Chlamydia Can Sometimes Go Away On Its Own
Some diseases and infections can go away on their own, so its not surprising that people wonder: does chlamydia go away on its own? The truth is, it sometimes does. In about 20% of people who have no symptoms, chlamydia may resolve spontaneously without treatment. It means that under certain circumstances host immune responses can control chlamydia naturally.
Untreated chlamydia can go on without any symptoms for a long period of time. Thats why its so important to get tested and catch it early. When chlamydia isnt treated, it can cause a number of serious complications. In women, the infection can spread to the uterus and uterine tubes, while in men, it can spread to the prostate gland. Chlamydia can also cause reactive arthritis, which affects your joints and eyes.
When chlamydia isnt treated, it can cause a number of serious complications.
Some people claim that chlamydia can be treated with home remedies like garlic and turmeric, but these methods are unproven and should be avoided. The only proven cure for chlamydia is treatment with antibiotics, which usually clear up the infection in a week or two.
Rates Of Sexually Transmitted Infections Likely Rose During The Pandemic
Experts warn that diseases such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis seem to be on the rise because routine testing was deferred in the midst of staffing and supply shortages.
Stay-at-home orders, coupled with a fear of exposure to COVID-19, seemingly kept many people confined at home and out of the arms of unknown partners throughout much of 2020. But in a counterintuitive twist, experts are warning of a probableand alarmingincrease in cases of sexually transmitted infections in the United States.
The main concern is that the pandemic hampered testing efforts for diseases such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis during the past two years. Testing is a critical part of controlling the spread of these infections, in part because both chlamydia and gonorrhea can initially appear without any symptoms.
Between 2015 and 2019, documented cases of all three diseases had increased by 30 percent. Then, from 2019 to 2020, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data suggested that chlamydia cases dropped by 14 percent, while cases of primary and secondary stages of syphilis experienced a modest decline of 0.9 percent. But experts now say this dip was not real, and that cases simply fell because we werent testing.
Though 2021 case numbers for sexually transmitted diseases are still being collected, there are worrying signs initial reports show that gonorrhea cases have climbed, and the CDC reports that there were more cases of infants with syphilis in 2020 than in 2019.
What Are The Symptoms Of Chlamydia
It is important to understand that focusing on signs and symptoms is not very useful in determining if someone is infected with chlamydia. First, the symptoms of chlamydia are similar to the symptoms of gonorrhea, and the two infections are often confused. Also, approximately, most women and about half of men do not experience symptoms. So, most people who are infected will not be able to tell from symptoms.
If a person does have symptoms, they usually develop within one to three weeks after exposure to chlamydia. How long a person remains infectious is difficult to determine since so many people are asymptomatic. A person must be considered infectious from the time they become infected until treatment is completed.
If a person does have symptoms, they may include:
- Proctitis , urethritis and conjunctivitis
- Soreness and redness in the throat or mouth (for chlamydia infection of the throat
- vaginal discharge
- pain or burning sensation during urination
- pus or watery or milky discharge from the penis
- pain or swelling of the testicle
If the infection spreads to the fallopian tubes, symptoms may include:
- lower abdominal and lower back pain
- pain during intercourse
- nausea or fever
Read Also: Which Antibiotics Treat Gonorrhea And Chlamydia
Clinical Features And Sequelae
- Genital infections with C. trachomatis present as urethritis and proctitis in men and women, cervicitis, salpingitis, endometritis and pelvic inflammatory disease in women, and orchitis, epididymitis and prostatitis in men.
- Perinatal transmission of C. trachomatis can result in conjunctivitis and pneumonia in newborns and young infants.
- Conjunctivitis and respiratory infections can be the result of contact with contaminated hands, or direct exposure to semen and vaginal fluids.
- At least 70% of genital C. trachomatis infections in women and 50% in men are asymptomatic at the time of diagnosis.
- The natural course of genital chlamydia infections is not well understood:
- Spontaneous resolution of asymptomatic infections is not uncommon.
- Asymptomatic infections, particularly endocervical infections, can persist for long periods.
- Many patients with asymptomatic infections will at some point develop symptoms and clinical disease.
- Asymptomatic infections can result in complications such as blocked tubes and pelvic inflammatory disease.
Why Are You Contagious Up To After 7 Days Of Chlamydia Exposure
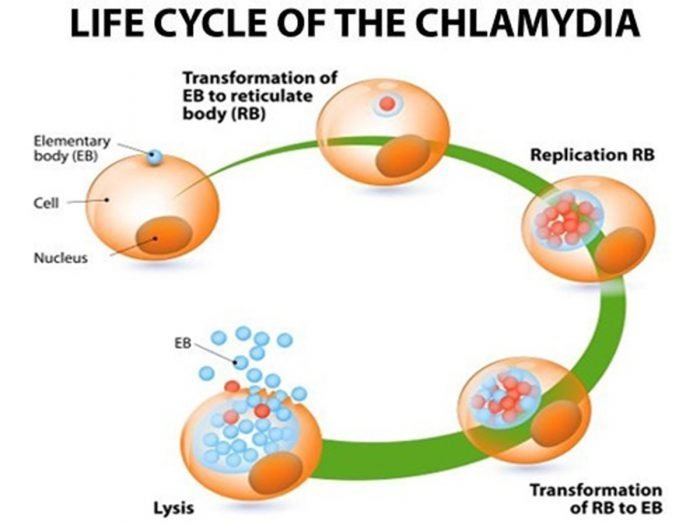
Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted infection that can be transferred through vaginal, anal, or oral intercourse or sex. Women can have Chlamydia infect their cervix, throat, or rectum whereas men can get infected in their urethra, throat and, rectum.
The biggest exposure to getting Chlamydia is to have unprotected sex, however, that might be. It is more common than young women and a part of the reason is that the symptoms of the infections do not show up until after you have been infected for 3 weeks which is a risk of going around and transmitting it to other people.
However, there are lab tests to diagnose Chlamydia, and sexually active people should have the test done frequently, pregnant women get that test at their first visit to the doctor.
Even though the symptoms of Chlamydia do not seem that harmful, it is only because the infection should not spread in the body. If spread in the body, Chlamydia can harm the uterus and the fallopian tubes in women, which can lead to serious consequences in the future like damage to the reproductive system, infertility, etc. In men, it does not usually cause bigger health problems but it can spread to the tube which carries the sperm, which can sometimes result in infertility.
Recommended Reading: Where Can I Buy Chlamydia Treatment Over The Counter
Behaviour Change Is Complex
Despite considerable efforts to identify simple interventions that can reduce risky sexual behaviour, behaviour change remains a complex challenge. Research has demonstrated the need to focus on carefully defined populations, consult extensively with the identified target populations, and involve them in design, implementation and evaluation.
Education and counselling can improve peoples ability to recognize the symptoms of STIs and increase the likelihood that they will seek care and encourage a sexual partner to do so. Unfortunately, lack of public awareness, lack of training among health workers, and long-standing, widespread stigma around STIs remain barriers to greater and more effective use of these interventions.
How Long Does It Take To Show Up In People With Penises
Theres no significant difference in the amount of time it takes for chlamydia symptoms to show up for people with penises as compared to people with vulvas.
The only major difference in the time it takes for symptoms to show up among people of various sexes may be related to how often symptoms show up.
According to the Childrens National Health System, 90 percent of people with vulvas dont ever experience any physical symptoms, while 70 percent of people with penises never notice any symptoms.
This difference in who actually experiences symptoms between these two groups may have some effect on how long it takes for symptoms show up. But theres never been any definitive link between your sex and when your symptoms appear.
You May Like: How Fast Do Signs Of Chlamydia Appear
How Long Can You Have Chlamydia Without Knowing
Chlamydia is sometimes called a silent infection because the majority of people who have chlamydia regardless of gender never notice symptoms. People who do notice symptoms often dont recognize the signs that they have chlamydia until a few weeks after theyve been infected. Because chlamydia cases are often asymptomatic, its easy to spread chlamydia to someone else without realizing it. And its easy to miss out on receiving the treatment needed to prevent the serious complications that can result from chlamydia.
How Often Should I Get Checked For Chlamydia
Sexual health check-ups are recommended for anyone who is sexually active. Frequency of testing also depends on your STI risk:
- An annual sexual health check-up is highly recommended if you are sexually active especially if you are under 25.
- Get checked more often during the year if you frequently change sexual partners.
- Remember, you are at greater risk if you have sex without a condom with 1 or multiple sexual partners.
Don’t Miss: Azithromycin 500 Mg Dosage For Chlamydia
What To Think About
Some people who have chlamydia may also have gonorrhea. In that case, treatment includes antibiotics that kill both chlamydia and gonorrhea. For more information, see the topic Gonorrhea.
Reinfection can occur. Symptoms that continue after treatment are probably caused by another chlamydia infection rather than treatment failure. To prevent reinfection, sex partners need to be evaluated and treated.
Repeated chlamydia infections increase the risk for pelvic inflammatory disease . Even one infection can lead to PID without proper treatment. Make sure to take your antibiotics exactly as prescribed. Take the full course of medicine, even if you feel better in a couple of days.
Some doctors recommend retesting 6 months after treatment to reduce the risk of complications from reinfection.footnote 3
If you have chlamydia, your doctor will send a report to the provincial or territorial health unit. Your personal information is kept confidential. The health unit may contact you about telling your sex partner or partners that they may need treatment.
Letting Partners Know You Have Chlamydia
Sexual partners may be infected too. If you have chlamydia, anyone you have had sex with from the last 6 months needs to be informed, tested and treated.
If they dont know, they could reinfect you or infect someone else if they are not treated. dont receive treatment.
Most people will appreciate being told they may have an infection and it is an important step in preventing further infection in the community.
Your local GP and sexual health centre can help you inform your partners and let them know that they need a test. This process is called partner notification. It can be done anonymously, and your confidentiality is always respected.
You can also anonymously notify your sexual partners of the need to get tested and treated for chlamydia via the Let Them Know website if you feel unable to speak to them personally.
There are also nurses who can help you anonymously notify your partners. They can be contacted on .
Also Check: How To Get Rid Of Chlamydia Without A Doctor
Read Also: What Medication Is Used For Chlamydia And Gonorrhea
Chlamydia Symptoms In Women
Many guys aren’t aware of chlamydia’s indications and symptoms. Some of the most common chlamydia symptoms in guys are as follows:
- Painful sexual intercourse
- Inflammation of the cervix
- Bleeding between periods
- Vaginal discharge
Chlamydia may infect the rectum as well. A woman with a chlamydia infection in the rectum may not have any symptoms. Rectal discomfort, discharge, and bleeding are all possible signs of a rectal infection
Stis Remain A Persistent And Endemic Health Threat Worldwide
Since the last published data for 2012, there has been no substantive decline in either the rates of new or existing infections. On average, approximately 1 in 25 people globally have at least one of these STIs, according to the latest figures,with some experiencing multiple infections at the same time.
STIs spread predominantly through unprotected sexual contact, including vaginal, anal and oral sex. Someincluding chlamydia, gonorrhoea, and syphiliscan also be transmitted during pregnancy and childbirth, or, in the case of syphilis,through contact with infected blood or blood products, and injecting drug use.
STIs are preventable through safe sexual practices, including correct and consistent condom use and sexual health education.
Timely and affordable testing and treatment are crucial for reducing the burden of STIs globally, alongside efforts to encourage people who are sexually active to get screened for STIs. WHO further recommends that pregnant women should be systematicallyscreened for syphilis as well as HIV.
All bacterial STIs can be treated and cured with widely available medications. However, recent shortages in the global supply of benzathine penicillin has made it more difficult to treat syphilis. Rapidly increasing antimicrobial resistance to gonorrhoeatreatments is also a growing health threat, and may lead eventually to the disease being impossible to treat.
Recommended Reading: Can Chlamydia Cause A Rash
How Is It Treated
Antibiotics are used to treat chlamydia. It’s important to take all of the medicine as directed. Otherwise the medicine may not work. Both sex partners need treatment to keep from passing the infection back and forth.
As soon as you find out you have chlamydia, be sure to let your sex partners know. Experts recommend that you notify everyone you’ve had sex with in the past 2 months. If you have not had sex in the past 2 months, contact the last person you had sex with.
Having a chlamydia infection that was cured does not protect you from getting it again. If you are treated and your sex partner is not, you probably will get it again.
Some people who have chlamydia also have other STIs, such as gonorrhea.
Finding out that you have an STI may make you feel bad about yourself or about sex. Counselling or a support group may help you feel better.
Chlamydia In Europe And The Us
According to figures from the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control the UK recorded the highest number of chlamydia cases of any country in Europe for 10 consecutive years between 2003 and 2012.
In 2012, there were 385,683 total reported cases in the European Economic Area. With 235,992 cases, the UK accounted for 61 percent of these however figures from Austria, the Czech Republic, Germany and Portugal were not included.
However, although the UK had the highest number of cases, it did not have the highest chlamydia prevalence per capita.
- Iceland recorded the highest number of chlamydia diagnoses per 100,000 of the population in 2013, with 677.
- Denmark had the second highest prevalence and Norway the third highest .
- The UK, by comparison, recorded 369.3 cases per 100,000.
Once again, this is discounting figures from the countries listed above whose data was not included.
The CDC reports that in the US in 2015, there were just over 1.5 million chlamydia diagnoses reported, which equates to 478.8 per 100,000. This represented an increase of 5.9 percent on the previous year, however the CDC speculate that the rise could be due to better screening coverage and more comprehensive reporting.
Globally, one study estimated that the number of female cases in 2012 was 68.5 million, and the number of male cases was 62.5 million.
You May Like: Does Medexpress Test For Chlamydia
How Does Chlamydia Affect A Pregnant Woman And Her Baby
In pregnant women, untreated chlamydia has been associated with pre-term delivery,34 as well as ophthalmia neonatorum and pneumonia in the newborn. In published prospective studies, chlamydial conjunctivitis has been identified in 18-44% and chlamydial pneumonia in 3-16% of infants born to women with untreated chlamydial cervical infection at the time of delivery.9-12 Neonatal prophylaxis against gonococcal conjunctivitis routinely performed at birth does not effectively prevent chlamydial conjunctivitis.37-39
Screening and treatment of chlamydia in pregnant women is the best method for preventing neonatal chlamydial disease. All pregnant women should be screened for chlamydia at their first prenatal visit. Pregnant women under 25 and those at increased risk for chlamydia should be screened again in their third trimester. Pregnant women with chlamydial infection should be retested 3 weeks and 3 months after completion of recommended therapy.40
Pandemic Didnt Slow The Spread Of Some Stds
The number of cases of some sexually transmitted diseases continued to increase during 2020, the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic, while overall STD cases dropped, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said in a new report.
Reports of gonorrhea, syphilis, and congenital syphilis rose in 2020 compared to 2019, the CDC said. However, reports of chlamydia dropped compared to 2019, as did the total number of STD cases. Overall, the U.S. had about 2.4 million STD cases in 2020, down from the 2.6 million cases in 2019, the CDC said.
The report said overall STD case numbers may have dropped for several reasons related to COVID-19: stay-at-home orders, increased unemployment that caused people to lose health insurance, and increased use of telemedicine in which no lab tests were taken.
âCOVID-19 continues to impact our healthcare system and STD program resources,â the report said. âIt is unclear how the pandemic will affect future STD surveillance data. However, there is no reason to believe we will be back to âbusiness as usualâ with STD case reporting anytime soon.â
The drop in reported chlamydia cases may have occurred because COVID put such a strain on health care systems, not because infections actually dropped, the report said.
The CDC reported the following case numbers:
- 1,579,885 cases of chlamydia were reported in 2020, down 13% from the previous year.
- 688,769 cases of gonorrhea were reported in 2020, a decrease of 10% over the previous year.
You May Like: What Treats Chlamydia And Gonorrhea
Chlamydia By Sexual Orientation
Chlamydia is most common among heterosexual women and heterosexual men. European surveillance statistics from 2013 state that:
- 91,289 cases were diagnosed in heterosexual women
- 72,729 cases were diagnosed in heterosexual men
- and 12,376 were diagnosed in men who have sex with men.
the sexual orientation of 207,980 cases were recorded as unknown.
In England in 2015, 21 percent of male chlamydia cases recorded in sexual health clinics were in men who have sex with men. This represents just six percent of the total number of chlamydia diagnoses.
You can read more about chlamydia on our information pages below.