Risk Factors And Demographic Factors For Chlamydia Trachomatis Infection
The most common demographic correlate of infection with chlamydial infection in women is young age . This could be explained by the anatomic differences in the cervix of the younger women, wherein the squamo-columnar junction, a primary host target for C. trachomatis, is everted and thus more exposed. Other factors associated with chlamydial infection include unmarried status, nulliparity, black race and poor socio-economic condition. A large number of sexual partners, a new sexual partner, lack of use of barrier contraceptive devices and concurrent gonococcal infection are also known to be associated with chlamydial infection. Cervical chlamydial infections are also found to be associated with the use of oral contraceptives.
When To Seek Medical Advice
If you have any symptoms of chlamydia, visit your GP, community contraceptive service or local genitourinary medicine clinic as soon as possible.
You should also get tested if you don’t have any symptoms but are concerned you could have a sexually transmitted infection .
If you’re a woman, sexually active and under 25 in England, it’s recommended that you have a chlamydia test once a year, and when you have sex with new or casual partners.
If you’re a man, sexually active and under 25 in England, it’s recommended that you have a chlamydia test once a year if you are not using condoms with new or casual partners.
Read more about chlamydia diagnosis.
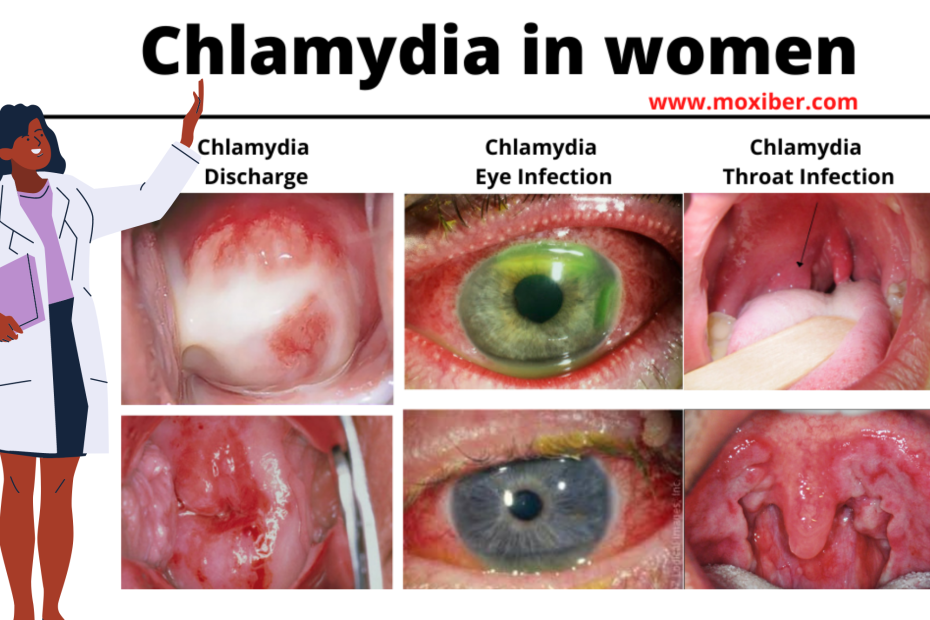
Chlamydia Symptoms In Women:
- testicular pain and/or swelling
- swollen skin around the anus
Depending on the localization of the infection, women, men and children may experience inflamed rectum, urethra or eyelids. The symptoms of mouth and throat infections are rare although a person can suffer a sore throat. Eyes infected with chlamydia can be itchy, swelled, cause painful sensations or produce discharge similar to conjunctivitis. Infection in the rectum results in bleeding, chlamydia discharge and pain.
Also Check: Symptoms For Chlamydia Or Gonorrhea
Who Should Get Tested For Chlamydia
Because chlamydia is very common and often has no symptoms, anyone who is sexually active should think about being tested. Because chlamydia is very common among young women, The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend sexually active women age 25 or younger get tested once per year. Chlamydia testing is also recommended for women with new or multiple sexual partners and pregnant women.
Anyone who is sexually active should talk with a healthcare provider about whether they need testing for chlamydia or other STIs. Dont be afraid to speak openly about your sex life, as you can get the best care by having an honest discussion with your healthcare provider.
What Are The Complications Of Untreated Chlamydia In Men
Because most men with chlamydia do not develop symptoms, many dont realize they have it and dont get the appropriate treatment. If left untreated, chlamydia infections may cause complications in men, including infertility, an abnormal narrowing of the rectum or urethra, and arthritis.
Untreated epididymitis from chlamydia may lead to infertility via two potential mechanisms :
- First, it has been suggested that untreated epididymitis can lead to scarring of the ducts that carry sperm.
- Secondly, chlamydia may directly impact the sperm and cause changes in sperm DNA.
However, a 2017 study found that infection with chlamydia did not harm sperm, nor did it affect fertility .
On the other hand, untreated proctitis caused by serovars L1, L2, or L3 does lead to long-term complications. Without appropriate antibiotic treatment, proctitis can cause fistulas and strictures of the rectum .
Also Check: Can You Get A Shot For Chlamydia
What Do The Results Mean
A positive result means you have been infected with chlamydia. The infection requires treatment with antibiotics. Your health care provider will give you instructions on how to take your medicine. Be sure to take all the required doses. In addition, let your sexual partner know you tested positive for chlamydia, so he or she can be tested and treated promptly.
Learn more about laboratory tests, reference ranges, and understanding results.
Effects Of The Disease
Chlamydia can cause infertility if it is not treated. It damages sperm and scars the reproductive tract. It also damages your sperm in ways that can make birth defects prevalent.
Chlamydia can also affect you in non-sexual ways. You can get recurring pink eye, reactive arthritis and rheumatological conditions.
Read Also: Could I Have Chlamydia For Years And Not Know
I Was Treated For Chlamydia When Can I Have Sex Again
You should not have sex again until you and your sex partner have completed treatment. If your doctor prescribes a single dose of medication, you should wait seven days after taking the medicine before having sex. If your doctor prescribes a medicine for you to take for seven days, you should wait until you have taken all of the doses before having sex.
How Can Chlamydia Be Prevented
Latex male condoms, when used consistently and correctly, can reduce the risk of getting or giving chlamydia.53 The surest way to avoid chlamydia is to abstain from vaginal, anal, and oral sex, or to be in a long-term mutually monogamous relationship with a partner who has been tested and is known to be uninfected.
Don’t Miss: Do They Test For Chlamydia When Donating Blood
How Often Should I Get Checked For Chlamydia
Sexual health check-ups are recommended for anyone who is sexually active. Frequency of testing also depends on your STI risk:
- An annual sexual health check-up is highly recommended if you are sexually active especially if you are under 25.
- Get checked more often during the year if you frequently change sexual partners.
- Remember, you are at greater risk if you have sex without a condom with 1 or multiple sexual partners.
How To Treat Chlamydia In Men
When the infection is caught early, chlamydia is easy to treat with a short course of antibiotics. Over 95% of people will be cured if they take the antibiotics correctly. The two types of antibiotics most commonly used to treat chlamydia are:
- Azithromycin: Taken as 24 tablets all at once.
- Doxycycline: Taken as 2 capsules each day for a week.
If your doctor is concerned about complications from chlamydia , they might prescribe a longer course of antibiotics.
Youll be advised not to have sex until you and your current sexual partner have finished treatment for chlamydia, or until a week after the 1-day treatment. Its also important to contact any other sexual partners who could have been exposed to infection. A sexual health clinic can help you contact people anonymously, if thats what youd prefer.
Recommended Reading: How Long Do You Have Chlamydia
Multidrug Resistant And Heterotypic Resistant Chlamydia Trachomatis
In 1980, Mourad et al were the first to report the reduced sensitivity to erythromycin. Decreased sensitivity to tetracycline was first reported by Jones et al in 1997. They identified five isolates from cases of tubal infertility which had minimum inhibitory concentration to tetracycline of 4 to > 8 mg/l, compared with control MICs of 0.125 to 0.25 mg/l. The isolates were also resistant to erythromycin, clindamycin and sulphonamide, but sensitive to ciprofloxacin and ofloxacin. Tetracycline resistance was also reported from France in 1997. In 2000, Somani et al reported multidrug resistant isolates of C. trachomatis associated with treatment failure with azithromycin.
There are no data regarding management of clinically resistant C. trachomatis infection. In vitro data suggest that resistance to ofloxacin imparts resistance to other fluoroquinolones, such as ciprofloxacin. Although many of the newer quinolones, including trovafloxacin, sparfloxacin, grepafloxacin and tosufloxacin have equal or greater MICs for C. trachomatis, these need to be tested against an ofloxacin-resistant strain,. Perhaps a prolonged course of therapy with a standard agent such as doxycycline or azithromycin would be effective against resistant C. trachomatis disease, because such therapy has been efficacious against C. pneumoniae infection in cases of relapse.
You Can Get Chlamydia More Than Once
With some diseases, having one infection makes you immune to future infections. That’s not the case with chlamydia. If you engage in sexual activity with a person who has a chlamydia infection, you can get it again, even if you’ve just completed treatment for it.
“Both partners should be treated before reinitiating sexual intercourse to prevent relapse,” Schaffir says.
Also Check: How Much Does Chlamydia Medication Cost
How Can I Reduce My Risk Of Getting Chlamydia
The only way to avoid STDs is to not have vaginal, anal, or oral sex.
If you are sexually active, you can do the following things to lower your chances of getting chlamydia:
- Be in a long-term mutually monogamous relationship with a partner who has been tested and has negative STD test results
- Use latex condoms the right way every time you have sex.
How Can You Protect Yourself From Getting Chlamydia
The only method that is 100% effective in preventing STDs is abstinence, but if youre sexually active, the best way to avoid chlamydia is to be mutually monogamous with someone who has testednegative for chlamydia. Condoms give good protection against chlamydia during vaginal sex and during oral sex on a male. Its important for both partners to get tested because its easy to get re-infected if one partner still has it. If you test positive for chlamydia, get tested again three months later to make sure you dont have it again. If youre sexually active and under 25, you should get tested for chlamydia every year better safe than sorry.
For protection against chlamydia during oral sex on a female, you can use a dental dam as a barrier between the mouth and vulva. A dental dam is a thin square of latex that is placed over a womans vulva before her partner performs oral sex on her and acts as a barrier between the vulva and the mouth. They are sold in some stores, but you can make your own dental dam using a latex glove or a male condom. For protection against Chlamydia during any type of anal sex , you can use a female condom.
Read Also: Will 250 Mg Of Azithromycin Cure Chlamydia
Chlamydia Is Caused By Sexually Transmitted Bacteria
The bacteria Chlamydia trachomatis causes chlamydia infection, which usually occurs in the genital tract, so the cervix in women and the penis in men. In both women and men, the bacteria may also infect the rectum and the throat.
“Infections are spread during any kind of sexual activity: vaginal, anal, or oral intercourse,” says Jonathan Schaffir, MD, an ob-gyn at Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center in Columbus.
Chlamydia trachomatis can also cause conjunctivitis if the bacteria come into contact with the eyelids or the clear membrane covering the white of the eye.
Because chlamydia infections often cause no symptoms, individuals who have one may not seek medical attention or get treated for it. However, anyone who is infected with chlamydia can pass it to other people, who can, in turn, pass it to others.
How Do You Prevent Chlamydia
Using a new male or female condom or dental dam every time you have sex is the best way to protect against chlamydia.
Chlamydia can be passed on by sharing sex toys. Always cover sex toys with a new condom and wash them after use to reduce your risk of getting chlamydia and other STIs.
Its important to regularly test for chlamydia, even if you dont have any symptoms, especially if youve had multiple sexual partners.
The contraceptive pill and other types of contraception wont prevent you getting chlamydia, and neither will PrEP.
Also Check: How Do You Get Treated For Chlamydia
What Causes Chlamydia
Chlamydia is caused by bacteria called Chlamydia trachomatis. Its the most common sexually transmitted infection in the U.S., accounting for close to three million new infections each year.
Chlamydia infections are almost always passed along through unprotected vaginal, anal, or oral sex. One key exception: Babies born to mothers with chlamydia can pick up the infection during delivery.
Using condoms during sex and having sex with only one person can reduce your risk of infection.
How Do You Get Tested
There are several different reliable tests for chlamydia. Newer tests, called NAATs , are very accurate and easy to take. Your healthcare provider can explain what testing options are available . If you dont have a regular healthcare provider, you can search here for a clinic near you.
People infected with chlamydia are often also infected with gonorrhea, so patients with chlamydia are often treated for gonorrhea at the same time, since the cost of treatment is generally less than the cost of testing.
If you live in Alaska, Maryland, or Washington, D.C., you can have a free at-home chlamydia test. Visit iwantthekit.org for more information.
Read Also: How Can You Get Chlamydia If No One Cheats
Chlamydia Infection May Have Long
For women, the long-term effects of an untreated chlamydia infection may include:
- Severe infection with pain and fever requiring a hospital stay
- Pelvic inflammatory disease, an infection of the upper reproductive tract
- Scarring in the reproductive tract that causes infertility
- Higher risk of ectopic pregnancy
Men are less likely than women to have major health problems linked to chlamydia, although they can develop epididymitis, an inflammation of a structure within the testicles called the epididymis that can result in infertility.
A chlamydia infection can sometimes result in reactive arthritis in both men and women.
The Health Risks Of Chlamydia
For up to 40 percent of infected women, untreated chlamydia can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease . PID effects include abdominal pain, fever, internal abscesses and long-lasting pelvic pain effects also include scarring of the fallopian tubes, which can cause infertility and increase the chance of potentially life-threatening ectopic or tubal pregnancies.
Men can develop scarring of the urethra, making urination difficult and occasionally causing infertility. Although rare, both sexes are at risk of a type of arthritis known as Reiter’s Syndrome that causes inflammation and swelling of the joints.
If a pregnant woman has chlamydia, her baby may be born prematurely, have eye infections or develop pneumonia.
Read Also: Can Chlamydia Go Away By Itself
How Can I Know If I Have Chlamydia
If you think you have chlamydia, or any STI, contact your healthcare provider. He or she will examine you and perform tests, if necessary, to determine if you have an STI.
To check for chlamydia, a woman is given a pelvic exam. A sample of fluid is taken from the vagina. In men, a sample of fluid may be taken from the penis. The fluid is sent to a laboratory for testing. The cultures can also be taken from a urine test. Your provider will discuss which way is the best way to check for an infection in your particular situation.
Letting Partners Know You Have Chlamydia
Sexual partners may be infected too. If you have chlamydia, anyone you have had sex with from the last 6 months needs to be informed, tested and treated.
If they dont know, they could reinfect you or infect someone else if they are not treated. dont receive treatment.
Most people will appreciate being told they may have an infection and it is an important step in preventing further infection in the community.
Your local GP and sexual health centre can help you inform your partners and let them know that they need a test. This process is called partner notification. It can be done anonymously, and your confidentiality is always respected.
You can also anonymously notify your sexual partners of the need to get tested and treated for chlamydia via the Let Them Know website if you feel unable to speak to them personally.
There are also nurses who can help you anonymously notify your partners. They can be contacted on .
Recommended Reading: How You Know If You Got Chlamydia
Penicillin And Other Natural Antibiotics
Observations about the growth of some microorganisms inhibiting the growth of other microorganisms have been reported since the late 19th century. These observations of antibiosis between microorganisms led to the discovery of natural antibacterials. observed, “if we could intervene in the antagonism observed between some bacteria, it would offer perhaps the greatest hopes for therapeutics”.
In 1874, physician Sir noted that cultures of the mold that is used in the making of some types of did not display bacterial contamination. In 1876, physicist also contributed to this field.
In 1895 , Italian physician, published a paper on the antibacterial power of some extracts of mold.
In 1928, Sir postulated the existence of , a molecule produced by certain molds that kills or stops the growth of certain kinds of bacteria. Fleming was working on a culture of bacteria when he noticed the of a green mold, , in one of his . He observed that the presence of the mold killed or prevented the growth of the bacteria. Fleming postulated that the mold must secrete an antibacterial substance, which he named penicillin in 1928. Fleming believed that its antibacterial properties could be exploited for chemotherapy. He initially characterized some of its biological properties, and attempted to use a crude preparation to treat some infections, but he was unable to pursue its further development without the aid of trained chemists.
What About Rectal And Oral Swabs
Rectal swabs and oral swabs may also be considered for those who have receptive anal sex or unprotected oral sex.
While neither rectal nor oral swabs are currently approved for the detection of chlamydia, research suggests that doing these extragenital tests is important.
For example, a 2017 study found that among men who have sex with men , 13% had a rectal chlamydia infection but only 3.4% had a positive urethral swab. In women in an urban setting in the United States, 3.7% were found to have an extragenital infection. Those under the age of 18 had the highest incidence of extragenital infection.
Also Check: Can You Buy Chlamydia Treatment Over The Counter