What If I Don’t Get Treated
The initial damage that chlamydia causes often goes unnoticed. However, chlamydia can lead to serious health problems.
If you are a woman, untreated chlamydia can spread to your uterus and fallopian tubes . This can cause pelvic inflammatory disease . PID often has no symptoms, however some women may have abdominal and pelvic pain. Even if it doesn’t cause symptoms initially, PID can cause permanent damage to your reproductive system and can lead to long-term pelvic pain, inability to get pregnant, and potentially deadly pregnancy outside the uterus.
Men rarely have health problems linked to chlamydia. Infection sometimes spreads to the tube that carries sperm from the testicles, causing pain and fever. Rarely, chlamydia can prevent a man from fathering children. Untreated chlamydia may also increase your chances of getting or giving HIV – the virus that causes AIDS.
Can Chlamydia Increase The Risk Of Getting Another Std
HIV is an STD. Chlamydia, gonorrhea, human papillomavirus infection, and syphilis are examples of other STDs. Having an STD can make it easier to get HIV. For example, an STD can cause a sore or a break in the skin, which can make it easier for HIV to enter the body. Having HIV and another STD may increase the risk of HIV transmission.
What Is The Difference Between An Std And Sti
The term STD is often used interchangeably with the term sexually transmitted infection . But despite this common misconception, STDs and STIs arent exactly the same. Each term has a specific meaning:
- STI. An STI is a sexually transmitted infection and doesnt cause any symptoms. Instead, an STI refers to the presence of the virus, bacteria, or other pathogens in your body.
- STD. An STD is a sexually transmitted disease, which does cause symptoms. It happens when the pathogens in your body have led to the cell damage that produces symptoms.
Put simply, an infection just means the presence of the pathogen is in your body, while a disease means youre having symptoms. A condition is only considered an STD if there are symptoms.
This might seem like a small difference, but the distinction is important. This is especially true for STIs that rarely cause symptoms, like chlamydia or gonorrhea. For many people, these STIs wont ever progress to STDs.
You May Like: Can Gonorrhea Or Chlamydia Go Away On Its Own
I Have Hiv How Can I Prevent Passing Hiv To Others
Take HIV medicines daily. Treatment with HIV medicines helps people with HIV live longer, healthier lives. One of the goals of ART is to reduce a person’s viral load to an undetectable level. An undetectable viral load means that the level of HIV in the blood is too low to be detected by a viral load test. People with HIV who maintain an undetectable viral load have effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to their HIV-negative partner through sex.
If your viral load is not undetectableâor does not stay undetectableâyou can still protect your partner from HIV by using condoms and choosing less risky sexual behaviors. Your partner can take medicine to prevent getting HIV, which is called pre-exposure prophylaxis, or PrEP. PrEP is an HIV prevention option for people who don’t have HIV but who are at risk of getting HIV. PrEP involves taking a specific HIV medicine every day to reduce the risk of getting HIV through sex or injection drug use. To learn more, read the Clinicalinfo Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis fact sheet.
Stds Can Increase The Risk Of Spreading Hiv
People with HIV are more likely to shed HIV when they have urethritis or a genital ulcer.4, 5 When a person with HIV gets another STD, such as gonorrhea or syphilis, it suggests that they were having sex without using condoms. If so, they may have spread HIV to their partners. Antiretroviral treatment for HIV can prevent the transmission of HIV even from persons who have other STDs.6
Also Check: Chlamydia Vs Yeast Infection Symptoms
Chlamydia Is Really Common
Chlamydia is a SUPER common bacterial infection that you can get from sexual contact with another person. Close to 3 million Americans get it every year, most commonly among 14-24-year-olds.
Chlamydia is spread through vaginal, anal, and oral sex. The infection is carried in semen , pre-cum, and vaginal fluids. Chlamydia can infect the penis, vagina, cervix, anus, urethra, eyes, and throat. Most people with chlamydia dont have any symptoms and feel totally fine, so they might not even know theyre infected.
Chlamydia can be easily cleared up with antibiotics. But if you dont treat chlamydia, it may lead to major health problems in the future. Thats why STD testing is so important the sooner you know you have chlamydia, the faster you can cure it. You can prevent chlamydia by using condoms every time you have sex.
Measures That Are Not Helpful
One factor that doesnt make things easier is the number of myths that surround STDs. Maybe youve heard some of these STD myths before or read about them online. For example, one myth says that rinsing your genitals with soda or alcohol after sexual intercourse will prevent STDs or pregnancy. However, that is false.
Washing your genitals or urinating after a sexual encounter will not prevent STDs. It can help prevent a urinary tract infection, but thats about it. Douching or washing is ineffective against STDs.
If you feel worried or panicked about possible exposure, try to stay calm and take the steps outlined here to do what you can to mitigate the risk after your sexual encounter. Schedule a test panel with Rapid STD Testing as soon as possible, especially if youre showingSTD symptoms.
If you had skin-to-skin contact with someone who has an STD, your chances of getting an STD from a one-night stand increase. Please get checked right away. Even if you arent showing symptoms, its still important to get an accurate test as quickly as possible.
Don’t Miss: Medicine To Treat Chlamydia And Gonorrhea
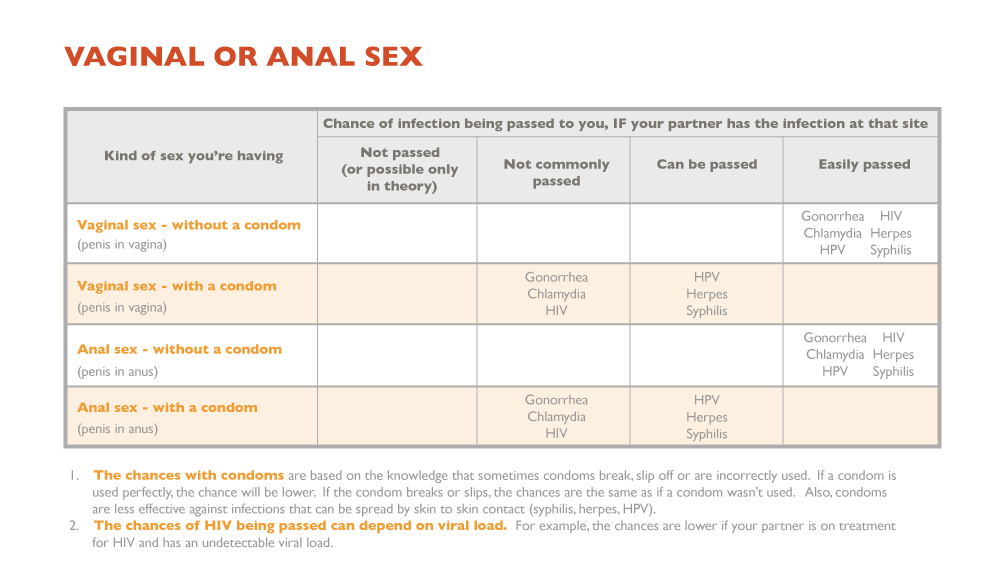
Unprotected Sex Std Risk
There is a significant likelihood of STD transmission from a single time of unprotected sex. As you can see, protection also does not completely take away the chances of contracting STD from one encounter. Abstinence is the only way to prevent the transmission completely. Nonetheless, you have a higher risk when you dont use protection, even just from one encounter.
Its best to assume that you have chances of STD transmission every time you have sex. Take precautions to prevent the spread by using protection every time. Also, you can greatly reduce the risk if you only have sexual contact with one other person, with both of you having been tested with negative results.
The only way to know for sure if youve picked up an STD from an unprotected sexual encounter is to get tested. If the person you were with told you they have a specific STD such as herpes or gonorrhea, it makes sense to get tested for that. But since youre not truly sure what STDs the person could have, you may want to do a complete STD test to be sure about your state of health. If you discover that you do have an STD, its nothing to be ashamed of. Its simply something that could impact your health in a negative way, especially if it goes untreated. Its important to find out if you have an STD so you can be treated.
Oral Sex Is Least Likely To Result In Hiv Transmission
The risk of transmission through oral sex is much lower than through anal or vaginal sex. This is because the oral cavity contains a thick epithelial layer, a low number of CD4 target cells, and antiviral antibodies.
A 2008 meta-analysis by Baggaley and others of 10 studies aimed at calculating the risk of HIV transmission through oral sex found that only 4 of the studies reported a non-zero estimate of risk from unprotected oral intercourse. For this reason, the CDC describes the chance of HIV transmission through oral sex as low.
You May Like: Could I Have Chlamydia For Years And Not Know
No 5 Having Vaginal Sex : 1 In 2500
A woman who is HIV positive can transmit the virus to her male partner through vaginal fluid and blood, which may pass through the urethra , the foreskin , or any open sores on the penis.
- Reduce the risk. Using a condom and water- or silicone-based lubricants, which can help lessen the chance that condoms will break or slip can help reduce a mans risk of getting HIV from an HIV-positive partner. Female condoms, which are made of a synthetic latex called nitrile and fit into the vagina during sex, are as protective as male condoms.
Other Complications Of Untreated Chlamydia In All People
- Conjunctivitis, spread by touching the infected area and then touching the hand to the eye
- Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the rectum , if the chlamydia is from anal sex
- Varied symptoms, such as joint and eye inflammation, caused by bacterial infection
- Lymphogranuloma venereum, or LGV. This is caused by a type of chlamydia that is usually rare in the United States, but it is becoming more common in men who have sex with men. It causes open sores in the genital area, headache, fever, fatigue, and swelling of the lymph nodes in the groin. It also causes proctitis in people who get chlamydia through anal sex.
You May Like: Signs Of Gonorrhea Or Chlamydia
What Complications Can Result From Chlamydial Infection
The initial damage that chlamydia causes often goes unnoticed. However, chlamydial infections can lead to serious health problems with both short- and long-term consequences.
In women, untreated chlamydia can spread into the uterus or fallopian tubes and cause pelvic inflammatory disease . Symptomatic PID occurs in about 10 to 15 percent of women with untreated chlamydia.30,31 However, chlamydia can also cause subclinical inflammation of the upper genital tract . Both acute and subclinical PID can cause permanent damage to the fallopian tubes, uterus, and surrounding tissues. The damage can lead to chronic pelvic pain, tubal factor infertility, and potentially fatal ectopic pregnancy.32,33
Some patients with chlamydial PID develop perihepatitis, or Fitz-Hugh-Curtis Syndrome, an inflammation of the liver capsule and surrounding peritoneum, which is associated with right upper quadrant pain.
In pregnant women, untreated chlamydia has been associated with pre-term delivery,34 as well as ophthalmia neonatorum and pneumonia in the newborn.
Reactive arthritis can occur in men and women following symptomatic or asymptomatic chlamydial infection, sometimes as part of a triad of symptoms formerly referred to as Reiters Syndrome.35
What Should I Do If I Have Chlamydia
Chlamydia is easy to treat. But you need to be tested and treated as soon as possible.
If you have chlamydia:
- See a doctor or nurse as soon as possible. Antibiotics will treat chlamydia, but they will not fix any permanent damage to your reproductive organs.
- Take all of your medicine. Even if symptoms go away, you need to finish all of the antibiotics.
- Tell your sex partner so they can be tested and treated. If they are not tested and treated you could get chlamydia again.
- Avoid sexual contact until you and your partner have been treated and cured. Even after you finish your antibiotics, you can get chlamydia again if you have sex with someone who has chlamydia.
- See your doctor or nurse again if you have symptoms that don’t go away within a few days after finishing the antibiotics.
Don’t Miss: Long Term Effects Of Chlamydia
Health Services For Screening And Treatment Of Stis Remain Weak
People seeking screening and treatment for STIs face numerous problems. These include limited resources, stigmatization, poor quality of services, and little or no follow-up of sexual partners.
- In many countries, STI services are provided separately and not available in primary health care, family planning and other routine health services.
- In many settings, services are often unable to provide screening for asymptomatic infections, lacking trained personnel, laboratory capacity and adequate supplies of appropriate medicines.
What Activities Can Put You At Risk For Stis
Behaviors that put people at risk for HIV also increase their risk for other STIs. These behaviors include:
- Having anal, vaginal, or oral sex without a condom.
- Having sex with multiple partners, especially anonymous partners.
- Having sex while using drugs or alcohol. Using drugs and alcohol can affect your judgment, which can lead to risky behaviors.
Don’t Miss: How You Know You Have Chlamydia
Ureaplasma Transmission: More Likely In Women With Multiple Sexual Partners
Ureaplasma infection can be caused by either Ureaplasma parvum or Ureaplasma urealyticum. We know that both naturally live on and in the human body. Under some circumstances, atypical bacteria can occur and colonize the body, causing an infection.
People can acquire the atypical bacteria through vaginal and oral sexual acts, which is why they are called opportunistic pathogens.
Research by Kokkayil and Dhawanin 2015 showed that the rate of vaginal colonization of Ureaplasma is from 8.5% to 77.5%. The colonization rate was found to be associated with having multiple sexual partners, and the transmission rate per sexual act is still unknown.
Protecting Your Sexual Partners
If you have HIV, are taking ART, and achieve and maintain an undetectable viral load, you have effectively no risk of passing HIV to your sexual partners. This is true even if you have an STI other than HIV. However, having an undetectable viral load will not prevent you from transmitting other STIs to your sexual partners.
If you have HIV and you do not have an undetectable viral load, untreated STIs may make it more likely that you will spread HIV to a sexual partner. But you can protect your partner from HIV by using condoms and choosing less risky sexual behaviors.
And if you have an HIV-negative partner who has another STI, they may have skin ulcers, sores, or inflammation that may increase their risk of getting HIV during sex.
An HIV-negative partner can take medicine to prevent HIV, called pre-exposure prophylaxis, or PrEP, but PrEP does not protect against other STIs. PrEP is an HIV prevention option for people who dont have HIV but who are at high risk of becoming infected with HIV. PrEP involves taking a specific HIV medicine every day to reduce the risk of HIV infection.
Read Also: How Fast Can Symptoms Of Chlamydia Show
Hiv/aids And Sexual Assault
It is not easy to get HIV infection. The risk of becoming infected from a single sexual contact is very small. Penetration of the vagina or anus by a penis, or contact with blood, is the most likely way HIV would be transmitted during a sexual assault.
HIV infection is diagnosed by a blood test. Immediately after a sexual assault, contact a physician and get tested. The physician will repeat the test at different intervals up to six months. If the test is still negative after six months, you can be assured that you do not have HIV infection.
What To Think About
Some people who have chlamydia may also have gonorrhea. In that case, treatment includes antibiotics that kill both chlamydia and gonorrhea. For more information, see the topic Gonorrhea.
Reinfection can occur. Symptoms that continue after treatment are probably caused by another chlamydia infection rather than treatment failure. To prevent reinfection, sex partners need to be evaluated and treated.
Repeated chlamydia infections increase the risk for pelvic inflammatory disease . Even one infection can lead to PID without proper treatment. Make sure to take your antibiotics exactly as prescribed. Take the full course of medicine, even if you feel better in a couple of days.
Some doctors recommend retesting 3 to 12 months after treatment to reduce the risk of complications from reinfection.footnote 4
If you have chlamydia, your doctor will send a report to the state health department. Your personal information is kept confidential. The health department may contact you about telling your sex partner or partners that they may need treatment.
Don’t Miss: Does Chlamydia Make You Poop A Lot
Std Testing And Treatment After Assault
After being sexually assaulted, it is important that you get a sexual assault examination as soon as possible. If you seek medical care within 120 hours of the assault, the health care provider who sees you may give you medications for certain STDs in case you were exposed to the diseases during the assault. Because these medications are not 100% effective in preventing disease, it is still important that you are aware of what to look for and return to your health care provider in two or three weeks to assure that you have been effectively treated.
For HIV risk, post-exposure prophylaxis of antiretroviral drugs may be offered if the assault took place within 72 hours of your medical evaluation. PEP lowers the chances of HIV infection taking hold in the body after an exposure to HIV.
If you do not have a health care provider, there are many places that can provide low-cost or free, confidential testing for HIV and other STDs/STIs for victims of sexual assault, or anyone else who may have an infection. See Getting Tested for STDs and HIV below for more information.
Safe, effective treatment is available to cure gonorrhea, chlamydia, and syphilis. Antibiotic treatment usually is based on the results of STD/STI tests. However, your physician may decide to treat you while waiting for the test results.
What Should You Do Next Time

While the statistics show that the likelihood of contracting an STD is relatively low, I encourage you to protect yourself during your sexual encounters. Always use protection. I also recommend that you get tested frequently. Nothing restores your peace of mind like a negative test.
While purpose of this article is to quell STD anxiety that can be overwhelming, it should in no way minimize the importance of protected sex or discourage monogamous relationships.
Responsible sexual behaviour keeps both you and your partner safe from STDs.
Also Check: What’s The Difference Between Chlamydia And Gonorrhea