia
Can Cranberry Juice Treat Gonorrhea
Fact Checked
While a gonorrhea infection can cause painful urination similar to a bladder infection, using cranberry juice to treat gonorrhea would be ineffective. Gonorrhea infections require prompt diagnosis and proper treatment to resolve the infection, prevent further spread and reduce your risk of experiencing complications. If you suspect you have gonorrhea, you should seek appropriate medical care.
If you are experiencing serious medical symptoms, seek emergency treatment immediately.
When Should You Test For Gonorrhea Or Chlamydia At Home
If youve recently had unprotected sex or potentially been exposed to gonorrhea or chlamydia, you may think that its important to get tested immediately. But taking an STD test too soon could actually lead to inaccurate results. Why? STDs such as gonorrhea and chlamydia will not be detectable in your system immediately following exposure. If you take a test too early, you may get a false negative result.
So how long should you wait to get tested for STDs? Every STD has a unique incubation period, which is the amount of time that it takes for the STD to be detectable in your system. The incubation period for chlamydia can range from 7 days to 21 days, whereas the incubation period for gonorrhea is up to 14 days.
Therefore, it is best to get tested for chlamydia and gonorrhea two to three weeks following the initial exposure. If you take a test within the first two to three weeks following exposure, its best to get tested again after several weeks to ensure your initial results were accurate.
Recommended Reading: How Many Mg Of Azithromycin To Treat Chlamydia
Feasibility Acceptability Cost And Equity
Screening is currently a part of primary care practice and therefore judged to be feasible and likely acceptable to primary care practitioners and patients. Notably, 1 included RCT showed that patients accepted screening 80% of the time that it was offered .
The task force anticipates that public health and other policymakers will find the recommendation to screen acceptable, given the number of people affected, increasing incidence of chlamydia and gonorrhea infection, and availability of effective treatment.
In the judgment of the task force, the recommendation would likely improve health equity by normalizing screening as routine for sexually active individuals and thereby reducing important barriers to screening, such as fear of disapproval or discrimination and feelings of stigmatization. Additionally, because females carry most of the burden of the clinical consequences of infection, screening of males may improve health equity for females.
Treatment For Chlamydia Is Quick And Easy

Two antibiotics are most often used for treating chlamydia:
- Azithromycin The main treatment for chlamydia is one gram of azithromycin, taken one time, says , deputy director of clinical services for public health with the Seattle and King County HIV and STD Program in Washington. That one gram comes as either two pills or four pills. It is not expensive.
- Doxycycline If your doctor prescribes doxycycline, you will take two pills daily for one week. It costs somewhat more than azithromycin.
Antibiotics can also cure chlamydia in infants, who can get the infection from their mothers, and treatment is essential for them. Without treatment, infants infected with chlamydia can develop conjunctivitis, which can cause blindness, or pneumonia, which can be fatal.
You May Like: Over The Counter Medicine For Chlamydia At Walmart