How Is Chlamydia Spread
You can get chlamydia by having vaginal, anal, or oral sex with someone who has chlamydia.
If your sex partner is male you can still get chlamydia even if he does not ejaculate .
If youve had chlamydia and were treated in the past, you can still get infected again. This can happen if you have unprotected sex with someone who has chlamydia.
Is It Possible To Prevent Chlamydia
Since most people who have the infection do not have symptoms and may not be aware they are infected, it is commonly spread, and it can be difficult to prevent the infection. Male condoms can reduce the risk of spreading or acquiring the infection. Having a mutually monogamous relationship with a partner who has been tested or treated also reduces the risk of contracting chlamydia infection.
How Do I Know If I Have Chlamydia
Most people who have chlamydia have no symptoms. If you do have symptoms, they may not appear until several weeks after you have sex with an infected partner. Even when chlamydia causes no symptoms, it can damage your reproductive system.
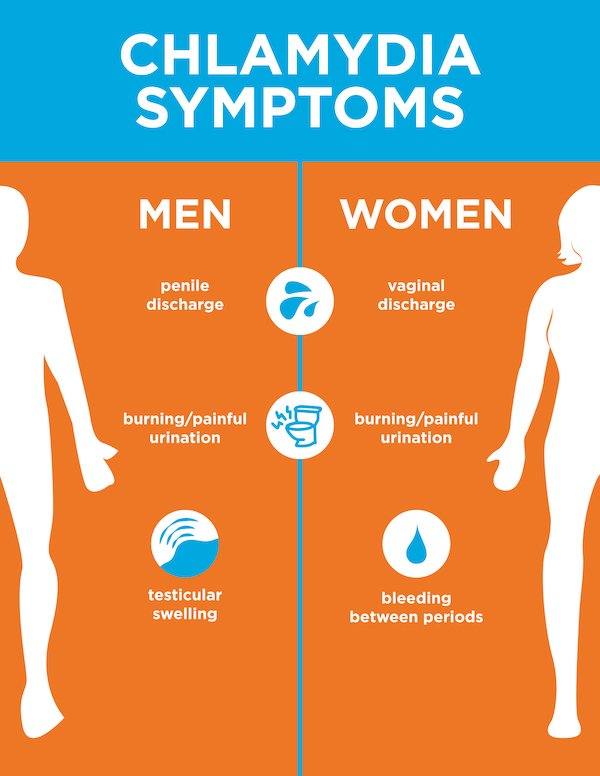
Women with symptoms may notice
- An abnormal vaginal discharge
- A burning sensation when urinating.
Symptoms in men can include
- A discharge from their penis
- A burning sensation when urinating
- Pain and swelling in one or both testicles .
Men and women can also get infected with chlamydia in their rectum. This happens either by having receptive anal sex, or by spread from another infected site . While these infections often cause no symptoms, they can cause
- Rectal pain
- Discharge
- Bleeding.
You should be examined by your doctor if you notice any of these symptoms or if your partner has an STD or symptoms of an STD. STD symptoms can include an unusual sore, a smelly discharge, burning when urinating, or bleeding between periods.
Also Check: Where To Get Free Chlamydia Treatment
How Easily Is Chlamydia Transmitted During Sexual Intercourse
Unfortunately, chlamydia is very easily transmitted through unprotected sexual contact. This is especially true because chlamydia infections are sometimes asymptomaticâmeaning they donât cause noticeable symptoms.
In fact, any time you come in contact with the bacteriaâeven if your sex partner doesnât ejaculate or you arenât fully penetratedâyou could become infected or pass along the chlamydial infection. This being the case, men and women should get tested for STIs before beginning any new sexual relationship.
How Do I Test For Chlamydia

You can get tested for chlamydia even if you dont have any symptoms.
Getting tested for chlamydia is easy and doesnt hurt. A healthcare professional will ask for a urine sample and/or take a swab from the area that might be infected. This is usually the lower part of the womb or the vagina for women, and the tip of the penis for men. If youve had anal or oral sex, you may have a swab taken from your anus or throat.
In some countries you can get a self-testing kit to do at home.
If you test positive for chlamydia, its important to tell any recent sexual partner/s so they can also get tested, and treated if necessary. If you need advice about how to do this, speak to your healthcare professional. You should also test for other STIs.
You May Like: Could I Have Chlamydia For Years And Not Know
How Common Is Chlamydia
In the United States, chlamydia infection rates are on the rise, making chlamydia the most commonly reported sexually transmitted infection in the country. In 2016, almost 1.6 million cases of chlamydia were reported to the Centers for Disease Control .
In the U.S., women are about twice as likely to be reported to have chlamydia as men. However, this is likely due to screening practices, since women are often screened during their annual pelvic exams. Men do not generally have similar annual screenings of their reproductive organs.
Since women are more likely to be asymptomatic, the number of people who actually have chlamydia could be even higher. Also, as testing becomes more sensitive and screening becomes more common and available, this trend is expected to continue to rise.
People aged 15 to 25 years old make up almost two thirds of all chlamydia cases reported in 2016 to the CDC . More specifically, up to 1 in 20 sexually active young women aged 14-24 could have chlamydia in the US .
Outside of the US, chlamydia is also very common. In 2012, the worldwide estimate of chlamydia infections was around 131 million new cases of chlamydia per year . This number is close to that of the entire population of Japan.
What Does Chlamydia Infection Mean For My Health
Chlamydia can be treated and cured easily, but that doesnt mean that chlamydia infection isnt potentially dangerous. If chlamydia isnt diagnosed and left untreated, it can cause serious complications.
Untreated chlamydia infections in women may lead to:
- Pelvic inflammatory disease , a serious infection of the reproductive organs . Left untreated, PID can cause infertility , chronic pelvic pain, or ectopic pregnancy.
- Cystitis
- A condition called mucopurulent cervicitis, characterized by a yellow discharge from the cervix
Untreated chlamydia in men may lead to:
- Prostatitis
- Scarring of the urethra
- Infertility
- Epididymitis
Recommended Reading: How Much Is Chlamydia Medicine
Chlamydia Symptoms & Treatment
FAST FACTS
- Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted infection that is normally passed on through sex without a condom or sharing sex toys with someone who has the infection.
- Using male or female condoms and dental dams during sex will help to protect you from getting chlamydia.
- Chlamydia is often symptomless however if left untreated it can lead to long-term health problems.
- Chlamydia is easily treated with antibiotics.
- Chlamydia can be passed on from mother to child during pregnancy, so its important for pregnant women to get tested.
An Overview & List Of Std Symptoms In Women
If youre worried youve contracted an STD, symptoms in women arent always obvious. Many women with sexually transmitted diseases dont see or feel any symptoms at all. When symptoms do appear, theyre often ambiguous or vague, making it hard to know the cause without getting tested. Women commonly confuse STD symptoms like discharge, odor, burning, and itching for something else, like a urinary tract infection or yeast infection.
According to the CDC, women are uniquely vulnerable to serious consequences of STDs.1 Women are less likely than men to show symptoms for common STDs such as chlamydia and gonorrhea. In addition, it can be harder for women to see symptoms because sores or ulcers may occur inside the vagina, where they arent easily visible.2 Without these first noticeable signs of an STD, infections can go unnoticed and untreated, which can cause long-lasting or even irreversible health problems, including infertility.
Read Also: What Can Cause Chlamydia To Come Back
Knowing Other Bodily Symptoms Of Chlamydia
Chlamydia Can Lead To Infertility
A lot of us don’t realize that some sexually transmitted diseases can cause no symptoms, meaning you could have an STD and not know it. And some STDs can silently lead to infertility, ectopic pregnancy, or chronic pelvic pain.
Chlamydia is one of those diseases. CDC estimates that more than 2.8 million people are infected each year.
Chlamydia is most common in sexually active young adults. More than half of all infections involve people ages 18 to 24. You can get chlamydia during oral, vaginal, or anal sexual contact with an infected partner. The disease can cause penile discharge in men and infertility in women. It can also cause serious health problems in newborn babies of infected mothers.
Many women, and some men, are infected with chlamydia but don’t know it. Even without symptoms, the disease can cause complications, particularly infertility. The longer the infection is untreated, the more damage that can be done.
If symptoms do show up, they usually occur within weeks of exposure. Men and women may face painful urination, an abnormal discharge from the urethra, or both. Women also may have abdominal pain, bleeding, and an abnormal discharge from the vagina. Symptoms usually appear within one to three weeks after being infected and may be very mild.
In pregnant women, chlamydia can cause premature delivery, the CDC says. A child born to an infected woman can develop an infection in their eyes and respiratory tracts.
You May Like: How Do I Tell Someone I Have Chlamydia
How Does Chlamydia Affect A Pregnant Woman And Her Baby
In pregnant women, untreated chlamydia has been associated with pre-term delivery, and can spread to the newborn, causing an eye infection or pneumonia. Screening and treatment of chlamydia during pregnancy is the best way to prevent these complications. All pregnant women should be screened for chlamydia at their first prenatal visit.
How is chlamydia diagnosed?
There are laboratory tests to diagnose chlamydia. Specimens commonly used for testing include a cotton swab of the vagina or a urine sample.
How is chlamydia treated?
Penicillin is not effective against chlamydia.
Chlamydia can be easily treated and cured with antibiotics. HIV-positive persons with chlamydia should receive the same treatment as those who are HIV-negative.
Persons with chlamydia should abstain from having sex for seven days after single dose antibiotics, or until completion of a seven-day course of antibiotics, to prevent spreading the infection to partners.
Repeat infection with chlamydia is common. Persons whose sex partners have not been appropriately treated are at high risk for re-infection. Having multiple chlamydial infections increases a woman’s risk of serious reproductive health complications, including pelvic inflammatory disease and ectopic pregnancy. Women and men with chlamydia should be retested about three months after treatment of an initial infection, regardless of whether they believe that their sex partners were successfully treated.
What Should I Do If I Have Chlamydia
Chlamydia is easy to treat. But you need to be tested and treated as soon as possible.
If you have chlamydia:
- See a doctor or nurse as soon as possible. Antibiotics will treat chlamydia, but they will not fix any permanent damage to your reproductive organs.
- Take all of your medicine. Even if symptoms go away, you need to finish all of the antibiotics.
- Tell your sex partner so they can be tested and treated. If they are not tested and treated you could get chlamydia again.
- Avoid sexual contact until you and your partner have been treated and cured. Even after you finish your antibiotics, you can get chlamydia again if you have sex with someone who has chlamydia.
- See your doctor or nurse again if you have symptoms that don’t go away within a few days after finishing the antibiotics.
Read Also: How To Get Rid Of Chlamydia In The Mouth
How Is Chlamydia Treated
Health care providers treat chlamydia with . All sexual partners from the past 2 months need treatment too, even if they don’t have signs of chlamydia.
You should not have sex again until:
- at least 7 days after you and your sexual partner take the antibiotics
- you and your sexual partner do not have signs of chlamydia
People can get chlamydia again if:
- their partners aren’t treated with antibiotics
- they get treated but then have sex with someone else who has chlamydia
Can A Urine Test Detect Stds
Urine testing is currently primarily used to detect bacterial STDs. Chlamydia and gonorrhea urine tests are widely available. Trichomoniasis urine tests are also available, but they are less common. The gold standard for diagnosing bacterial STDs, such as chlamydia and gonorrhea, used to be bacterial culture.
You May Like: What Medicine Is Used To Treat Gonorrhea And Chlamydia
Can Chlamydia Be Mistaken For Uti
The symptoms The main symptom that chlamydia does not share with UTIs is penile or vaginal discharge. A chlamydial infection can cause a yellowish, strong-smelling vaginal discharge or a watery, milky penile discharge. Urinary tract infections are not known to cause any sort of abnormal genital discharge.
How Do People Get Chlamydia
People get chlamydia by having sex with someone who has the infection. Chlamydia can still be transmitted even if a man does not ejaculate. People who have had chlamydia and have been treated can get infected again if they have sex with an infected person.
Chlamydia can be spread from an infected woman to her baby during childbirth.
Don’t Miss: Can Chlamydia Cause Prostate Cancer
Other Complications Of Untreated Chlamydia In All People
- Conjunctivitis, spread by touching the infected area and then touching the hand to the eye
- Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the rectum , if the chlamydia is from anal sex
- Varied symptoms, such as joint and eye inflammation, caused by bacterial infection
- Lymphogranuloma venereum, or LGV. This is caused by a type of chlamydia that is usually rare in the United States, but it is becoming more common in men who have sex with men. It causes open sores in the genital area, headache, fever, fatigue, and swelling of the lymph nodes in the groin. It also causes proctitis in people who get chlamydia through anal sex.
What Happens If I Dont Get Treated
The initial damage that chlamydia causes often goes unnoticed. However, chlamydia can lead to serious health problems.
If you are a woman, untreated chlamydia can spread to your uterus and fallopian tubes . This can cause pelvic inflammatory disease . PID often has no symptoms, however some women may have abdominal and pelvic pain. Even if it doesnt cause symptoms initially, PID can cause permanent damage to your reproductive system. PID can lead to long-term pelvic pain, inability to get pregnant, and potentially deadly ectopic pregnancy .
Men rarely have health problems linked to chlamydia. Infection sometimes spreads to the tube that carries sperm from the testicles, causing pain and fever. Rarely, chlamydia can prevent a man from being able to have children.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Hiv And Chlamydia At The Same Time
How Do You Get Tested
There are several different reliable tests for chlamydia. Newer tests, called NAATs , are very accurate and easy to take. Your healthcare provider can explain what testing options are available . If you dont have a regular healthcare provider, you can search here for a clinic near you.
People infected with chlamydia are often also infected with gonorrhea, so patients with chlamydia are often treated for gonorrhea at the same time, since the cost of treatment is generally less than the cost of testing.
If you live in Alaska, Maryland, or Washington, D.C., you can have a free at-home chlamydia test. Visit iwantthekit.org for more information.
I Was Treated For Chlamydia When Can I Have Sex Again

You should not have sex again until you and your sex partner have completed treatment. If your doctor prescribes a single dose of medication, you should wait seven days after taking the medicine before having sex. If your doctor prescribes a medicine for you to take for seven days, you should wait until you have taken all of the doses before having sex.
Also Check: How Soon Can You Treat Chlamydia
Recognizing Symptoms Of Chlamydia In The Genital Region
Symptoms Can Differ For Men And Women
By and large, most cases of chlamydia are asymptomatic they are picked up by screening, which is why it’s so important to have good screening programs in place, notes Dr. Stoner. Men or women who have chlamydia symptoms may experience painful urination.
Women may also have these symptoms:
- Smelly discharge from the cervix
- Pain during sex
And men may have these symptoms:
- Discharge from the penis
Also Check: Can Strep Throat Antibiotics Cure Chlamydia
Who Is At Risk For Chlamydia
Any sexually active person can be infected with chlamydia. Anyone with genital symptoms such as discharge, burning during urination, unusual sores, or rash should refrain from having sex until they are able to see a health care provider about their symptoms.
Also, anyone with an oral, anal or vaginal sex partner who has been recently diagnosed with an STD should see a health care provider for evaluation.
Because chlamydia is usually asymptomatic, screening is necessary to identify most infections. Screening programs have been demonstrated to reduce rates of adverse sequelae in women. CDC recommends yearly chlamydia screening of all sexually active women age 25 or younger and older women with risk factors for chlamydial infections . Pregnant women should be screened during their first prenatal care visit. Pregnant women younger than 25 or at increased risk for chlamydia should be screened again in their third trimester. Any woman who is sexually active should discuss her risk factors with a health care provider who can then determine if more frequent screening is necessary.
Routine screening is not recommended for men. However, the screening of sexually active young men should be considered in clinical settings with a high prevalence of chlamydia when resources permit and do not hinder screening efforts in women.
What are the symptoms?
What kinds of complications can the infection cause?