How Is Chlamydia Spread
You can get chlamydia by having vaginal, anal, or oral sex with someone who has chlamydia.
If your sex partner is male you can still get chlamydia even if he does not ejaculate .
If youve had chlamydia and were treated in the past, you can still get infected again. This can happen if you have unprotected sex with someone who has chlamydia.
When Should I Do A Home Test For Chlamydia
If you had unprotected intercourse not too long ago or you are worried your partner might have carried an infection, then you should get tested. The best time to do a test kit for chlamydia is two weeks after youve been exposed.
Gonorrhea and chlamydia need around two weeks to show up on test results, but for any other infection, like HIV, for example, you will need around four weeks.
Chlamydia is easy to detect and treat, so its crucial that you get tested as much as you can. The best way to know for sure if you are carrying the infection is by getting tested every 3 to 12 months. If you have a history of STIs, you should get tested more often.
How To Treat Oral Chlamydia
Oral chlamydia is treated in the same way as other chlamydia infections: with antibiotics. The CDC recommends:
- Doxycycline two times a day for seven days
Alternative treatments include:
- Azithromycin in a single dose
- Levofloxacin once a day for seven days
A single dose of azithromycin may be the simplest way to treat chlamydia. However, people have developed resistance to this antibiotic, whereas doxycycline has a nearly 100% cure rate.
After being diagnosed with a chlamydia infection, all sexual partners need to be told and treated as well. You should also refrain from having any sex for seven days after completing treatment.
Chlamydia is easily treated and cured, but you can get chlamydia again. If you are sexually active, it is essential to test for sexually transmitted infections regularly.
Don’t Miss: When Can You Test For Chlamydia
Types Of Chlamydia Testing
Lab tests allow doctors to confidently diagnose chlamydia. Types of chlamydia testing include:
- Urine testing You pee into a cup, and the sample is sent to a lab to analyze for the presence of the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis. This is the method we use for chlamydia testing.
- Swab Your urethra, vagina, cervix, throat, anus, or eye is swabbed to take cell samples. This method may be considered for non-genital chlamydia, like if you had unprotected oral sex or receptive anal sex.
- Blood More rarely, a small blood sample can be drawn for your arm to detect the presence of antibodies specific to chlamydia.
Should I Get A Chlamydia Test
It can be a good idea to screen for chlamydia and other STIs if youâre considering having sexual intercourse with a new partner. If you believe you have been exposed to chlamydia or are experiencing symptoms , consider screening for infection by visiting a local clinicâ âor take a chlamydia test at home.
Also, according to the CDC, if youre a sexually active woman younger than 25, you should test for chlamydia and gonorrhea at least once a year . You should also get tested yearly if youre 25 or older and have risk factors like new or multiple sex partners. The CDC also recommends annual gonorrhea and chlamydia testing for gay and bisexual men.
Read Also: Can Chlamydia Be Cured Without Antibiotics
How Can Chlamydia Be Prevented
The most reliable ways to avoid infection with chlamydia or any sexually transmitted disease are to abstain from oral, vaginal, and anal sex or to be in a long-term, mutually monogamous relationship with an uninfected partner. People who are sexually active should correctly and consistently use condoms to reduce the risk of infection with chlamydia and other STDs.
Chlamydia In The Throat: Symptoms Treatment & More
When it comes to avoiding sexually transmitted infections , some people think oral sex is safer than intercourse. But several STIssuch as chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphiliscan spread through oral sex.
In this article, Ill focus on chlamydia and oral sex. Like chlamydia in the genital area, chlamydia in the throat may not cause any symptoms, so its important to practice safe oral sex, talk to your sexual partners about their health, and get tested for STIs.
In many cases, chlamydia is curable with antibiotics, however an untreated chlamydia infection can result in serious health problems, including ectopic pregnancy and infertility.
So if you think you may have chlamydia, its important to see a healthcare provider.
Read on to learn how you can get chlamydia from oral sex, what the symptoms are, how to get diagnosed and treated for it, and when to see your doctor.
Also Check: Signs Of Chlamydia In Mouth
What Are The Signs Of Chlamydia Or Gonorrhea
Many people who have chlamydia or gonorrhea dont have any signs or symptoms. When there are symptoms, chlamydia and gonorrhea cause very similar things.
Women with symptoms may have:
- Abnormal discharge from the vagina
- Burning when they urinate
Men with symptoms may have:
- Abnormal discharge from the penis
- Burning when they urinate
- Painful or swollen testicles
How To Treat Chlamydia In Men
When the infection is caught early, chlamydia is easy to treat with a short course of antibiotics. Over 95% of people will be cured if they take the antibiotics correctly. The two types of antibiotics most commonly used to treat chlamydia are:
- Azithromycin: Taken as 24 tablets all at once.
- Doxycycline: Taken as 2 capsules each day for a week.
If your doctor is concerned about complications from chlamydia , they might prescribe a longer course of antibiotics.
Youll be advised not to have sex until you and your current sexual partner have finished treatment for chlamydia, or until a week after the 1-day treatment. Its also important to contact any other sexual partners who could have been exposed to infection. A sexual health clinic can help you contact people anonymously, if thats what youd prefer.
Recommended Reading: How Long Does It Take To See Signs Of Chlamydia
How Much Does The Test Cost
The cost of chlamydia testing varies based on many factors. Chlamydia testing may be paid for by health insurance when ordered by a doctor. Because health plans vary, its important for patients to discuss the cost of testing, including any copays or deductibles, with their health plan.
For patients without health insurance coverage, the cost of testing may include the cost of the office visit and sample collection as well as technician fees. Testing may also be available for free or at low cost through community-based organizations and local health departments.
What Does A Positive Chlamydia Test Result Mean
If the test is positive, the lab detected the bacteria that cause chlamydia. This means you have a chlamydia infection and will need treatment . You will also need to notify your sexual partners, so they can get tested, too.
After finishing treatment, you will need additional follow-up chlamydia tests. You may need another test three weeks after treatment and possibly another test three months later. Ask your provider when you should get a follow-up test.
Also Check: Is Chlamydia Medication Over The Counter
Complications Of Chlamydia In Male Patients
Chlamydia is an infection that is far more prevalent among women, particularly during young adulthood, compared to the prevalence of the condition in men. Still, men do need to understand that the condition can affect them and will often not yield any symptoms. This, however, does not mean the bacterial infection poses no harm.
In cases where symptoms do develop in a male patient, the individual may experience the following signs of chlamydia:
- There may be a discharge from the mans penis
- The testicles may become painful
- There may be pain during urination
- The lower abdominal might also develop pain conditions
Since chlamydia is a bacterial infection in nature, men do need to understand that there are certain complications that can develop. These complications can sometimes be serious and require medical attention.
Urethritis is a common complication of chlamydia in men. The condition causes a bacterial infection to develop in the urethra. This is a tube that runs throughout the patients penis it is used to expel both urine and semen from the body.
Urethritis causes irritation in the tip of the patients penis and can make the inside of the penis feel itchy. There may also be a burning or stinging sensation within the penis this is the urethra showing signs of the infection. A discharge can also occur from the penis.
What Happens If I Dont Get Treated
The initial damage that chlamydia causes often goes unnoticed. However, chlamydia can lead to serious health problems.
If you are a woman, untreated chlamydia can spread to your uterus and fallopian tubes . This can cause pelvic inflammatory disease . PID often has no symptoms, however some women may have abdominal and pelvic pain. Even if it doesnt cause symptoms initially, PID can cause permanent damage to your reproductive system. PID can lead to long-term pelvic pain, inability to get pregnant, and potentially deadly ectopic pregnancy .
Men rarely have health problems linked to chlamydia. Infection sometimes spreads to the tube that carries sperm from the testicles, causing pain and fever. Rarely, chlamydia can prevent a man from being able to have children.
Also Check: Can Garlic Cure Chlamydia Infections
Men May Experience The Following Symptoms:
- pain when peeing.
- discharge from the tip of the penis .
- pain in the testicles
- burning or itching in the genital area.
Remember: most people have no symptoms, so if you notice any of the above, get a full sexual health check at your local GUM/STI clinic.
The best way to make sure you dont get chlamydia is to use condoms.
When To Get Tested For Chlamydia
Now is the right time to get tested if you are sexually active, havent been tested recently, have a new sex partner, or believe you are at risk. The CDC recommends the following guidelines:
Sexually active women under 25 should test for chlamydia every year. Women who are older than 25 with new or multiple sex partners should also test yearly.
Anyone who has a sex partner who has an STD should be tested.
Pregnant women who are at risk should be tested for chlamydia early in the pregnancy and again at the third trimester. Plus, they need tests for gonorrhea, syphilis, HIV, and hepatitis B.
Men who have sex with men should get tested once a year, or more frequently if they have multiple partners.
Men who are exposed to an infected partner should be tested.
If you believe youve been exposed, chlamydia testing can take place within 1-5 days from exposure, but is most accurate after five.
How often to get tested for chlamydia: The CDC recommends that men and women at increased risk be tested every 3-6 months, and that sexually active women under 25 years be screened for chlamydia annually . Clinicians also test for the infection during initial pregnancy screenings and again in the third trimester.
For general STD testing, see our page about when to get tested for each one.
Recommended Reading: What To Take For Chlamydia
What To Think About
- If a chlamydia infection is suspected, do not have sexual intercourse until the test results have come back. If you have a chlamydia infection, do not have sexual intercourse for 7 days after the start of treatment. Your sex partner should also be treated for a chlamydia infection so that you don’t get reinfected and so that others don’t get infected.
- Only one laboratory test is needed to diagnose chlamydia. Your doctor can choose which test to use.
- Screening for and treating chlamydia can help prevent pelvic inflammatory disease . To learn more about the treatment of a chlamydia infection, see the topic Chlamydia.
- Other sexually transmitted infections may be present at the same time as chlamydia. So it is important to be tested and treated for all STIs. Chlamydia as well as other STIs can also increase the chance of getting human immunodeficiency virus . An HIV test may be offered at the same time as a test for chlamydia or other STIs.
Questions For Your Doctor After At
After at-home chlamydia testing, you may find it helpful to ask your doctor questions about your test result and need for future STD testing. Questions for a doctor may include:
- What is the significance of my test result?
- Are additional tests recommended to confirm my test result?
- When should I be tested again for chlamydia?
- What other STD tests are recommended for me?
- If I tested positive, should I share this information with sexual partners?
You May Like: How To Treat Gonorrhea And Chlamydia
Urine Testing For Sexually Transmitted Infections
Several sexually transmitted infections can be detected using urine testing, which is becoming more and more available. Urine chlamydia tests and gonorrhea tests are a lot more pleasant than having to have your cervix or urethra swabbed and are quickly becoming standard practice.
It may be more difficult to find urine testing for other STIs, such as trichomoniasis or human papillomavirus , however. This article will discuss urine testing for STIs.
I Was Treated For Chlamydia When Can I Have Sex Again
You should not have sex again until you and your sex partner have completed treatment. If your doctor prescribes a single dose of medication, you should wait seven days after taking the medicine before having sex. If your doctor prescribes a medicine for you to take for seven days, you should wait until you have taken all of the doses before having sex.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Get Gonorrhea Or Chlamydia
How Can You Get Rid Of Chlamydia
If your chlamydia test comes back positive, you may be wondering how to get chlamydia treated. Itâs important to discuss treatment options with your healthcare provider. Most likely, you will be treated for chlamydia with oral antibiotics. With treatment, infections often clear up in one to two weeks.
Even if your symptoms resolve sooner, however, itâs very important to complete your healthcare providerâs entire course of prescribed antibiotics. Otherwise, the infection may not be completely eliminated and you could be at risk for reinfection. You could also still pass chlamydia to a partner if you donât complete the recommended course of antibiotics.
Finally, as part of your treatment for chlamydia, connect with any sexual partners you may have unintentionally exposed to this infection. Your healthcare provider may also recommend antibiotics for your partner. This is a key part of chlamydia treatment, since it can help prevent reinfection when you resume sexual intercourse.
Chlamydia is a potentially harmful infection, but fortunately, itâs easy to test for. Itâs also simple to treat when you have a confirmed diagnosis. The important thing is stay informed and know your statusâsomething you can do from the privacy and comfort of home with our STD Test for women.
References
1. Overview: Chlamydia. National Health Service. URL. Accessed March 27, 2020.
2. Chlamydia – CDC Fact Sheet. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. URL. Accessed March 27, 2020.
How Is Chlamydia Diagnosed
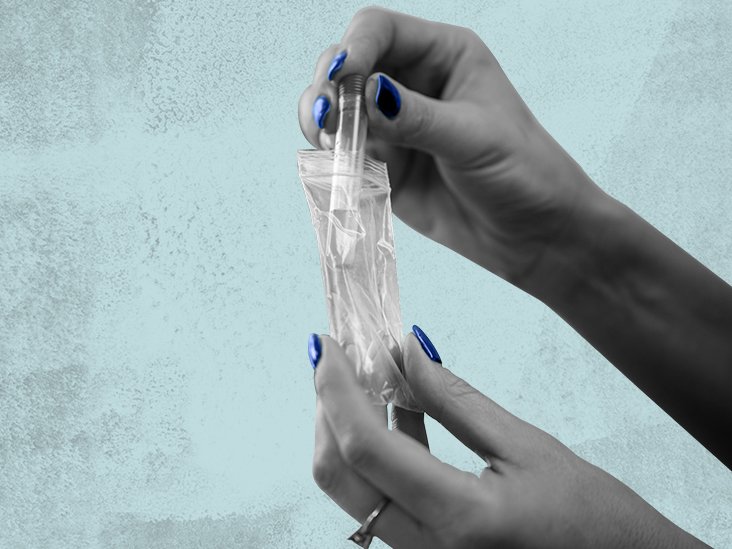

There are a number of diagnostic tests for chlamydia, including nucleic acid amplification tests , cell culture, and others. NAATs are the most sensitive tests, and can be performed on easily obtainable specimens such as vaginal swabs or urine.43
Vaginal swabs, either patient- or clinician-collected, are the optimal specimen to screen for genital chlamydia using NAATs in women urine is the specimen of choice for men, and is an effective alternative specimen type for women.43 Self-collected vaginal swab specimens perform at least as well as other approved specimens using NAATs.44 In addition, patients may prefer self-collected vaginal swabs or urine-based screening to the more invasive endocervical or urethral swab specimens.45 Adolescent girls may be particularly good candidates for self-collected vaginal swab- or urine-based screening because pelvic exams are not indicated if they are asymptomatic.
NAATs have demonstrated improved sensitivity and specificity compared with culture for the detection of C. trachomatis at rectal and oropharyngeal sites.40 Certain NAAT test platforms have been cleared by FDA for these non-genital sites and data indicate NAAT performance on self-collected rectal swabs is comparable to clinician-collected rectal swabs. 40
Don’t Miss: How Fast Can Chlamydia Spread
Who Should Be Tested For Chlamydia
You should go to your health provider for a test if you have symptoms of chlamydia, or if you have a partner who has a sexually transmitted disease. Pregnant women should get a test when they go to their first prenatal visit.
People at higher risk should get checked for chlamydia every year:
- Sexually active women 25 and younger
- Older women who have new or multiple sex partners, or a sex partner who has a sexually transmitted disease
- Men who have sex with men
What About Rectal And Oral Swabs
Rectal swabs and oral swabs may also be considered for those who have receptive anal sex or unprotected oral sex.
While neither rectal nor oral swabs are currently approved for the detection of chlamydia, research suggests that doing these extragenital tests is important.
For example, a 2017 study found that among men who have sex with men , 13% had a rectal chlamydia infection but only 3.4% had a positive urethral swab. In women in an urban setting in the United States, 3.7% were found to have an extragenital infection. Those under the age of 18 had the highest incidence of extragenital infection.
You May Like: Azithromycin How To Take For Chlamydia
Chlamydia Cdc Fact Sheet
Chlamydia is a common sexually transmitted disease that can be easily cured. If left untreated, chlamydia can make it difficult for a woman to get pregnant.
Basic Fact Sheet | Detailed Version
Basic fact sheets are presented in plain language for individuals with general questions about sexually transmitted diseases. The content here can be syndicated .