Symptoms Of Gonorrhea And Chlamydia
Sometimes someone with gonorrhea or chlamydia does not show any symptoms.
In fact, 75% of women and 50% of men with chlamydia exhibit no symptoms.
It is unclear how common it is with gonorrhea, but some estimates are that the majority of men and women show no symptoms.
Even with no symptoms, it is still possible to transmit the disease and damage the reproductive system. The key signs of gonorrhea and chlamydia can appear within one to three weeks after having sex with a partner with the STD.
There are some differences in how both STDs present in men vs women, but in general the most common reported symptoms in both men and women are:
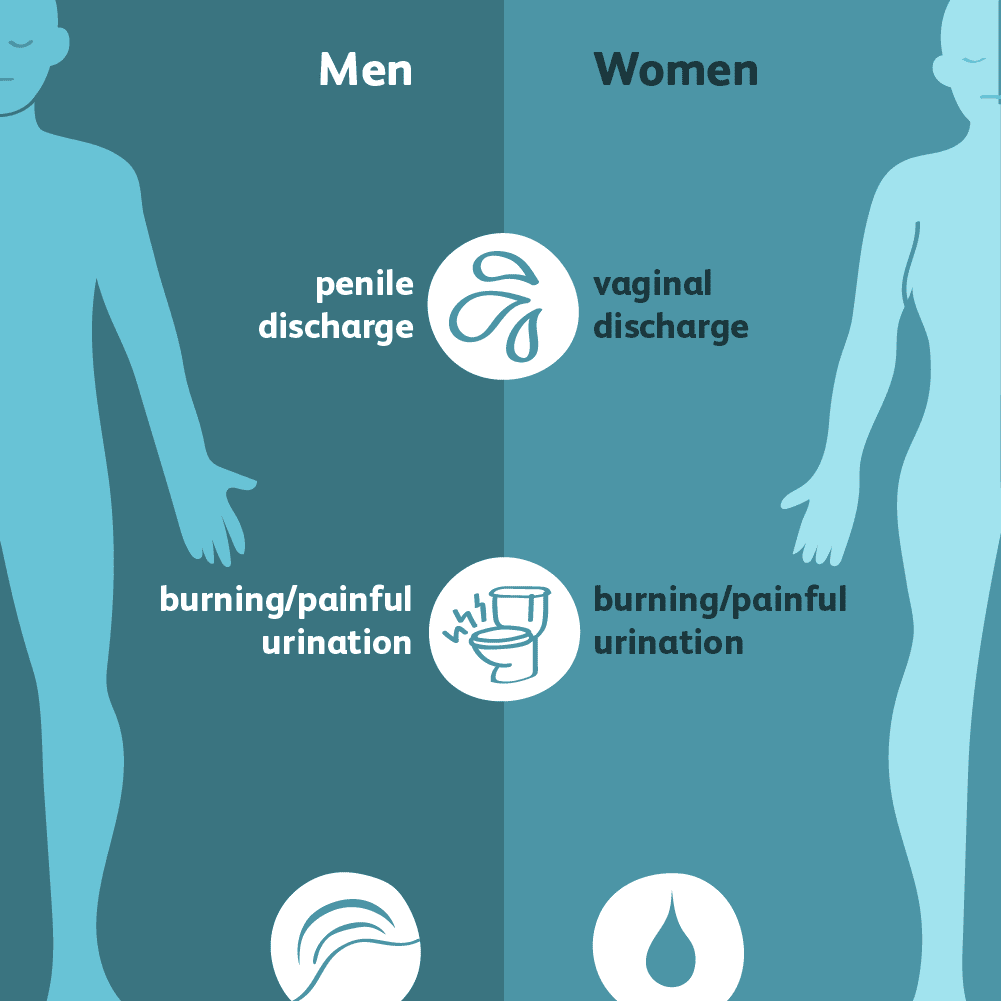
- Discharge For chlamydia, women may have vaginal discharge that has a strong odor or is yellowish, and men may have cloudy or clear discharge around the tip of the penis. For Gonorrhea, women and men may have discharge from the vagina or penis that is green, yellow, or white.
- Burning sensation while urinating Also called dysuria, this symptom is common with other STDs and is an important sign to get tested.
- Painful, burning sensations in infected area For both STDs, this is most common inside the vagina for women and the penal opening for men. Additionally, throat infections from oral sex are common and can result in swollen glands in the throat.
Women can also have painful periods, bleeding between periods, pain during sex, abdominal pain, or a fever.
- Discharge
Recommended Reading: Could I Have Chlamydia For Years And Not Know
Where Can I Get Tested For Chlamydia
You can get tested for chlamydia and other STDs at your doctors office, a community health clinic, the health department, or your local Planned Parenthood health center. In some states, you can do an online visit and take a chlamydia test at home.
STD testing isnt always part of your regular checkup or gynecologist exam you have to ask for it. Be open and honest with your nurse or doctor so they can help you figure out which tests you may need. Dont be embarrassed: Your doctor is there to help, not to judge.
Read Also: Where Can You Get Tested For Chlamydia
How Is Gonorrhea Treated
Health care providers treat gonorrhea with an antibiotic. It is given as a shot in the doctors office. It is important to get tested again 3 months after treatment to make sure the infection is cured .
All sexual partners from the past 2 months need treatment too, even if they dont have signs of gonorrhea.
If someone still has symptoms after treatment, they may need treatment with different antibiotics. Or they may have been infected with gonorrhea again.
You should not have sex again until:
- at least 7 days after you and your sexual partner take the antibiotics
- you and your sexual partner do not have signs of gonorrhea
People can get gonorrhea again if:
- Their partners arent treated.
- They get treated but then have sex with someone else who has gonorrhea.
Also Check: What Is The Difference Between Chlamydia And Gonorrhea
Infection In The Rectum Throat Or Eyes
Both men and women can develop an infection in the rectum, throat or eyes by having unprotected anal or oral sex.
If infected semen or vaginal fluid comes into contact with the eyes, you can also develop conjunctivitis.
Infection in the rectum can cause discomfort, pain or discharge. Infection in the eyes can cause irritation, pain, swelling and discharge, and infection in the throat usually causes no symptoms.
Common Signs Of Chlamydia
Like gonorrhea, chlamydia often displays few symptoms and can easily go unnoticed for a considerable amount of time. Men and women infected with chlamydia may notice one or more of the following symptoms:
- Abnormal vaginal discharge or penile discharge
- Painful, burning urination
- In women, bleeding between periods
- In men, swollen or sore testicles
- Rectal pain, bleeding, or discharge
- Lower abdominal pain
Don’t Miss: How Long Until Chlamydia Makes You Infertile
How Do You Get Chlamydia And Gonorrhea
- Engaging with multiple sexual partners in one year The more partners who engage with, the more likely you will be exposed to an infected person and contract an STD.
- Having unprotected sex Condoms can reduce the likelihood of you contracting an STD however, condoms are never 100% effective. If you are concerned you may have an STD, you should get tested regardless of whether you used a condom in your last sexual encounter.
- Younger than 24 Individuals younger than 24 tend to practice unprotected sex more often than other age groups and are less likely to be tested.
- Previous diagnosis of an STD Having already contracted an STD increases your bodys susceptibility to contracting another STD. It can be common for those who have contracted chlamydia to be at risk for contracting gonorrhea or HIV. If you contract gonorrhea, you are at a greater risk of contracting HIV.
How To Get Tested
A person can meet with a doctor to get a diagnosis for either of these infections.
The doctor will collect bodily fluids to test for the infection. The test can use either a urine sample or a sample from the vagina or penis, which a doctor will collect with a cotton swab.
Most health insurance plans, including Medicare, cover sexually transmitted infection testing completely. If a person does not have health insurance, they can go to a free clinic, their local health departments STI clinic, a student health center, or an urgent care clinic.
Because both chlamydia and gonorrhea can present with no symptoms, it is important that people who are sexually active get tested regularly.
After a doctor has determined which infection a person has contracted, they will prescribe an antibiotic.
People should take the full course of antibiotics and wait an additional 7 days before having sex again. This helps prevent a person from spreading the infection to another person and possibly reinfecting themselves later.
A person can contract both chlamydia and gonorrhea again, even if they have already experienced and treated the STI before.
Also Check: Gc Chlamydia Urine Test Quest
Chlamydia Cdc Fact Sheet
Chlamydia is a common sexually transmitted disease that can be easily cured. If left untreated, chlamydia can make it difficult for a woman to get pregnant.
Basic Fact Sheet | Detailed Version
Basic fact sheets are presented in plain language for individuals with general questions about sexually transmitted diseases. The content here can be syndicated .
What Is Chlamydia And Gonorrhea
Both gonorrhea and chlamydia are common sexually transmitted infections occurring in men and women. So how do you get gonorrhea and chlamydia? They are transmitted through vaginal, anal, or oral sex with someone whoâs infected.
Both infections are caused by bacteriaâChlamydia trachomatis in cases of chlamydia and Neisseria gonorrhoeae in cases of gonorrhea.
Although gonorrhea is a common sexually transmitted infection, chlamydia has a higher prevalenceâwith over 1.7 million cases of chlamydia reported in the United States in 2017.
Risk factors for getting gonorrhea and chlamydia are often identical and include:
- Having multiple sex partners. Youre more likely to be exposed to someone with a sexually transmitted infection if you have multiple sex partners.
- Unprotected sex. Condom usage during sex substantially reduces the risk of getting a sexually transmitted infection, so your risk is higher if you have unprotected sex.
- Having other STIs: If you already have a sexually transmitted infection, you can be at a greater risk of getting another STI. For example, if you contract chlamydia, you could be more likely to contract gonorrhea.
Read Also: 2 Pill Treatment For Chlamydia
Im Pregnant How Does Gonorrhea Affect My Baby
If you are pregnant and have gonorrhea, you can give the infection to your baby during delivery. This can cause serious health problems for your baby. If you are pregnant, it is important that you talk to your health care provider so that you get the correct examination, testing, and treatment, as necessary. Treating gonorrhea as soon as possible will make health complications for your baby less likely.
Symptoms In Men And Those With A Penis
A person with a penismay not develop noticeable symptoms for several weeks. Some men may never develop symptoms.
Typically, symptoms begin to show a week after transmission. The first noticeable symptom in men is often a burning or painful sensation during urination.
As it progresses, other symptoms may include:
In rare instances, gonorrhea can continue to cause damage to the body, specifically the urethra and testicles. The condition will stay in the body for a few weeks after the symptoms have been treated.
Pain may also spread to the rectum.
You May Like: How Soon After Sex Can You Test Positive For Chlamydia
What Are The Treatments For Chlamydia
Antibiotics will cure the infection. You may get a one-time dose of the antibiotics, or you may need to take medicine every day for 7 days. Antibiotics cannot repair any permanent damage that the disease has caused.
To prevent spreading the disease to your partner, you should not have sex until the infection has cleared up. If you got a one-time dose of antibiotics, you should wait 7 days after taking the medicine to have sex again. If you have to take medicine every day for 7 days, you should not have sex again until you have finished taking all of the doses of your medicine.
It is common to get a repeat infection, so you should get tested again about three months after treatment.
When To See A Healthcare Provider
Its important to talk to your healthcare provider if you have any signs or symptoms of chlamydia, any other symptoms that concern you, or if you know or think youve been exposed to the infection.
According to the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, women 25 and under and those who are sexually active should be screened for chlamydia every year, as should older women who have an increased risk of infection.
Screening for other STIs/STDs is important as well, as the risk factors for chlamydia also increase the likelihood of contracting these other infections. If you are treated for chlamydia, be sure to tell your healthcare provider if any symptoms persist.
You May Like: Signs And Symptoms Of Chlamydia In Females
Recommended Reading: How Do You Get Tested For Chlamydia
How Common Is Chlamydia
CDC estimates that there were four million chlamydial infections in 2018.3 Chlamydia is also the most frequently reported bacterial sexually transmitted infection in the United States.4 However, a large number of cases are not reported because most people with chlamydia are asymptomatic and do not seek testing. Chlamydia is most common among young people. Two-thirds of new chlamydial infections occur among youth aged 15-24 years.3 It is estimated that 1 in 20 sexually active young women aged 14-24 years has chlamydia.5
Disparities persist among racial and ethnic minority groups. In 2019, reported chlamydia rates for African Americans/Blacks were nearly six times that of Whites.4 Chlamydia is also common among gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men . Among MSM screened for rectal chlamydial infection, positivity has ranged from 3.0% to 10.5%.6,7 Among MSM screened for pharyngeal chlamydial infection, positivity has ranged from 0.5% to 2.3%.7.8
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
In the United States and other developed countries, the prevention of sexually transmitted genital infections and complications mainly focuses on screening and treating nonpregnant sexually active women aged 25 years or younger on an annual basis. Screening for pregnant women is recommended, and screening and treatment of women over 25 years of age are recommendations if there are identifiable risk factors, such as new or multiple sexual partners. Screening of young men in high-risk settings should be a consideration if resources allow. Urine or endocervical NAAT are the recommended screening tests. The partner should be screened and treated at the same time.
Healthcare workers and nurse practitioners should educate patients on the importance of using a condom during sex, practicing safe sex or abstaining from sexual activity to prevent chlamydia.
Pharmacists should verify dosing and agent selection for antimicrobial therapy, check for drug interactions, and report any concerns to the prescriber.
The prognosis is excellent with prompt initiation of treatment early, and with the completion of the entire course of antibiotics, antibiotic treatment is 95% effective for first-time therapy.
No vaccine is currently available for either trachoma or chlamydial genital infections.
Read Also: Can Chlamydia Come Back On Its Own
Discharge From The Vagina
Small amounts of discharge, especially from the vagina, is often normal.
But some sexually transmitted conditions can cause discharge from the genitals. Depending on the condition, the color, texture, and volume of the discharge may vary.
Though many people with chlamydia , this condition sometimes produces a mucus- or pus-like vaginal discharge.
With trichomoniasis, or trich, the vaginal discharge looks frothy or foamy and has a strong, unpleasant odor.
A yellowish or yellow-green vaginal discharge can be a symptom of gonorrhea, although most people who contract it will have no symptoms at all.
Who Is At Risk For Chlamydia
Any sexually active person can be infected with chlamydia. It is a very common STD, especially among young people.3 It is estimated that 1 in 20 sexually active young women aged 14-24 years has chlamydia.5
Sexually active young people are at high risk of acquiring chlamydia for a combination of behavioral, biological, and cultural reasons. Some young people dont use condoms consistently.15 Some adolescents may move from one monogamous relationship to the next more rapidly than the likely infectivity period of chlamydia, thus increasing risk of transmission.16 Teenage girls and young women may have cervical ectopy .17 Cervical ectopy may increase susceptibility to chlamydial infection. The higher prevalence of chlamydia among young people also may reflect multiple barriers to accessing STD prevention services, such as lack of transportation, cost, and perceived stigma.16-20
Men who have sex with men are also at risk for chlamydial infection since chlamydia can be transmitted by oral or anal sex. Among MSM screened for rectal chlamydial infection, positivity has ranged from 3.0% to 10.5%.6.7 Among MSM screened for pharyngeal chlamydial infection, positivity has ranged from 0.5% to 2.3%.7.8
Recommended Reading: Pills To Get Rid Of Chlamydia
How Are Chlamydia And Gonorrhea Treated
Since they are caused by different bacteria, chlamydia and gonorrhea require different treatment plans. Chlamydia is usually treated with one of the following medications:
- Azithromycin : a single pill or course of daily pills taken over approximately one week.
- Doxycycline : Two pills daily for approximately one week.
Since gonorrhea invades the cells, it requires a more aggressive treatment approach. You will usually receive both of the following treatments:
- Ceftriaxon injection.
- Azithromycin : a single pill or course of daily pills taken over approximately one week.
No matter which condition you have, you should follow your medical teams advice carefully to resolve it. Take the full course of medications prescribed, even if you start feeling better, to ensure the infection is totally gone. If you dont complete the antibiotics you may also develop an antibiotic resistance. This can make treating the condition difficult if you catch it again in the future.
You should also postpone sex until your infection has totally cleared up as you can still pass it on to your sexual partners, even if you arent showing symptoms anymore. They can then pass it back to you. If you follow your medical teams treatment plan, both gonorrhea and chlamydia should clear up in one to two weeks.
Telling A Sexual Partner About A Gonorrhea Diagnosis
If you don’t feel comfortable telling a sexual partner directly, services like Partner Notification Services may help.
This program works with local and state health departments and helps find and notify partners to anonymously advise them of their exposure to STIs. They then help provide testing and referrals to other services.
You can learn more about the program, including how to contact your local health department, here.
You May Like: How Long Does It Take To Get Treated For Chlamydia
When Should I Call My Doctor About A Chlamydia Test
A note from Cleveland Clinic
A chlamydia test is essential to limiting the spread of this sexually transmitted infection. Its especially important to get screened for chlamydia regularly if youre at a higher risk of this STI. Untreated, the infection can cause health problems and you can spread it to your partner. While youre waiting for results and during treatment, avoid having sex. Wait until your provider says its safe to have sex again. Be sure to use a condom and practice safe sex to avoid getting an STI.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 01/28/2022.
References
About The Chlamydia & Gonorrhoea Test For Women

-
What the test is for
This kit tests women for chlamydia and gonorrhoea in the vagina. The kit is for you if you do NOT have any symptoms, and if you have sex with men and/or women.
If you are unsure whether you need this test, you can take our free STI assessment. If you have symptoms, we recommend attending your local sexual health clinic.
-
Required samples for the chlamydia and gonorrhoea test
To test for chlamydia and gonorrhoea, you will need to provide a vaginal swab.
The test kit contains all the information and equipment you will need to safely collect this sample at home.
-
When to take the chlamydia and gonorrhoea test
We recommend doing the test 2 weeks after the unprotected sex. Tests done too early may not be accurate.
However, if you think you might have chlamydia or gonorrhoea, you can test immediately and repeat the test two weeks after having sex .
-
Accessing results
Test results are normally ready within 3 working days of your sample arriving at our partner laboratory. You will receive a text and an email when your results are ready.
If you dont receive your results within seven days of posting your sample, contact us via your Patient Record.
You May Like: How Long For Chlamydia Results