Other Approaches To Prevention
The USPSTF has issued recommendations on screening for other STIs, including hepatitis B, genital herpes, HIV, and syphilis. The USPSTF has also issued recommendations on behavioral counseling for all sexually active adolescents and for adults who are at increased risk for STIs. These recommendations are available at .
How Chlamydia Diagnosis Process Is Carried On In Men
Early treatment of Chlamydia is essential to have a healthy life ahead. In case if you had unprotected sex with your recent partner then you must get tested for STIs as soon as possible. This test can be carried out at any local GUM clinic or GP. With improved facilities of digital world, patients can also order Chlamydia test kits to their home from online sources.
Once this test is carried out then depending upon its results further treatment will be carried out. Note that, Chlamydia disease is very common between age groups of 16 to 25 so most of the clinics these days are offering free tests to identify this disease on time. In case if you had oral or anal sex with your new partner who is suspected to be infected then it is good to undergo an oral swab test pr rectal swab test.
When To Get Tested
Also Check: What’s The Difference Between Chlamydia And Gonorrhea
When Should I Get Chlamydia Testing
As most people infected with chlamydia do not experience symptoms, doctors rely on screening to detect most cases of chlamydia. Screening guidelines vary based on many factors, including a persons anatomy, health, and sexual practices. Regular screening for chlamydia is recommended for several groups:
Certain factors increase the risk of contracting chlamydia and may affect how often a person should be screened. Risk factors include having:
- Sex with a new partner
- More than one sexual partner or a partner who has sex with mutiple people
- A sex partner diagnosed with an STD
Testing for chlamydia is more frequently conducted in asymptomatic people in settings where infection rates are high, which often includes correctional facilities, adolescent health clinics, the military, and sexual health clinics.
Diagnostic chlamydia testing is recommended for anyone with signs or symptoms of this infection. When symptoms do occur, they may not appear until a few weeks after exposure. Signs and symptoms of chlamydia can vary based on the site of infection but may include:
- Burning during urination
- Abnormal discharge from the vagina, penis, or rectum
- Vaginal bleeding after sex or pain during intercourse
- Pain, tenderness, or swelling in the testicles or scrotum
- Rectal pain
How Long Does It Take To Show Up On A Test
There are several tests that you doctor might use to diagnose chlamydia:
- Urine test. Youll pee in a cup thats sent off to a laboratory testing facility to see if any chlamydia bacteria are present in your urine.
- Blood test. Your doctor will use a sterile needle to draw some of your blood and send it to a lab to see if antibodies to the chlamydia bacteria are present in your bloodstream.
- Swab. Your doctor will use a cotton round or stick to take a small sample of tissue or fluid that carries the infection, which is then sent to a lab to be cultured so that lab technicians can see what bacteria grows from the sample.
How long it takes for the results to show up depends on the test and on your specific health insurance plan.
- Urine tests take about 2 to 5 days to show a positive or negative result.
- Blood tests can come back with results in a few minutes if the blood is analyzed on site. But they can take a week or more if sent to an off-site lab.
- Swab results take about 2 to 3 days to show a positive or negative.
1 to 3 weeks to show up in people with vulvas.
Symptoms may take up a few months to show up. This is because bacteria are living creatures and have an incubation period that affects how long it takes them to cluster together and become infectious.
This incubation period is dependent on a variety of factors, including:
You May Like: Places To Get Tested For Chlamydia
What Can Happen If Chlamydia Is Not Treated
In women
Chlamydia can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease . PID is a serious infection of the reproductive organs. PID can cause:
- Infertility.
- Tubal pregnancies, which can lead to death of the mother and unborn child.
- Inflammation surrounding the liver.
A mother also can pass the infection to her child during birth. Infection in newborns can lead to:
- Eye infections .
Summary Of Recommendations And Evidence
The USPSTF recommends screening for chlamydia in sexually active women aged 24 years or younger and in older women who are at increased risk for infection . B recommendation.
Screening for Chlamydia and Gonorrhea: Clinical Summary of the USPSTF Recommendation
Population
note: For a summary of the evidence systematically reviewed in making this recommendation, the full recommendation statement, and supporting documents, go to .
HIV = human immunodeficiency virus STI = sexually transmitted infection USPSTF = U.S. Preventive Services Task Force.
Screening for Chlamydia and Gonorrhea: Clinical Summary of the USPSTF Recommendation
Population
note: For a summary of the evidence systematically reviewed in making this recommendation, the full recommendation statement, and supporting documents, go to .
HIV = human immunodeficiency virus STI = sexually transmitted infection USPSTF = U.S. Preventive Services Task Force.
The USPSTF recommends screening for gonorrhea in sexually active women aged 24 years or younger and in older women who are at increased risk for infection. B recommendation.
See the Clinical Considerations section for a description of populations at increased risk for infection.
The USPSTF concludes that the current evidence is insufficient to assess the balance of benefits and harms of screening for chlamydia and gonorrhea in men. I statement.
You May Like: Naat Testing For Gonorrhea And Chlamydia
Limits Of Urine Tests For Gonorrhea And Chlamydia
In 2018, 1.8 million cases of chlamydia were reported to the CDC in addition to 583,405 cases of gonorrhea. These numbers show an increment of 19% and 63% since 2014 for the two diseases respectively.
Most infections with gonorrhea and chlamydia are asymptomatic. The fact that many people have no symptoms means that the only way to detect and treat these infections is through screening.
In men, these diseases most commonly infect the urethra, and in women the cervix. However, it is possible to get both of these diseases in the throat, from oral sex. Anal sex can also lead to rectal chlamydia and rectal gonorrhea infections.
Neither rectal nor oral/throat infections will be detected by urine testing. It is therefore important to let your healthcare provider know if you have unprotected oral or anal sex. Testing should be done separately for those sites.
Currently, it is recommended that men who have sex with men undergo urine, throat, and anal screening once a year. Other people who regularly have unprotected oral or anal sex should consider a similar screening regimen. People who only engage in vaginal intercourse can get by with urine testing alone for gonorrhea and chlamydia.
What Happens If I Dont Get Treated
The initial damage that chlamydia causes often goes unnoticed. However, chlamydia can lead to serious health problems.
If you are a woman, untreated chlamydia can spread to your uterus and fallopian tubes . This can cause pelvic inflammatory disease . PID often has no symptoms, however some women may have abdominal and pelvic pain. Even if it doesnt cause symptoms initially, PID can cause permanent damage to your reproductive system. PID can lead to long-term pelvic pain, inability to get pregnant, and potentially deadly ectopic pregnancy .
Men rarely have health problems linked to chlamydia. Infection sometimes spreads to the tube that carries sperm from the testicles, causing pain and fever. Rarely, chlamydia can prevent a man from being able to have children.
Read Also: What Are Symptoms Of Chlamydia In Males
Submission And Collection Notes
Unsuitable specimens: Urine and seminal fluid are not acceptable specimen sites for Chlamydia trachomatis culture. Dry swabs and swabs in bacteriological transport media are not acceptable collection kits for Chlamydia trachomatis culture and testing will not be performed.
Do not use expired kits.
Follow the collection instructions in the Chlamydia trachomatis culture or Kit Instruction Sheet.
Are Test Results Accurate
Although chlamydia testing is an important method of finding and treating this common STD, test results could be impacted by the following:
- The use of antibiotics within several days before testing
- Urinating within one hour of sample collection
- Vaginal douching within 24 hours of testing
- Improper sample collection
- Contamination of rectal samples with fecal matter
Don’t Miss: Can Chlamydia Develop On Its Own
Benefits Of Early Detection And Intervention Or Treatment
The USPSTF found adequate direct evidence that screening reduces complications of chlamydial infection in women who are at increased risk, with a moderate magnitude of benefit.
The USPSTF found adequate evidence that screening for gonorrhea results in a moderate magnitude of benefit based on the large proportion of cases that are asymptomatic, the effectiveness of antibiotic treatment to reduce infections, and the high morbidity associated with untreated infections.
The USPSTF found inadequate evidence that screening for chlamydia and gonorrhea reduces complications of infection and transmission or acquisition of either disease or HIV in men. The magnitude of benefit is unknown.
How Does Lab Test Work
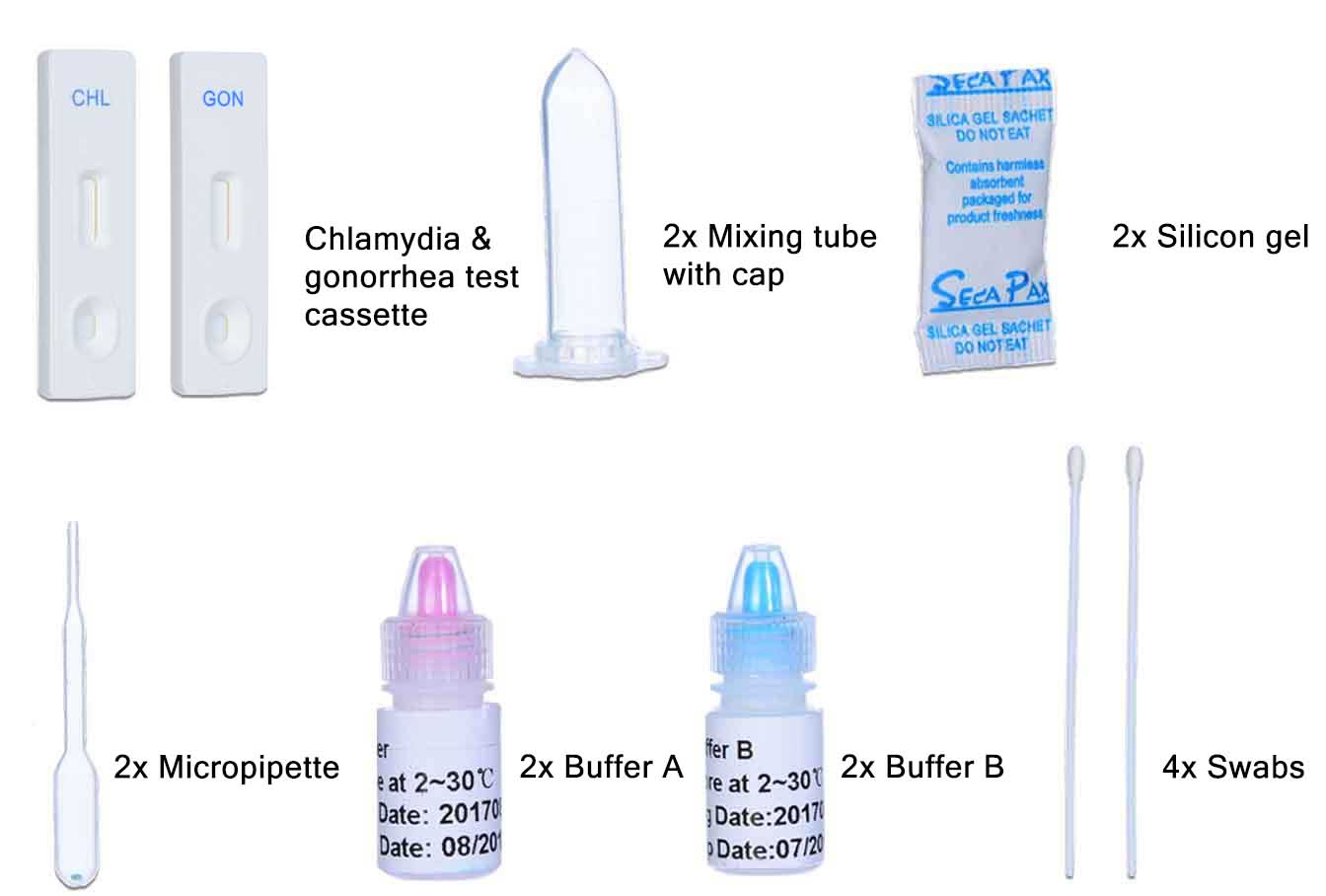
Lab test is a process of finding which things irritate your body or which things we have to give for bettering our self. Like in this case for this infection, this is a sexual transmission infection so for check it we have to do test the sample of our body and check it where of this is going,
So for men we take urine for testing and for woman we take swab for testing,
- They check all the things of your body.
- They do many hidden test for related your body.
- If significant things available then its marked in report of your body.
- Gives solution and suggestion related to your body.
Also Check: Can You Clear Chlamydia Without Treatment
Is There Anything Else I Need To Know About A Chlamydia Test
Chlamydia testing enables diagnosis and treatment of the infection before it can cause serious health problems. If you are at risk for chlamydia due to your age and/or lifestyle, talk to your health care provider about getting tested.
You can also take steps to prevent getting infected with chlamydia The best way to prevent chlamydia or any sexually transmitted disease is to not have vaginal, anal or oral sex. If you are sexually active, you can reduce your risk of infection by:
- Being in a long-term relationship with one partner who has tested negative for STDs
- Using condoms correctly every time you have sex
If You Have Further Questions Contact Your Ob
Don’t have an ob-gyn? Search for doctors near you.
FAQ071
Copyright 2021 by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. All rights reserved. Read copyright and permissions information.
This information is designed as an educational aid for the public. It offers current information and opinions related to women’s health. It is not intended as a statement of the standard of care. It does not explain all of the proper treatments or methods of care. It is not a substitute for the advice of a physician. Read ACOGs complete disclaimer.
Recommended Reading: Are There Other Ways To Get Chlamydia
How Chlamydia Is Treated
Chlamydia can usually be treated easily with antibiotics.
You may be given a course of doxycycline to take for a week or azithromycin to take once a day for 3 days.
If you have doxycycline, you should not have sex until you and your current sexual partner have finished treatment.
If you have azithromycin, you should wait 7 days after treatment before having sex .
It’s important that your current sexual partner and any other recent sexual partners you have had are also tested and treated to help stop the spread of the infection.
Under-25s who have chlamydia should be offered another test 3 to 6 months after being treated.
This is because young adults who test positive for chlamydia are at increased risk of catching it again.
Sexual health or genitourinary medicine clinics can help you contact your sexual partners.
Either you or the clinic can speak to them, or they can be sent a note advising them to get tested.
The note will not have your name on it, so your confidentiality will be protected.
Symptoms In The Throat
Chlamydia symptoms can sometimes appear in the throat, although this is uncommon. When it does occur, the time frame is likely to be similar to that of chlamydia infections of the genitals.
In people who experience symptoms, the main one is a persistent sore throat. A doctor may refer to a chlamydia infection in the throat as pharyngeal chlamydia.
Testing for chlamydia in the throat is not a common practice in STI testing, as it does not have approval from the Food and Drug Administration . However, if a person suspects that they have pharyngeal chlamydia, a doctor may take a swab from the throat.
A person can undergo testing for chlamydia at their:
- doctors office
- local health department
- local planned parenthood center
A person can also order a chlamydia test online, take it at home, and then send it off for testing.
If people are at high risk of chlamydia, they may need screening for all types of chlamydia every 36 months.
At risk groups include people who have:
- multiple or unknown sexual partners
- sex in combination with illegal drug use
- sexual partners who use illegal drugs or have multiple partners
7 days .
People should avoid having sex until their treatment is complete. If a person is experiencing symptoms even after the treatment, they should see a doctor.
People who menstruate should notice that their periods return to normal or that bleeding between periods stops by their next period.
Read Also: How You Know If You Got Chlamydia
Frequently Asked Questionsexpand All
- What is a sexually transmitted infection ?
A sexually transmitted infection is an infection spread by sexual contact. There are many STIs. This FAQ focuses on chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis. These STIs can cause long-term health problems and problems during pregnancy. Having an STI also increases the risk of getting human immunodeficiency virus if you are exposed to it.
- What is chlamydia?
Chlamydia is the most commonly reported STI in the United States. Chlamydia is caused by a type of bacteria, which can be passed from person to person during vaginal sex, oral sex, or anal sex. Infections can occur in the mouth, reproductive organs, urethra, and rectum. In women, the most common place for infection is the cervix .
- What are the risk factors for chlamydia?
The following factors increase the risk of getting chlamydia:
-
Having a new sex partner
-
Having more than one sex partner
-
Having a sex partner who has more than one sex partner
-
Having sex with someone who has an STI
-
Having an STI now or in the past
-
Not using condoms consistently when not in a mutually monogamous relationship
-
Exchanging sex for money or drugs
Chlamydia usually does not cause symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they may show up between a few days and several weeks after infection. They may be very mild and can be mistaken for a urinary tract or vaginal infection. The most common symptoms in women include
yellow discharge from the vagina or urethra
yellow vaginal discharge
Is Chlamydia Serious
Although chlamydia does not usually cause any symptoms and can normally be treated with a short course of antibiotics, it can be serious if it’s not treated early on.
If left untreated, the infection can spread to other parts of your body and lead to long-term health problems, especially in women.
In women, untreated chlamydia can cause pelvic inflammatory disease , ectopic pregnancy and infertility.
In men, in rare cases, chlamydia can spread to the testicles and epididymis , causing them to become painful and swollen. This is known as epididymitis or epididymo-orchitis .
It can also sometimes cause reactive arthritis in men and women.
This is why it’s important to get tested and treated as soon as possible if you think you might have chlamydia.
Testing for chlamydia is done with a urine test or a swab test.
You do not always need a physical examination by a nurse or doctor.
Anyone can get a free and confidential chlamydia test at a sexual health clinic, a genitourinary medicine clinic or a GP surgery.
In England, if you’re a woman under 25 years old, you may be offered a chlamydia test when you visit some health services, for example a pharmacy or GP. This offer is part of the National Chlamydia Screening Programme .
If you’re offered a chlamydia test you should consider taking it.
If you’re a woman, sexually active and under 25 in England, it’s recommended that you have a chlamydia test once a year, and when you have sex with new or casual partners.
You May Like: How Much Is Chlamydia Testing At Planned Parenthood
Why It Is Done
A test for chlamydia is done to:
- See if your symptoms of a sexually transmitted infection are caused by a chlamydia infection.
- Check people who are at high risk for being infected with chlamydia. A chlamydia infection doesn’t always cause symptoms.
- Retest people several months after they have been treated for chlamydia.
- Check for infection in your newborn if you had a chlamydia infection at the time of delivery.