Sensitivity Of Mif Test For Twar Laboratory Diagnosis
shows results of laboratory diagnoses from our four major studies of respiratory infections. Two were done during TWAR epidemics and the other two in nonepidemic periods. We had complete control of specimen collection and patient data. The serologic positives include four-fold antibody titer rise, IgM antibody > 16, and high titer IgG antibody 512. Of the MIF-positive patients, 63%75% had the organism demonstrated by isolation, polymerase chain reaction , or both. The organism was found more frequently in the two studies that used PCR in addition to isolation. Only 1 isolation- or PCR-positive subject failed to show an acute MIF antibody response and that patient had an IgG titer of 128. Isolation and, to a lesser extent, PCR have been dependent on careful maintenance of the cold chain from patients to laboratory. Even in the best circumstances, demonstration of the organism has been less successful than MIF serology in identifying acute infection .
Results of C. pneumoniae laboratory diagnostic tests in four studies of acute respiratory tract infections.
Interpretation Of Serologic Results
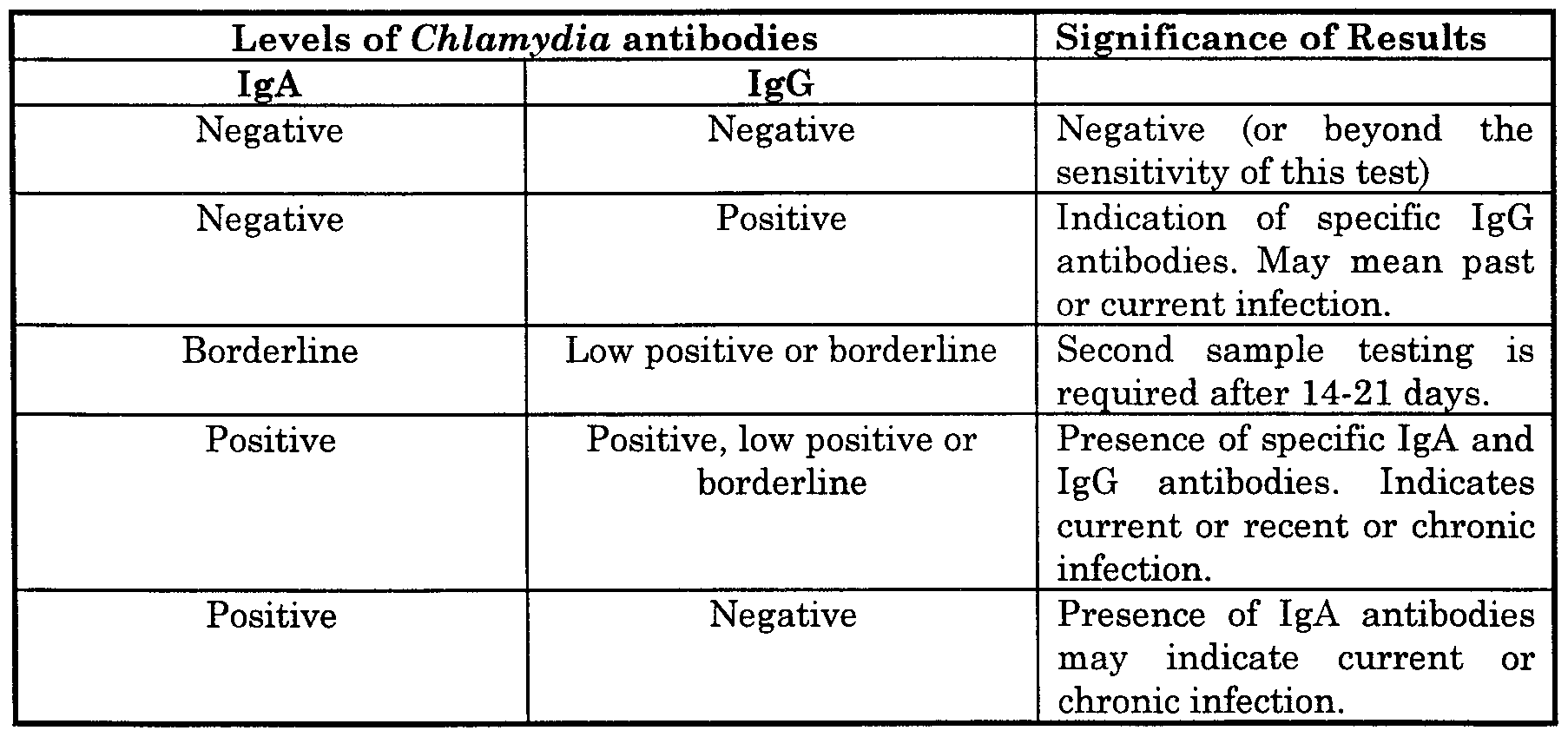
shows six types of MIF test results with TWAR antigen. We first screen each serum sample for IgM and IgG antibody at a 1:8 dilution. Positive reactions are then tested at two-fold dilutions to 1:1024. The first pair was negative in the screening test and not tested further. For the second pair, IgG was tested at dilutions and both the first and second serum had antibody at 1:128. This is interpreted as preexisting antibody, like that seen in most adults without acute infection. The last four pairs show different types of antibody patterns that are considered to indicate acute TWAR infection. On the basis of our experience, we consider MIF serologic positives for acute infection to include those with 4-fold antibody titer rise, IgM antibody titer 16, and IgG titer 512 . High antibody titer alone provides less definite proof of current infection as it may instead be associated with recent infection. While single serum samples may provide presumptive diagnostic information, paired or serial sera allow determination of antibody changes that offer more precise serologic diagnosis.
MIF test results for detection of TWAR infections.
Deterrence And Patient Education
Vaccines have not been developed for Chlamydia but there are ways to prevent this infection.
Patients should be counseled on refraining themselves from smoking and alcohol. Respiratory precautions should be followed to limit the spread of infection which includes regular hand washing, use of masks, and covering of mouth and nose while coughing or sneezing.
Atypical pneumonia caused by the chlamydial species can be fatal if not promptly addressed, particularly in patients with older age, immunocompromised state, and chronic comorbidities. Such a group of people with presentations suggesting respiratory tract infections should seek immediate care so that appropriate intervention can be done on time.
C. psittaci patients should also consult a veterinarian if they possibly acquired the disease from the contact with infected pet birds so that the birds can be treated after evaluation. The mother of an infant with C. trachomatis infection should be evaluated as well and treated along with her sexual partners. Women less than 25 years, and those at increased risk should be encouraged to get screened for chlamydial infections to prevent transmission to the infant.
Don’t Miss: How Do I Get Rid Of Chlamydia
What Is The Treatment For Chlamydia
Since its a bacterial infection, chlamydia is treated with oral antibiotics. Depending on the severity of the infection, youll need to take your prescription for 5 to 10 days. Be sure to finish the entire prescription. Just because your symptoms improve, doesnt mean the infection has fully cleared.
Youll also need to avoid all sexual activity during the course of your treatment until the infection clears up. This will reduce the risk of reinfection or transmitting the infection.
Due to the prevalence of chlamydia, its important to get annual tests if you:
- are under the age of 25 and are also sexually active, especially if youre female
- have sex with multiple partners
- have a history of STIs, or are treating another type of STI
- dont use condoms regularly
- are male and you have sex with other men
- have a partner who has told you theyve recently tested positive for chlamydia
You may need to get tested more often than once a year.
If youre pregnant, youll need to get a chlamydia test during your first prenatal appointment. Your gynecologist or midwife may also recommend another test later in your pregnancy if you have any of the above risk factors.
Chlamydia can cause complications in pregnant women, but also lead to problems at birth, such as pneumonia and eye infections.
After youve had chlamydia, you should get retested
What Are The Symptoms Of Chlamydia Pneumoniae
Like the STI, Chlamydia pneumonia doesnt show symptoms in most people most people who have Chlamydia pneumoniae are asymptomatic, meaning that they dont show signs or symptoms at all, or they only have very mild symptoms.
Possible symptoms if you do show symptoms, these can take at least 21 days since the date you were exposed to the bacteria to show up. Common symptoms are:
- A blocked or runny nose
- Tiredness
- Loss of appetite
- Confusion
Laryngitis this is sometimes a sign of pneumonia that is caused by Chlamydia pneumoniae bacteria. It isnt a typical symptom of pneumonia caused by other types of bacterial infection.
Don’t Miss: Will Chlamydia Show Up In A Blood Test
Chlamydia Trachomatis Igg Test
Chlamydia Trachomatis is the most common sexually transmitted diseases worldwide. Chlamydia Trachomatis can be implicated in a variety of infections among humans. It is one of the common causes of Non-gonococcal urethritis and Cervicitis. It causes Pelvic Inflammatory disease, Salpingitis & Endometritis in females. Among males, it can lead to Epididymitis & Reiter’s syndrome. Any sexually active person is at risk of contracting chlamydia since the bacteria can be transmitted via anal, vaginal, or oral sex. Chlamydia Trachomatis can be detected by Nucleic acid amplification tests , EIA, and DFA tests.
You don’t need any specific preparations for taking this test. Usually, urogenital infections are diagnosed by testing urine or by collecting swab.In case of taking the urine test, you have to make sure you haven’t urinated at least one hour before. You need to test pregnant women at least once, including those who are planning to terminate the pregnancy.Samples are taken using a swab from the vagina in women and urine from the urethra in men.For persons engaging in receptive anal intercourse, testing is done by obtaining a specimen via rectal swab.
Chlamydia Pneumonia In Infancy
- 5 to 30% of infected neonates will develop pneumonia. Approximately half of these infants will have a history of C. Trachomatis conjunctivitis.
- The condition is generally recognized between 4 and 12 weeks of age, although most infants are symptomatic as early as 8 weeks of age.
- Cough and nasal congestion without discharge are common, although discharge can be thick.
- Onset is insidious and characteristic features include a staccato cough, tachypnea. Rales is common upon auscultation, but wheezing is not. The liver and spleen may be palpable secondary to hyperinflated lungs.
- The patient is usually afebrile, and does not appear particularly ill.
- Premature neonates have had apnea spells secondary to Chlamydia pneumonia.
- WBC is normal, but eosinophils can be elevated.
- Arterial blood gas shows moderate hypoxemia.
- Chest X-ray shows hyperinflation with bilateral, symmetrical interstitial infiltrates.
You May Like: If I Take Antibiotics Will It Cure Chlamydia
How Can Chlamydia Be Prevented
The most reliable ways to avoid infection with chlamydia or any sexually transmitted disease are to abstain from oral, vaginal, and anal sex or to be in a long-term, mutually monogamous relationship with an uninfected partner. People who are sexually active should correctly and consistently use condoms to reduce the risk of infection with chlamydia and other STDs.
What Are The Clinical Manifestations Of Infection With This Organism
The most common manifestations are respiratory tract infections manifested as pneumonia or pharyngitis.
C. pneumoniae and chronic disease
-
Asthma
Chronic persistent infection with C. pneumoniae has been associated with asthma, arthritis, and atherosclerosis.
In the early 1990s, workers in the United States reported an association between serologic evidence of acute C. pneumoniae infection and asthma. Since then, a number of studies have been done in different countries to determine if this is a true association. Intranasal inoculation of mice with C. pneumoniae results in sustained airway hyper-responsiveness and airway inflammation. A recent systematic review concludes that C. pneumoniae seems to be involved more with asthma persistence than acute exacerbations. A Cochrane review of marcolide treatment in chronic asthma revealed an overall positive effect on symptoms and eosinophilic markers of inflammation.
-
C. pneumoniae and Alzheimers disease
In one study, a high proportion of brain samples from patients with Alzheimers disease were PCR positive for C. pneumonia, whereas those from age/sex matched non-Alzheimers disease control subjects were not. In one study, a 3-month course of doxycycline was administered to AD patients, and at 6 months the treated group had less cognitive decline than the control group.
-
Other associations
There is no association between pre-eclampsia and C. pneumoniae infection.
Recommended Reading: How To Get Treated For Chlamydia
What Might Affect My Test Results
As with most blood tests, the variables that may affect your test results are your nutritional diet, lifestyle and any other existing medications you’re currently on. Doctors should be informed if you’re using any supplements or prescription medications before the test is administered.
When it comes to testing the sputum, when collecting the sample, it should be made sure that the patient’s mouth is sterilised, clean and free from any foreign matter. Thus, the patient must rinse their mouth with filtered or sterilised water.
What Is This Test
Chlamydia pneumoniae IgG test is used to measure the levels of chlamydia IgG antibodies in the blood. This test helps in diagnosing chlamydia infection. This infection is associated with the mucous membranes of the urogenital system, eye, and upper respiratory tract. This test also helps in detecting the site of infection, previous exposure to this antigens, duration of the disease. Mostly this infection is seen in sexually active individuals. This can be transmitted sexually. If individuals are reinfected with chlamydia infection, IgG antibodies may not appear.
What is Chlamydia infection?
Why this test is performed?
Frequency:
If you are sexually active this test may be recommended once a year. If you are diagnosed with chlamydia infection this test may be recommended for 3 months after the treatment.
Precautions:
If women use any vaginal creams or douches should be stopped 24 hours before undergoing the test. Some antibiotics may interfere with the test results, hence inform about your current medical condition and medications to the doctor or technician before the test.
Read Also: What Medication Is Used For Chlamydia And Gonorrhea
Specific Recommendations For Culture
Specimen types. Specimens obtained for detection of C. pneumoniae respiratory tract infection by use of culture include swabs of the nasopharynx or oropharynx, sputum specimens, bronchoalveolar lavage specimens, and tissue biopsy specimens. C. pneumoniae has not been successfully cultured from blood samples, although the DNA can be detected in samples of peripheral blood mononuclear cells, and the organism has been recovered from a limited number of vascular tissue specimens.
Specimen collection. Swab specimens should be collected only on swabs with a Dacron tip and an aluminum or plastic shaft. Swabs with calcium alginate or cotton tips and wooden shafts may inhibit the growth of the organism, depending on the adhesive used, and are unacceptable. Swabs should be placed in 2SP transport medium and not removed before transport. Bronchoalveolar lavage, sputum, and pleural fluid samples should be collected in 2SP at a ratio of specimen to medium of 1:2.
Specimen transport. All specimens that can be processed in the laboratory within 24 h should be held and shipped at 4°C . Samples that cannot be processed within 24 h should be frozen and held at 70°C.
Recommendations for use of culture for Chlamydia pneumoniae.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Only with the combined effort of the interprofessional team can efficient patient care be delivered comprehensively. Health care providers should be vigilant for the non-specific signs in atypical pneumonia as the lab investigations usually take time, and the patients are easily treated with appropriate empirical antibiotics. While the condition can be treated in a primary care setting, complicated illness should be referred to higher care facilities or specialists. Clinicians should ensure the patients get all recommended vaccines as mixed infections are common.
Nursing care providers should ensure hospitalized patients get appropriate care, which includes but not limited to, monitoring vitals, bedside care, medication administration, and assisting patients to recover and regain functionality. The role of pharmacists is important in ascertaining that the right medication with the right dose has been prescribed before they reach the patients.
Read Also: How Does It Take To Get Rid Of Chlamydia
Chlamydia Conjunctivitis In Infancy
- Conjunctivitis is the most common neonatal manifestation of C. Trachomatis infection.
- The incubation period is 5-14 days after birth. Presentation before 5 – 14 days is rare, but has occurred with premature rupture of membranes.
- Initially the disease presents as watery discharge that becomes purulent.
- This can progress to marked swelling of eyelids with red and thickened conjunctiva .
- A pseudomembrane may form over the conjunctiva, which can become friable, resulting in bloody discharge.
- A membrane of granulation tissue may form after about two weeks if the condition is left untreated.
- Untrested infection may last for months and cause corneal and conjunctival scarring.
- N. Gonorrhea conjunctivitis presents earlier and progresses more rapidly, but must be considered in the differential diagnosis.
How Is Chlamydia Pneumoniae Treated
Normally with antibiotics the standard treatment for Chlamydia pneumoniae is a course of antibiotics, which are medicines that target specific bacteria in the body. Antibiotics tend to be the most effective form of medical treatment for the infection, and there are several different types of antibiotics that can be used.
Recovering without treatment many people with the infection will recover without any medical treatment at all, but everyone reacts differently to infection.
Its always worth getting help if you are showing the signs of a chlamydia pneumoniae infection, and you suspect that you have been in close contact with someone who is currently sick with it, you should make an appointment with your local nurse or GP for an assessment.
In order to properly diagnose the infection, you will either have:
- A blood test
- Or a swab test
With treatment, you should start to notice your symptoms disappear within a couple of weeks however, there is always the chance that your symptoms will reappear. In these cases, your doctor may decide to put you on a secondary course of treatment .
Read Also: Can Chlamydia Cause Prostate Cancer
Ophthalmia Neonatorum Caused By C Trachomatis
A chlamydial etiology should be considered for all infants aged 30 days who experience conjunctivitis, especially if the mother has a history of chlamydial infection. These infants should receive evaluation and age-appropriate care and treatment.
Preventing Ophthalmia Neonatorum Caused by C. trachomatis
Neonatal ocular prophylaxis with erythromycin, the only agent available in the United States for this purpose, is ineffective against chlamydial ophthalmia neonatorum . As an alternative, prevention efforts should focus on prenatal screening for C. trachomatis, including
Neonates born to mothers for whom prenatal chlamydia screening has been confirmed and the results are negative are not at high risk for infection.
Diagnostic Considerations
Treatment
Erythromycin base or ethylsuccinate 50 mg/kg body weight/day orally, divided into 4 doses daily for 14 days*
* An association between oral erythromycin and azithromycin and infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis has been reported among infants aged < 6 weeks. Infants treated with either of these antimicrobials should be followed for IHPS signs and symptoms.
Although data regarding use of azithromycin for treating neonatal chlamydial infection are limited, available data demonstrate that a short therapy course might be effective . Topical antibiotic therapy alone is inadequate for treating ophthalmia neonatorum caused by chlamydia and is unnecessary when systemic treatment is administered.
Follow-Up
Antimicrobials In Chlamydial Pneumonias
The goals of pharmacotherapy are to eradicate infection, reduce morbidity, and prevent complications.
Tetracyclines and macrolides are the drugs of choice for chlamydial pneumonias. Tetracyclines are bacteriostatic in nature they work by inhibiting protein synthesis. As a class, tetracyclines have similar antimicrobial profiles, and cross-resistance is likely. Macrolides inhibit bacterial growth, possibly by blocking dissociation of peptidyl t-RNA from ribosomes, thus causing cessation of RNA-dependent protein synthesis.
Don’t Miss: How To Treat Gonorrhea Or Chlamydia
Life Cycle And Method Of Infection
Chlamydia pneumoniaeChlamydiaChlamydia
Chlamydia pneumoniae is a small gram-negative bacterium that undergoes several transformations during its life cycle. It exists as an elementary body between hosts. The EB is not biologically active, but is resistant to environmental stresses and can survive outside a host for a limited time. The EB travels from an infected person to the lungs of an uninfected person in small droplets and is responsible for infection. Once in the lungs, the EB is taken up by cells in a pouch called an endosome by a process called phagocytosis. However, the EB is not destroyed by fusion with lysosomes, as is typical for phagocytosed material. Instead, it transforms into a reticulate body and begins to replicate within the endosome. The reticulate bodies must use some of the host’s cellular metabolism to complete its replication. The reticulate bodies then convert back to elementary bodies and are released back into the lung, often after causing the death of the host cell. The EBs are thereafter able to infect new cells, either in the same organism or in a new host. Thus, the lifecycle of C. pneumoniae is divided between the elementary body, which is able to infect new hosts but cannot replicate, and the reticulate body, which replicates but is not able to cause a new infection.
C. pneumoniae has also been found in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients diagnosed with multiple sclerosis.