What Happens During A Gonorrhea Test
If you are a man, your provider may take a swab from the opening of your urethra.
For both men and women, a sample may be taken from a suspected area of infection, such as the mouth or rectum. Urine tests are also used for both men and women.
Some gonorrhea tests can be done with an at-home STD test kit. If your health care provider recommends at-home testing, be sure to follow all directions carefully.
Your health care provider may order tests for other STDs when you get a gonorrhea test. These may include tests for chlamydia, syphilis, and/or HIV.
Read Also: How Easy Is It To Get Rid Of Chlamydia
So How Does Someone Get Chlamydia Or Gonorrhea
The bacteria that cause chlamydia or gonorrhea can spread very easily through any type of sexual contact The tricky thing is that a lot of people dont know they have an STI, at least in the first few weeks. a hidden epidemic). In the meantime, an infected person can unintentionally get someone else sick. Condoms may help reduce that risk, but they are not 100% effective, even when used correctly. The only way to protect oneself against these STIs is to either abstain from any sexual activity or to be in a long-term, trusted, and monogamous relationship such as marriage.
In Both Males And Females
Complications that may be seen in anyone include:
- Other STIs. Chlamydia and gonorrhea both make you more susceptible to other STIs, including human immunodeficiency virus . Having chlamydia can also increase your risk of developing gonorrhea, and vice versa.
- Reactive arthritis . Also called Reiters syndrome, this condition results from an infection in your urinary tract or intestines. Symptoms of this condition cause pain, swelling, or tightness in your joints and eyes, and a variety of other symptoms.
- Infertility. Damage to reproductive organs or to sperm can make it more challenging or, in some cases, impossible to become pregnant or to impregnate your partner.
Recommended Reading: How To Know If You Have Chlamydia Male
Why Am I Being Asked To Get Tested For Gonorrhea And Chlamydia During My Pregnancy
In the past, all babies were automatically treated with antibiotic eye drops in case their mother had untreated gonorrhea. Silver nitrate drops are not used anymore because they caused irritation to a babys eyes. The antibiotic ointment that is now used in Canada is called erythromycin ointment. Because many bacteria are now resistant to erythromycin, it may not work as well as the silver nitrate did and can sometimes irritate the eyes.Instead of treating all babies with the ointment, a better way of preventing these types of conjunctivitis is for all pregnant women to be tested for gonorrhea and chlamydia infections at their first prenatal visit. If they are infected, they need to be treated before the baby is born. This helps the mother as well as the baby. Most women with gonorrhea or chlamydia have no symptoms. Their partners may also not have symptoms. The only way to diagnose all cases is to test all pregnant women.If you were not tested for gonorrhea and chlamydia during your pregnancy, you should be tested at the time of delivery or before you take your baby home. To be tested, you need to either have a swab of your cervix done or provide a urine sample.
Dont Miss: How Long Does Chlamydia Last
Gonorrhea Symptoms During Pregnancy
Not all pregnant women who are infected will show gonorrhea symptoms. However, in addition to the symptoms mentioned above, pregnant women with untreated gonorrhea may also experience miscarriage, preterm birth, and ectopic pregnancy . Itâs also possible for the infection to be transmitted to the baby during delivery, which can cause serious health complications for the newborn.
According to the CDC, pregnant women younger than 25 should get screened for gonorrhea and other STIs at the first prenatal visit. This helps lower the risk of STIs causing pregnancy complications or harming the babyâs health.
You May Like: Are Uti And Chlamydia Antibiotics The Same
What Other Problems Can Chlamydia Cause
In women, an untreated infection can spread to your uterus and fallopian tubes, causing pelvic inflammatory disease . PID can cause permanent damage to your reproductive system. This can lead to long-term pelvic pain, infertility, and ectopic pregnancy. Women who have had chlamydia infections more than once are at higher risk of serious reproductive health complications.
Men often don’t have health problems from chlamydia. Sometimes it can infect the epididymis . This can cause pain, fever, and, rarely, infertility.
Both men and women can develop reactive arthritis because of a chlamydia infection. Reactive arthritis is a type of arthritis that happens as a “reaction” to an infection in the body.
Babies born to infected mothers can get eye infections and pneumonia from chlamydia. It may also make it more likely for your baby to be born too early.
Untreated chlamydia may also increase your chances of getting or giving HIV/AIDS.
Risks Of Unprotected Sex
Patients should also be counseled about the additional risks of unprotected sex, including the acquisition of more serious or lifelong infections such as herpes, hepatitis B, and HIV, and, of course, about the risks of pregnancy. The emotional aspect of sexual relationships may also need to be addressed, especially in teenage girls. Teenagers are vulnerable in that they are sexually mature but not yet emotionally mature.
Patient education materials are also available at The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Website and from many local public health departments.
References
Workowski KA, Bolan GA. Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines, 2015. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2015 Jun 5. 64 :1-137. . .
Dawe RS, Sweeney G, Munro CS. A vesico-pustular rash and arthralgia. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2001 Jan. 26:113-4. .
Belding ME, Carbone J. Gonococcemia associated with adult respiratory distress syndrome. Rev Infect Dis. 1991 Nov-Dec. 13:1105-7. .
Walters DG, Goldstein RA. Adult respiratory distress syndrome and gonococcemia. Chest. 1980 Mar. 77:434-6. .
Thiéry G, Tankovic J, Brun-Buisson C, Blot F. Gonococcemia associated with fatal septic shock. Clin Infect Dis. 2001 Mar 1. 32:E92-3. .
St Cyr S, Barbee L, Workowski KA, Bachmann LH, Pham C, Schlanger K, et al. Update to CDCs Treatment Guidelines for Gonococcal Infection, 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020 Dec 18. 69 :1911-1916. .
Cucurull E, Espinoza LR. Gonococcal arthritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1998 May. 24:305-22. .
Also Check: Chlamydia And Gonorrhea Home Test
Questions To Ask Your Doctor
- Do I have an STI? Can it be cured?
- What kind of treatment will I need?
- Can I have sex with my partner without passing on my STI?
- Can I spread an STI if I dont have symptoms and dont even know I have it?
- How do I prevent getting an STI?
- What long-term problems might I have if I have an STI?
- If Im pregnant, can I pass my STI onto my baby?
- Are there any STI support groups in my area?
Recommended Reading: How Long Before Chlamydia Shows Up
What Is The Treatment For Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea can be cured with the right treatment. CDC now recommends a single 500 mg intramuscular dose of ceftriaxone for the treatment of gonorrhea. Alternative regimens are available when ceftriaxone cannot be used to treat urogenital or rectal gonorrhea. Although medication will stop the infection, it will not repair any permanent damage done by the disease. Antimicrobial resistance in gonorrhea is of increasing concern, and successful treatment of gonorrhea is becoming more difficult 21. A test-of-cure follow-up testing to be sure the infection was treated successfully is not needed for genital and rectal infections however, if a persons symptoms continue for more than a few days after receiving treatment, he or she should return to a health care provider to be reevaluated. A test-of-cure is needed 7-14 days after treatment for people who are treated for pharyngeal gonorrhea.
Because re-infection is common, men and women with gonorrhea should be retested three months after treatment of the initial infection, regardless of whether they believe that their sex partners were successfully treated.
Recommended Reading: Can Chlamydia Cause Pain During Intercourse
How Is It Treated
Antibiotics are used to treat gonorrhea. Its important to take all of the medicine as directed. Otherwise the medicine may not work. Both sex partners need treatment to keep from passing the infection back and forth.
Getting treatment as soon as possible helps prevent the spread of the infection and lowers your risk for other problems, such as pelvic inflammatory disease.
Many people who have gonorrhea also have chlamydia, another STI. If you have gonorrhea and chlamydia, you will get medicine that treats both infections.
Avoid all sexual contact while you are being treated for an STI. If your treatment is a single dose of medicine, you should not have any sexual contact for 7 days after treatment so the medicine will have time to work.
Having a gonorrhea infection that was cured does not protect you from getting it again. If you are treated and your sex partner is not, you probably will get it again.
Finding out that you have an STI may make you feel bad about yourself or about sex. Counselling or a support group may help you feel better.
How Do I Know If I Have Gonorrhea
Some men with gonorrhea may have no symptoms at all. However, men who do have symptoms, may have:
- A burning sensation when urinating
- Painful or swollen testicles .
Most women with gonorrhea do not have any symptoms. Even when a woman has symptoms, they are often mild and can be mistaken for a bladder or vaginal infection. Women with gonorrhea are at risk of developing serious complications from the infection, even if they dont have any symptoms.Symptoms in women can include:
- Painful or burning sensation when urinating
- Increased vaginal discharge
- Vaginal bleeding between periods.
Rectal infections may either cause no symptoms or cause symptoms in both men and women that may include:
- Painful bowel movements.
You should be examined by your doctor if you notice any of these symptoms or if your partner has an STD or symptoms of an STD, such as an unusual sore, a smelly discharge, burning when urinating, or bleeding between periods.
You May Like: At Home Chlamydia Urine Test
Exactly How Usual Is Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is a really usual transmittable illness. CDC approximates that approximately 1.6 million new gonococcal infections happened in the USA in 2018, and over half take place amongst young people aged 15-24.
Gonorrhea is the 2nd most frequently reported bacterial sexually transmitted infection in the USA.2 Nonetheless, lots of infections are asymptomatic, so documented situations only record a fraction of truth worry.
Also Check: How To Get Rid Of Chlamydia Smell
How To Prevent Chlamydia And Gonorrhea
Practicing abstinence can eliminate your risk of getting either disease, but practicing safe sex is often a more sustainable preventive measure.
To prevent the spread of these infections during sex, use latex condoms correctly. Condoms have other benefits too, including reducing the risk of other STIs and unplanned pregnancy.
Recommended Reading: How To Get Rid Of Gonorrhea And Chlamydia
Research And Statistics: How Many People Have Gonorrhea
The number of reported cases of gonorrhea can depend on many factors that go beyond the actual occurrence of the infection, including things like differences in screening practices in different locations or the use of different kinds of tests. Nonetheless, reported cases can still be a useful way to track the disease and identify areas where the infection is on the rise or in decline.
What Are The Risks Of Chlamydia Or Gonorrhea During Pregnancy
Getting chlamydia or gonorrhea while pregnant can lead to:
- Miscarriage: some studies have found a link between chlamydia infection and miscarriage, which is a spontaneous loss of pregnancy before the baby is viable outside of the womb. Researchers believe it could be due to inflammation of the placenta caused by bacteria, as well as the rupture of membranes.
- Stillbirth: bacterial infections, including chlamydia and gonorrhea, might cause stillbirth , even though more research is needed to confirm this risk.
- Preterm delivery: which is when a baby is born before the 37th week of pregnancy. This can be problematic as the earlier a baby is delivered the higher the risk of health complications.
Also Check: Cure For Chlamydia And Gonorrhea
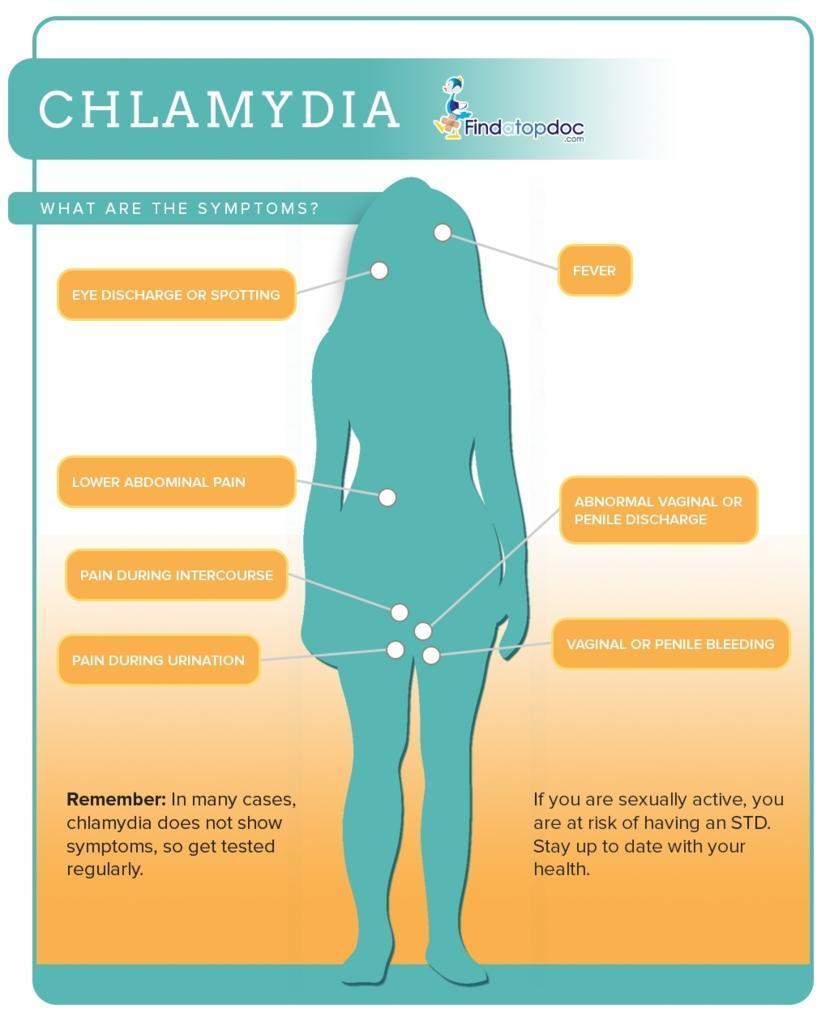
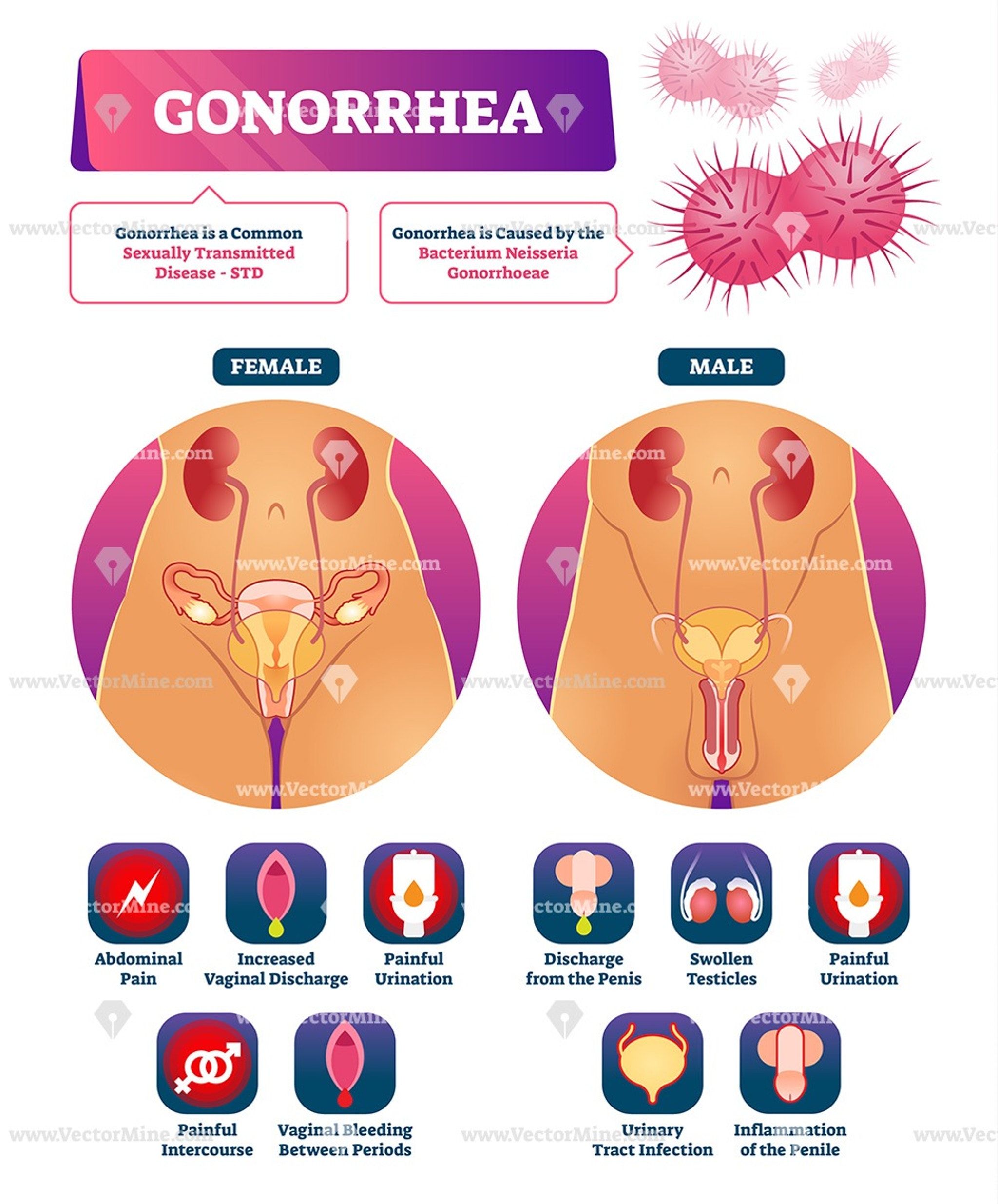
Symptoms Of Gonorrhoea And Chlamydia
Gonorrhoea and chlamydia are sexually transmitted diseases that can cause serious health problems if not treated promptly.
Both infections are caused by Neisseria gonorrhoea and Chlamydia trachomatis, respectively.
Both conditions are treatable with antibiotics. Gonorrhoea is curable in most cases, but it may lead to pelvic inflammatory disease, resulting in infertility or ectopic pregnancy.
Chlamydia causes PID as well as pelvic pain and bleeding between periods. The infection may be asymptomatic, or you may have a mild case.
According to the centre for disease control, In 2020 alone, there were about 820,000 new cases of gonorrhoea and over 300,000 new cases of chlamydia.
This means that more than 1 million people got infected with these two types of STDs. It is essential to know what they look like so you can get tested and treated quickly. The following are 5 symptoms of gonorrhoea and chlamydia:
What Are The Treatments For Chlamydia
Antibiotics will cure the infection. You may get a one-time dose of the antibiotics, or you may need to take medicine every day for 7 days. Antibiotics cannot repair any permanent damage that the disease has caused.
To prevent spreading the disease to your partner, you should not have sex until the infection has cleared up. If you got a one-time dose of antibiotics, you should wait 7 days after taking the medicine to have sex again. If you have to take medicine every day for 7 days, you should not have sex again until you have finished taking all of the doses of your medicine.
It is common to get a repeat infection, so you should get tested again about three months after treatment.
Read Also: How To Know If You Have Chlamydia Female
How Is Gonorrhea Transmitted
You can contract or transmit gonorrhea by having oral, , or vaginal sex.
Using a condom or other barrier method when engaging in sexual activity can go a long way toward lowering your chances of transmitting or contracting STIs like gonorrhea. Just keep in mind these barrier methods wont always completely eliminate your risk, especially if you dont use them properly.
Some evidence also suggests that oral gonorrhea may also be transmitted through French kissing, or kissing with tongue. However, more research is needed to truly understand the potential risk of transmission.
If youve developed gonorrhea before, you have a higher chance of contracting it again. Untreated gonorrhea can also
Toxicity And Side Effect Management
In neonates being treated for chlamydial infection, both azithromycin and erythromycin are associated with a risk of infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. This is particularly a concern for infants two weeks old or younger. Parents and physicians should observe infants closely for any signs of intestinal obstruction.
You May Like: How Long To Wait To Get Tested For Chlamydia
Who Gets Gonorrhea
Sexually active people of any age or sex can get gonorrhea and spread it to their partners. You can pass the infection on to your baby during childbirth.
Youre at greater risk of infection if you:
- Have a history of STIs.
- Dont use condoms or dental dams each time you have sex.
- Are having sex with one or more partners who havent tested negative for gonorrhea.
How To Get Tested
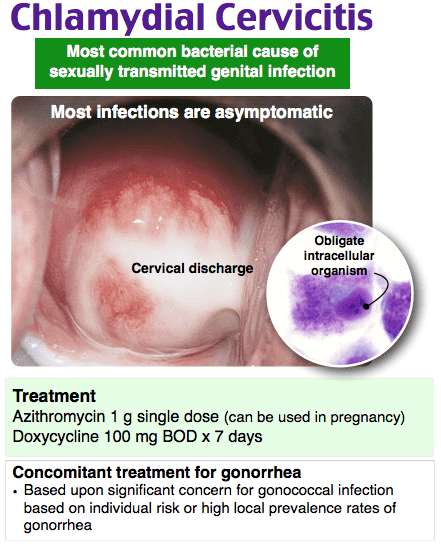
A person can meet with a doctor to get a diagnosis for either of these infections.
Most health insurance plans, including Medicare, cover sexually transmitted infection testing completely. If a person does not have health insurance, they can go to a free clinic, their local health departments STI clinic, a student health center, or an urgent care clinic.
Because both chlamydia and gonorrhea can present with no symptoms, it is important that people who are sexually active get tested regularly.
After a doctor has determined which infection a person has contracted, they will prescribe an antibiotic.
People should take the full course of antibiotics and wait an additional 7 days before having sex again. This helps prevent a person from spreading the infection to another person and possibly reinfecting themselves later.
A person can contract both chlamydia and gonorrhea again, even if they have already experienced and treated the STI before.
Recommended Reading: How To Get Rid Of Chlamydia And Gonorrhea
Don’t Miss: How Long After Being Treated For Chlamydia
Complications From Chlamydia And Gonorrhea
Because these two diseases often have no symptoms, some people go untreated.
Even with those who have symptoms, stigma, access, or other reasons get in the way of getting medical attention.
Not receiving prompt and proper treatment can create serious health problems.
For women, chlamydia and gonorrhea that goes untreated can spread through your uterus to your fallopian tubes.
Fallopian tubes connect the ovaries to the uterus and transport fertilized eggs during pregnancy. If untreated bacteria that cause gonorrhea and chlamydia spread to this area, the result is pelvic inflammatory disease , affecting around 5% of women in the US.
Pelvic inflammatory disease, similar to chlamydia and gonorrhea, can have no symptoms or just some pelvic or abdominal pain initially.
Unfortunately, PID can do permanent damage to a womenâs reproductive system, including:
For men, gonorrhea and chlamydia can also lead to serious health problems.
One difference is that chlamydia can also spread to the urethra, causing Non-Gonococcal urethritis, which is an infection of the tube that carries urine resulting in inflammation, pain, and fever.
This cannot be caused by the bacteria that causes gonorrhea. However, for both diseases, it is possible for either to cause:
For both women and men, chlamydia and gonorrhea can develop into a form of arthritis:
Symptoms of DGI include joint pain, fever, and skin rashes or sores.
Women are four times more likely to develop DGI than men.