What Are The Treatments For Chlamydia
Antibiotics will cure the infection. You may get a one-time dose of the antibiotics, or you may need to take medicine every day for 7 days. Antibiotics cannot repair any permanent damage that the disease has caused.
To prevent spreading the disease to your partner, you should not have sex until the infection has cleared up. If you got a one-time dose of antibiotics, you should wait 7 days after taking the medicine to have sex again. If you have to take medicine every day for 7 days, you should not have sex again until you have finished taking all of the doses of your medicine.
It is common to get a repeat infection, so you should get tested again about three months after treatment.
How Does Chlamydia Spread
As chlamydial infection often has no symptoms, a person may have the infection and pass it on to a sexual partner without knowing.
It is not possible to pass on chlamydia through:
- contact with a toilet seat
- sharing a sauna
- touching a surface that a person with chlamydia has touched
- standing close to a person who has the infection
- coughs or sneezes
- sharing an office or house with a colleague who has the infection
- conjunctivitis or pneumonia in the newborn
Chlamydia And Abstaining From Sex
Until you and your partner are STD-free, avoid having sex, especially if you took Doxycycline to treat the STD. But if you had a prescription for Azithromycin, you may indulge in the activity after a week post-treatment. This ensures that the risk of passing the STD to your partner becomes negligible.
Don’t Miss: How To Deal With Chlamydia
Who Should Be Tested For Chlamydia
You should go to your health provider for a test if you have symptoms of chlamydia, or if you have a partner who has a sexually transmitted disease. Pregnant women should get a test when they go to their first prenatal visit.
People at higher risk should get checked for chlamydia every year:
- Sexually active women 25 and younger
- Older women who have new or multiple sex partners, or a sex partner who has a sexually transmitted disease
- Men who have sex with men
Clinical Features And Sequelae
- Genital infections with C. trachomatis present as urethritis and proctitis in men and women, cervicitis, salpingitis, endometritis and pelvic inflammatory disease in women, and orchitis, epididymitis and prostatitis in men.
- Perinatal transmission of C. trachomatis can result in conjunctivitis and pneumonia in newborns and young infants.
- At least 70% of genital C. trachomatis infections in women and 50% in men are asymptomatic at the time of diagnosis.
- The natural course of genital chlamydia infections is not well understood:
- Spontaneous resolution of asymptomatic infections is not uncommon.
- Asymptomatic infections, particularly endocervical infections, can persist for long periods.
- Many patients with asymptomatic infections will at some point develop symptoms and clinical disease.
- Asymptomatic infections can result in complications such as blocked tubes and pelvic inflammatory disease.
Recommended Reading: How Can You Get Chlamydia If No One Cheats
Also Check: Cpt Code For Chlamydia And Gonorrhea Screening
What Happens If Chlamydia Isn’t Treated
Only some people who have chlamydia will have complications. If chlamydia is treated early, its unlikely to cause any long-term problems. But, without proper treatment, the infection can spread to other parts of the body. The more times you have chlamydia the more likely you are to get complications.
- If you have a vulva, chlamydia can spread to other reproductive organs causing pelvic inflammatory disease . This can lead to long-term pelvic pain, blocked fallopian tubes, infertility and ectopic pregnancy .
- In people with a vulva, chlamydia can also cause pain and inflammation around the liver, though this is rare. This usually gets better with the correct antibiotic treatment.
How Often Should I Get Checked For Chlamydia
Sexual health check-ups are recommended for anyone who is sexually active. Frequency of testing also depends on your STI risk:
- An annual sexual health check-up is highly recommended if you are sexually active especially if you are under 25.
- Get checked more often during the year if you frequently change sexual partners.
- Remember, you are at greater risk if you have sex without a condom with 1 or multiple sexual partners.
Don’t Miss: Where Can I Buy Azithromycin For Chlamydia
Causes And Risk Factors
Chlamydia is an STI caused by a specific strain of bacteria known as Chlamydia trachomatis.
Chlamydia is more common in women than in men. In fact, its estimated that the overall rate of infection is for women than men in the United States.
Some of the other risk factors for infection include:
- not using barrier methods like condoms consistently with new sexual partners
- having a sexual partner who is having sex with other people
- having a history of chlamydia or other STIs
How Will I Know If The Chlamydia Has Affected My Fertility
Chlamydia is just one of many factors that can affect your fertility. Most people whove had chlamydia wont become infertile or have an ectopic pregnancy . If youve had chlamydia you wont normally be offered any routine tests to see if youre fertile unless you or a partner are having difficulty getting pregnant. If youre concerned, talk to your doctor or practice nurse.
Also Check: Cpt Code For Chlamydia Screening
Recommended Reading: Where Do You Get Tested For Chlamydia
Top Things To Know About Chlamydia:
- Chlamydia is often asymptomatic, meaning that many people donât know they have it
- Chlamydia symptoms can include pus-like yellow discharge frequent or painful urination spotting between periods or after sex and/or rectal pain, bleeding, or discharge
- Untreated, it can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease, chronic pelvic pain, ectopic pregnancy, and/or infertility in women and people with female reproductive tracts
- Antibiotics are used to treat chlamydia infections
What Happens If I Dont Get Treated
The initial damage that chlamydia causes often goes unnoticed. However, chlamydia can lead to serious health problems.
If you are a woman, untreated chlamydia can spread to your uterus and fallopian tubes . This can cause pelvic inflammatory disease . PID often has no symptoms, however some women may have abdominal and pelvic pain. Even if it doesnt cause symptoms initially, PID can cause permanent damage to your reproductive system. PID can lead to long-term pelvic pain, inability to get pregnant, and potentially deadly ectopic pregnancy .
Men rarely have health problems linked to chlamydia. Infection sometimes spreads to the tube that carries sperm from the testicles, causing pain and fever. Rarely, chlamydia can prevent a man from being able to have children.
Also Check: Where Can I Buy Chlamydia Pills
Do I Need To Have A Test To Check That The Chlamydia Has Gone
If you take the treatment according to the instructions, you wont usually need a test to check the chlamydia has gone.
If youre aged under 25, you should be offered a repeat test 3 months after finishing the treatment. This is because youre at a higher risk of getting chlamydia again.
Whatever your age, you may need a repeat test or more treatment if:
- you think youve come into contact with chlamydia again
- you had sex without a condom with a partner before the treatment for both of you was finished
- you didnt complete the treatment or didnt take it according to the instructions
- the signs and symptoms dont go away
- your test was negative but you develop signs or symptoms of chlamydia
- youre pregnant.
A repeat test can be done 56 weeks after the first test.
If the chlamydia was in your rectum , you may need another test around 3 weeks after finishing the treatment. Your doctor, nurse or clinic will let you know if you need another test.
You can go back to the doctor, nurse or clinic if you have any questions or need advice on how to protect yourself from infection in the future.
Theres A Cure For Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea can cause permanent and serious health issues if it’s left untreated. In women, the bacteria can spread to the uterus or fallopian tubes and cause pelvic inflammatory disease, which can lead to infertility, the CDC says. Men may also develop infertility from gonorrhea, although its rare.
Fortunately, gonorrhea can be treated. Treatment consists of a dose of the antibiotic ceftriaxone given once via injection, per the CDC. If gonorrhea has spread upwards into the pelvis, hospital admission for IV antibiotics may be required, Phillips says. And, she notes, its a good idea to be tested again two to four weeks after treatment to make sure the treatment worked and that you werent reinfected by a partner.
Don’t Miss: Everything You Need To Know About Chlamydia
Signs And Symptoms Of Chlamydia In Cats
There are some signs and symptoms of chlamydia in cats. Lets see what the symptoms and signs of it:
If your cat suffers from influenza, you can check whether your cats recover from flu by reading these signs of cats recovering from flu.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Know If You Have Chlamydia
What Happens If Chlamydia Goes Untreated
If a person is not treated for chlamydia, complications may occur. Women frequently develop pelvic inflammatory disease . PID can cause infertility , chronic pelvic pain, tubal pregnancies, and the continued spread of the disease. In men, untreated chlamydia can cause urethral infection and complications such as swollen and tender testicles. Chlamydia infection during pregnancy may result in premature rupture of membranes, preterm delivery and possible tubal pregnancy in a small percent of women. In addition, chlamydia can cause conjunctival and pneumonic infection in the newborn. Persons with a chlamydia infection have an increased chance of getting other infections such as gonorrhea or HIV.
Also Check: How To Clear Up Chlamydia Infection
Male Complications Of Untreated Chlamydia
Men can also experience complications when chlamydia is left untreated. The epididymis the tube that holds the testicles in place may become inflamed, causing pain. This is known as epididymitis.
The infection can also spread to the prostate gland, causing a fever, painful intercourse, and discomfort in the lower back. Another possible complication is male chlamydial urethritis.
These are just some of the most common complications of untreated chlamydia, which is why its important to get medical attention right away. Most people who get treatment quickly have no long-term medical problems.
Benefits Of Chlamydia Testing
Carrying out a test for chlamydia is the most reliable way to know if you have the disease Knowing if you have the infection is the first step to getting the proper treatment.
Treating chlamydia is vital to avoid complications that may cause long-term damage. Knowing your chlamydia status also helps you protect your partner from getting the infection.
You May Like: Can You Go To The Hospital For Chlamydia
How To Help Partners Get Treatment
If you are not sure whether your sexual partner will seek treatment, ask your doctor for extra chlamydia medication . You can give it to them so they can be treated as soon as possible.
This is known as patient delivered partner therapy for chlamydia. Talk to your doctor to see if PDPT is right for you and your sexual partner.
What Is The Treatment For Chlamydia
Antibiotics can easily cure chlamydia. Treatment options are the same, whether a person also has HIV or not.
Patients treated with single-dose antibiotics should not have sex for seven days. Patients treated with a seven-day course of antibiotics should not have sex until they complete treatment, and their symptoms are gone. This helps prevent spreading the infection to sex partners. It is important to take all medicine prescribed to cure chlamydia. Medicine should not be shared with anyone. Although treatment will cure the infection, it will not repair any long-term damage done by the disease. If a persons symptoms continue for more than a few days after receiving treatment, a healthcare provider should reevaluate them.
Repeat infection with chlamydia is common.49 Women whose sex partners do not receive appropriate treatment are at high risk for re-infection. Having multiple chlamydial infections increases a womans risk of serious reproductive health problems .50,51A healthcare provider should retest those with chlamydia about three months after treatment of an initial infection. Retesting is necessary even if their partners receive successful treatment.40
Infants with chlamydia may develop conjunctivitis and/or pneumonia.10 Healthcare providers can treat infection in infants with antibiotics.
Also Check: What Is Used To Cure Chlamydia
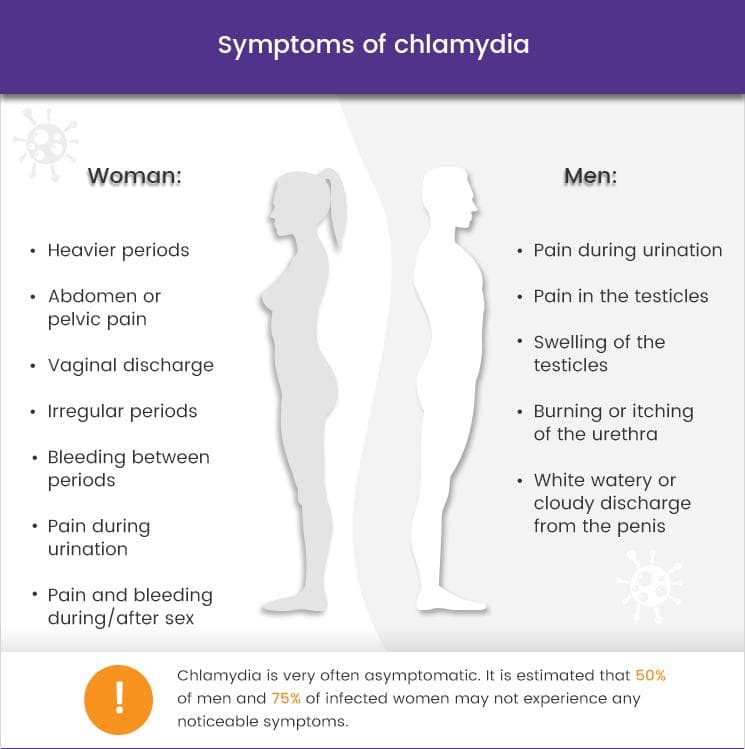
What Are The Symptoms Of Chlamydia
If you do notice symptoms, youll likely experience them differently based on your reproductive anatomy. Many of the symptoms that cisgender women experience can also affect transgender men and nonbinary individuals with vaginas. Many of the symptoms that cisgender men notice can affect transgender women and nonbinary individuals with penises, too.
Chlamydia bacteria often cause symptoms that are similar to cervicitis or a urinary tract infection . You may notice:
- Pus in your urine .
- Increased need to pee.
- Dull pain in the lower part of your abdomen.
Chlamydia bacteria most often infect your urethra, causing symptoms that are similar to nongonococcal urethritis. You may notice:
- Pain or a burning sensation when you pee .
Signs of chlamydia that all genders may notice
Chlamydia can affect parts of your body other than your reproductive organs, such as your:
- You may notice pain, discomfort, bleeding or a mucus-like discharge from your bottom.
- Throat. You may have a sore throat, but you usually wont notice symptoms if the bacterias in your throat.
- Eyes. You may notice symptoms of conjunctivitis if C. trachomatis bacteria gets in your eye. Symptoms include redness, pain and discharge.
See your healthcare provider immediately if you notice any of these symptoms.
How Long Can You Have Chlamydia Without Knowing

Chlamydia is sometimes called a silent infection because the majority of people who have chlamydia regardless of gender never notice symptoms. People who do notice symptoms often dont recognize the signs that they have chlamydia until a few weeks after theyve been infected. Because chlamydia cases are often asymptomatic, its easy to spread chlamydia to someone else without realizing it. And its easy to miss out on receiving the treatment needed to prevent the serious complications that can result from chlamydia.
Also Check: How Effective Is Chlamydia Treatment
How Does Chlamydia Affect A Pregnant Person And Their Baby
In newborns, untreated chlamydia can cause:
- ophthalmia neonatorum ,
Prospective studies show that chlamydial conjunctivitis and pneumonia occur in 18-44% and 3-16%, respectively, of infants born to those with chlamydia. 9-12 Neonatal prophylaxis against gonococcal conjunctivitis routinely performed at birth does not effectively prevent chlamydial conjunctivitis.37-39
Screening for and treating chlamydia in pregnant people is the best way to prevent disease in infants. At the first prenatal visit and during the third trimester, screen:
- All pregnant people under age 25 and
- All pregnant people 25 years and older at increased risk for chlamydia .
Retest those with infection four weeks and three months after they complete treatment.40
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
In the United States and other developed countries, the prevention of sexually transmitted genital infections and complications mainly focuses on screening and treating nonpregnant sexually active women aged 25 years or younger on an annual basis. Screening for pregnant women is recommended, and screening and treatment of women over 25 years of age are recommendations if there are identifiable risk factors, such as new or multiple sexual partners. Screening of young men in high-risk settings should be a consideration if resources allow. Urine or endocervical NAAT are the recommended screening tests. The partner should be screened and treated at the same time.
Healthcare workers and nurse practitioners should educate patients on the importance of using a condom during sex, practicing safe sex or abstaining from sexual activity to prevent chlamydia.
Pharmacists should verify dosing and agent selection for antimicrobial therapy, check for drug interactions, and report any concerns to the prescriber.
The prognosis is excellent with prompt initiation of treatment early, and with the completion of the entire course of antibiotics, antibiotic treatment is 95% effective for first-time therapy.
No vaccine is currently available for either trachoma or chlamydial genital infections.
You May Like: Having Chlamydia For A Month
Chlamydial Bumps On Shaft
Sexually transmitted infections are a huge problem in the United States and globally.
A chlamydia diagnosed male with herpes can present with bumps on the shaft or scrotum. These bumps are usually painless but can be itchy.
Diagnosing bumps on the shaft can be tricky because they can be confused with other STDs or STIs.
To determine if the bumps are indeed chlamydia, your doctor will ask the following questions:
- When did you first notice the bumps?
- Do the bumps itch or hurt?
- Are the bumps filled with pus?
- Have you had unprotected sex in the past three months?
- Have you been diagnosed with chlamydia before?
Your doctor will also conduct a physical examination, and your doctor may take a swab from the bumps to test for the presence of chlamydia.
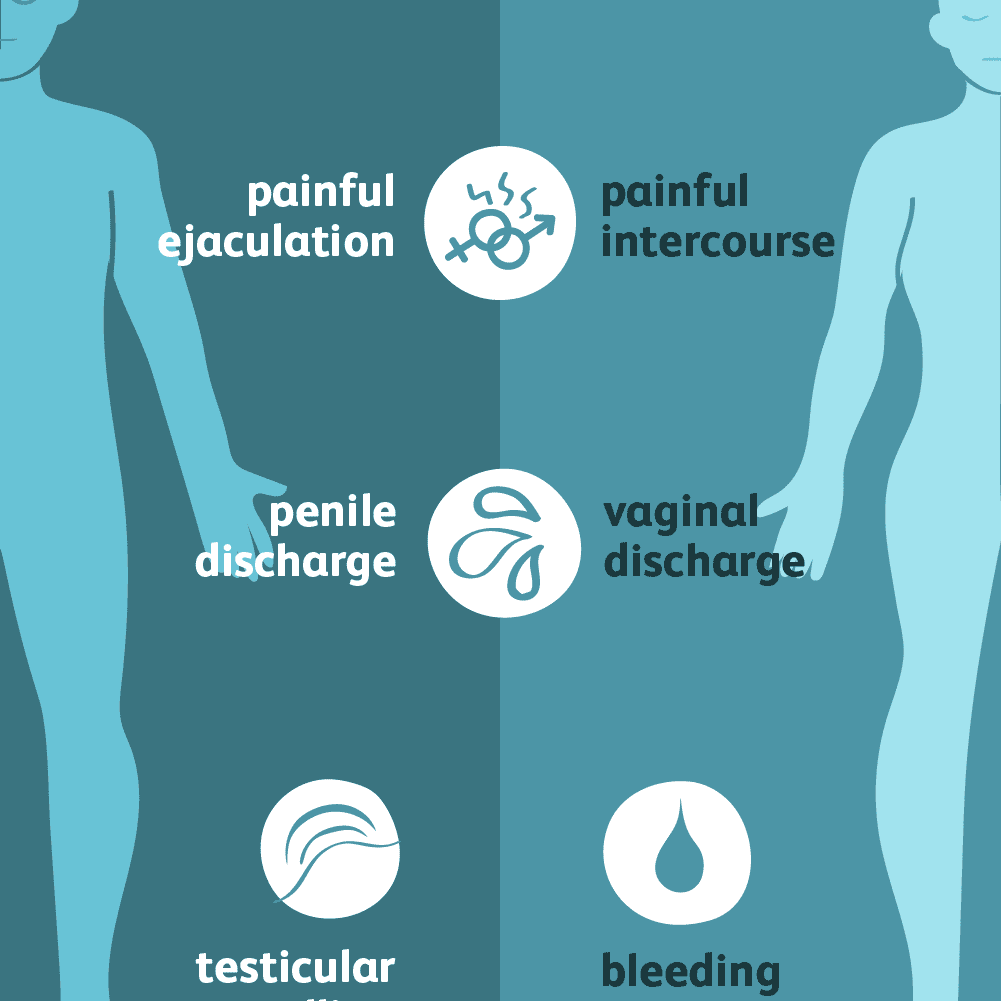
Symptoms Can Differ For Men And Women
By and large, most cases of chlamydia are asymptomatic they are picked up by screening, which is why it’s so important to have good screening programs in place, notes Dr. Stoner. Men or women who have chlamydia symptoms may experience painful urination.
Women may also have these symptoms:
- Smelly discharge from the cervix
- Pain during sex
And men may have these symptoms:
You May Like: How Long After Azithromycin Is Chlamydia Gone