How Can You Be Sure Youre Experiencing A New Bout
Chlamydia is treated with antibiotics, usually azithromycin or doxycycline.
In order to make sure chlamydia is cured, you need to take the full course of antibiotics as prescribed by your doctor. You need to take every single dose dont stop taking the antibiotics until there are none left.
If youve taken all your antibiotics but you still have symptoms, contact your doctor or another healthcare professional.
According to the Center for Disease Control , youll need a follow-up test three months after treatment to ensure that the infection is cured.
There are a few reasons why you might contract chlamydia a second time:
- The initial infection wasnt cured because the course of antibiotics wasnt completed as directed.
- A sexual partner transmitted chlamydia to you.
- You used a sex toy that was contaminated with chlamydia.
A 2014 study suggests that chlamydia can live in the gastrointestinal tract and reinfect the genitals, causing chlamydia symptoms to reappear after the genital infection went away.
However, this study only looked at animal models of chlamydia. Research on human participants is needed.
The symptoms of chlamydia typically disappear once you finish your antibiotics. This can vary in time, as some chlamydia antibiotic courses are one dose taken on one day, while others last longer.
What Is The Treatment For Chlamydia
Chlamydia can be easily cured with antibiotics. HIV-positive persons with chlamydia should receive the same treatment as those who are HIV-negative.
Persons with chlamydia should abstain from sexual activity for 7 days after single dose antibiotics or until completion of a 7-day course of antibiotics, to prevent spreading the infection to partners. It is important to take all of the medication prescribed to cure chlamydia. Medication for chlamydia should not be shared with anyone. Although medication will stop the infection, it will not repair any permanent damage done by the disease. If a persons symptoms continue for more than a few days after receiving treatment, he or she should return to a health care provider to be reevaluated.
Repeat infection with chlamydia is common. Women whose sex partners have not been appropriately treated are at high risk for re-infection. Having multiple chlamydial infections increases a womans risk of serious reproductive health complications, including pelvic inflammatory disease and ectopic pregnancy. Women and men with chlamydia should be retested about three months after treatment of an initial infection, regardless of whether they believe that their sex partners were successfully treated.
Infants infected with chlamydia may develop ophthalmia neonatorum and/or pneumonia. Chlamydial infection in infants can be treated with antibiotics.
What Will Happen If Chlamydia Infections Is Ignored So Long
Trachoma of the eye. Progression of trachoma. Trachoma, an infection of the eye caused by Chlamydia trachomatis. Trachoma is a bacterial infection that affects your eyes
If you are thinking hard to know about how is chlamydia transmitted then the only answer is via sexual contact. Unfortunately, the side effects of Chlamydia over male infertility are generally underestimated. But it is observed that this infection can damage sperm and may also lead to some serious or non curable reproductive disorder like permanent infertility.
Males that are suffering with Chlamydia use to have DNA level 3 times higher than its normal amount in DNA. It clearly means that the genetic material is not perfectly packed inside and it is more susceptible to breakage.
Structure of Mycoplasma cell. the bacterium is the causative agent of sexually transmitted diseases, pneumoniae, atypical pneumonia and other respiratory disorders. unaffected by many antibiotics.
Mycoplasma is also similar kind of disease and it is also transferred with sexual contact both these diseases can have direct effect on sperm production in male body. Once a person gets infected with Chlamydia then his rate of abnormal sperm reproduction gets increased up to 80% and it has about 10% lesser mobility inside body when compared with normal peers.
Other than this, male Chlamydia patients are observed to experience urethritis, conjunctivitis and rheumatological conditions along with reactive arthritis issues.
You May Like: I Had Chlamydia And Got Treated
Why Do I Need A Chlamydia Test
Chlamydia is a very common STD, especially in sexually active people ages 15 to 24. But chlamydia usually doesn’t cause symptoms, so the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and other health organizations recommend regular screening tests if your risk of getting chlamydia is high.
If you are a woman or a transgender or gender diverse person with a cervix , you should:
- Get tested for chlamydia at least once a year if you are:
- Younger than 25 and having sex
- Age 25 or older and have a higher risk of getting chlamydia because you:
- Have a new sex partner or more than one partner
- Have a sex partner who is having sex with others
- Have a sex partner with an STD
- Don’t use condoms correctly every time
Regular chlamydia testing at least once a year is also recommended if you:
The best testing schedule for you may be different than the recommendations. Ask your provider how often you should get tested.
Your provider will order a test if your sex partner has been diagnosed with chlamydia or if you have symptoms. Symptoms of chlamydia may include:
- An unusual discharge from your genitals or rectum
- Irritation or itching around your genitals
- Pain or burning when you urinate
- Rectal pain or bleeding if chlamydia infects the rectum
How Is Chlamydia Transmitted
Chlamydia is a bacterial infection caused by Chlamydia trachomatis. Itâs also considered a sexually transmitted infection , which means that it can spread between sex partners through any kind of sexual contact. This contact is not limited to vaginal intercourse you can also contract oral chlamydia through oral sex, although it is a less common cause of Chlamydia trachomatis infections. Because sexual contact increases your risk, itâs a good idea to know if you have an STD before you have intercourse with a new partner.
In short, there are many different ways you can contract or spread chlamydia. To protect your sexual health and the health of your sexual partner, get tested for chlamydia before beginning any new relationship.
Read Also: How Long Is Chlamydia Contagious Without Treatment
How Can I Reduce My Chances Of Getting Chlamydia
If you are sexually active, you can do the following things to lower your chances of getting chlamydia:
PrEP, Pre Exposure Prophylaxis, a pill taken daily to prevent HIV infection, will NOT protect you from chlamydia. PrEP is also known by the brand name Truvada or Descovy.
Having chlamydia once does NOT protect you from getting it again.
For more information, visit CDCs chlamydia webpage featuring factsheets, posters, videos, statistics and more. Please contact your local health department for questions and reporting issues.
To submit a question or comment to the HIV/STD/HepC Program, please click on the suggestion box to access our online form.
- Learn More About
More On Chlamydia At Thebodycom
To find out more about chlamydia and its treatment, we recommend the following articles:
- Pointers on Chlamydia Prevention and Care for People With HIV
In addition, our Q& A experts sometimes address questions about chlamydia in our Ask the Experts forums. Here are some of those questions and our experts responses:
- Over the counterWhat over the counter drugs if any are effective against chlamydia?
- How can I get rid of resistant Chlamydia?I have read online of resistant forms of Chlamydia. Are resistant forms impossible to get rid of? Should I ask my doctor about azithromycin?
You May Like: What Causes Chlamydia In Males
Diagnosis And Treatment Of Chlamydia Trachomatis Infection
KARL E. MILLER, M.D., University of Tennessee College of Medicine, Chattanooga, Tennessee
Am Fam Physician. 2006 Apr 15 73:1411-1416.
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
Azithromycin or doxycycline is recommended for the treatment of uncomplicated genitourinary chlamydial infection.
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
Azithromycin or doxycycline is recommended for the treatment of uncomplicated genitourinary chlamydial infection.
Get Retested Following Treatment
Many people have more than one chlamydia infection. If youre a girl or woman and your sex partners are not treated for the infection, you will be at high risk for reinfection. Repeated infections with chlamydia make it much more likely that your ability to have children will be affected. Repeated infections also raise your risk of painful complications, such as pelvic inflammatory disease.
Both women and men with chlamydia should be retested about three months after they are first diagnosed and treated. Go to be retested even if you think your sex partners were successfully treated.
Also Check: What Happens If Chlamydia Goes Untreated
Don’t Miss: Where To Buy Azithromycin For Chlamydia
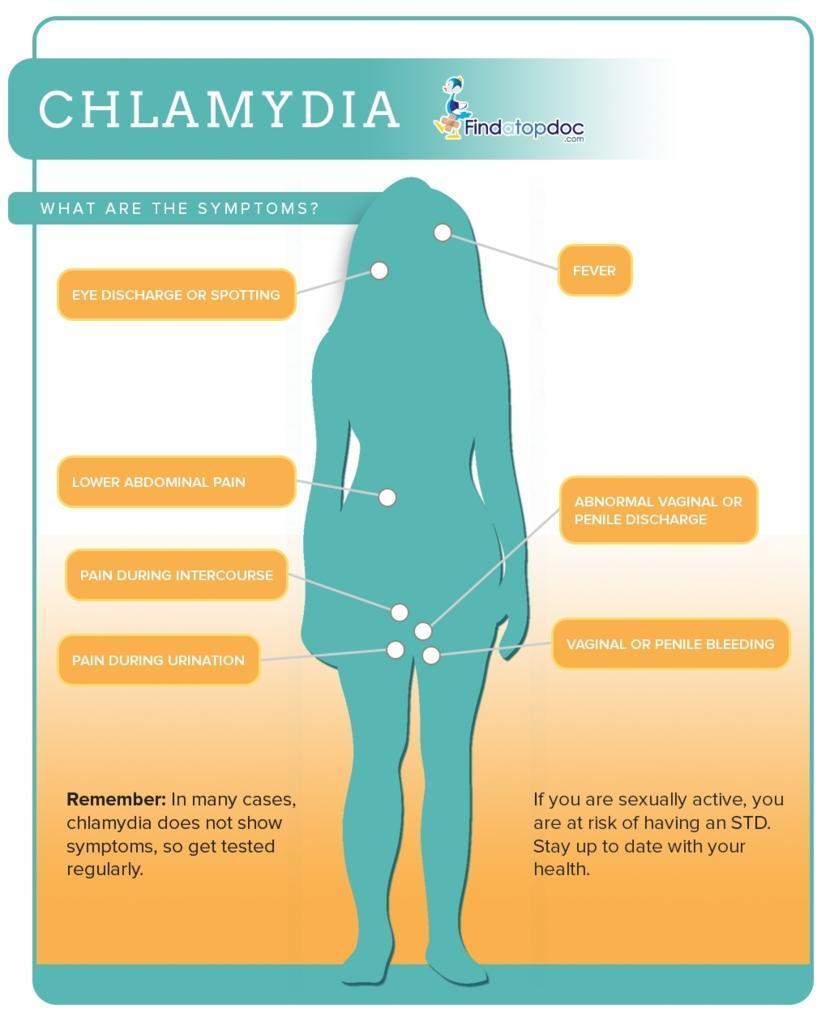
What Are The Symptoms Of Chlamydia
If you do notice symptoms, youll likely experience them differently based on your reproductive anatomy. Many of the symptoms that cisgender women experience can also affect transgender men and nonbinary individuals with vaginas. Many of the symptoms that cisgender men notice can affect transgender women and nonbinary individuals with penises, too.
Chlamydia bacteria often cause symptoms that are similar to cervicitis or a urinary tract infection . You may notice:
- Pus in your urine .
- Increased need to pee.
- Dull pain in the lower part of your abdomen.
Chlamydia bacteria most often infect your urethra, causing symptoms that are similar to nongonococcal urethritis. You may notice:
- Pain or a burning sensation when you pee .
Signs of chlamydia that all genders may notice
Chlamydia can affect parts of your body other than your reproductive organs, such as your:
- You may notice pain, discomfort, bleeding or a mucus-like discharge from your bottom.
- Throat. You may have a sore throat, but you usually wont notice symptoms if the bacterias in your throat.
- Eyes. You may notice symptoms of conjunctivitis if C. trachomatis bacteria gets in your eye. Symptoms include redness, pain and discharge.
See your healthcare provider immediately if you notice any of these symptoms.
How To Help Partners Get Treatment
If you are not sure whether your sexual partner will seek treatment, ask your doctor for extra chlamydia medication . You can give it to them so they can be treated as soon as possible.
This is known as patient delivered partner therapy for chlamydia. Talk to your doctor to see if PDPT is right for you and your sexual partner.
Also Check: How Early Can You Detect Chlamydia
What Do I Need To Know If I Get Treated For Chlamydia
If youre getting treated for chlamydia:
- Take all of your medicine the way your nurse or doctor tells you to, even if any symptoms you may be having go away sooner. The infection stays in your body until you finish the antibiotics.
- Your partner should also get treated for chlamydia so you dont re-infect each other or anyone else.
- Dont have sex for 7 days. If you only have 1 dose of medication, wait for 7 days after you take it before having sex. If youre taking medicine for 7 days, dont have sex until youve finished all of your pills.
- Get tested again in 3-4 months to make sure your infection is gone.
- Dont share your medicine with anyone. Your nurse or doctor may give you a separate dose of antibiotics for your partner. Make sure you both take all of the medicine you get.
- Even if you finish your treatment and the chlamydia is totally gone, its possible to get a new chlamydia infection again if youre exposed in the future. Chlamydia isnt a one-time-only deal. So use condoms and get tested regularly.
Causes And Risk Factors
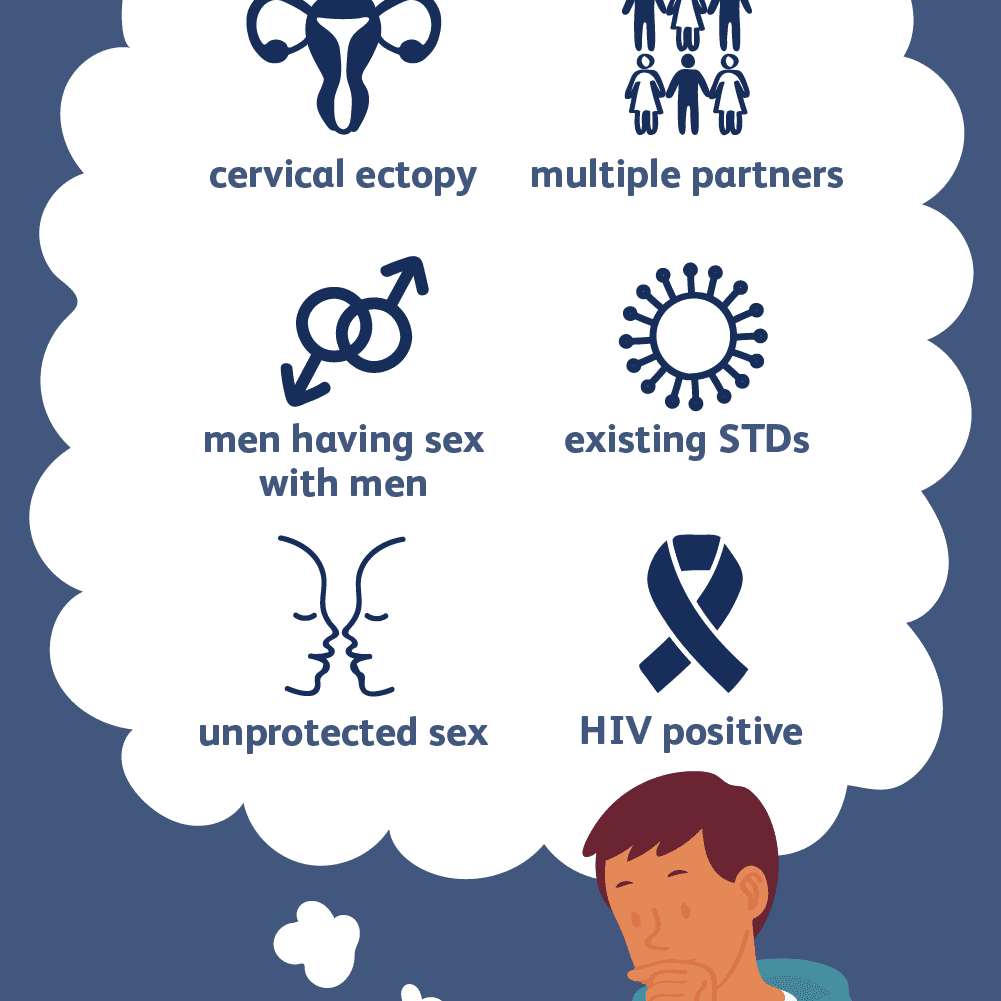
Chlamydia is an STI caused by a specific strain of bacteria known as Chlamydia trachomatis.
Chlamydia is more common in women than in men. In fact, its estimated that the overall rate of infection is for women than men in the United States.
Some of the other risk factors for infection include:
- not using barrier methods like condoms consistently with new sexual partners
- having a sexual partner who is having sex with other people
- having a history of chlamydia or other STIs
Also Check: Can I Get A Chlamydia Test At A Pharmacy
Inflammation Of The Testicles
In men, chlamydia can spread to the testicles and epididymis , causing them to become painful and swollen. This is known as epididymitis or epididymo-orchitis. This is very rare.
The inflammation is usually treated with antibiotics. If its not treated, theres a possibility it could affect your fertility.
You May Like: How To Check If You Have Chlamydia
Why Do I Keep Getting A Chlamydia Infection
You can get chlamydia even after treatment. You may get it again for several reasons, including:
- You did not complete your course of antibiotics as directed and the initial chlamydia did not go away.
- Your sexual partner has untreated chlamydia and gave it to you during sexual activity.
- You used an object during sex that was not properly cleaned and was contaminated with chlamydia.
Recommended Reading: Signs Of Chlamydia In Throat
What Does A Positive Chlamydia Test Result Mean
If the test is positive, the lab detected the bacteria that cause chlamydia. This means you have a chlamydia infection and will need treatment . You will also need to notify your sexual partners, so they can get tested, too.
After finishing treatment, you will need additional follow-up chlamydia tests. You may need another test three weeks after treatment and possibly another test three months later. Ask your provider when you should get a follow-up test.
Does Chlamydia Cause Cervical Cancer
No, chlamydia doesnt cause cervical cancer.
Its possible to get a sexually transmitted infection by having sex with someone who has an STI, even if they have no symptoms.
The following measures will help protect you from most STIs including chlamydia, gonorrhoea and HIV.
If you have an STI, theyll also help prevent you from passing it on to someone:
- Avoid sharing sex toys. If you do share them, wash them or cover them with a new condom before anyone else uses them.
You May Like: How Do I Treat Chlamydia
Rules For Successful Treatment
The patient should make sure that the doctor is informed if the patient is pregnant or has any allergies. These conditions influence the choice of the medicine prescribed. No matter which antibiotic the patient takes treating chlamydia the following points should be remembered:
- The treatment of all partners on the infected person is obligatory
- Abstain from sex contacts during the treatment and until the negative result on chlamydia test is received
- It is unadvisable to interrupt the course of antibiotics treatment as it will result in the necessity to start again from the beginning. Although the symptoms may disappear, the infection may still remain in the body
- It is necessary to get tested after 34 months after the end of the treatment to make sure the infection is no longer in the body.
Am I At Risk For Chlamydia
If you are sexually active, have an honest and open talk with your healthcare provider. Ask them if you should get tested for chlamydia or other STDs. Gay or bisexual men and pregnant people should also get tested for chlamydia. If you are a sexually active woman, you should get tested for chlamydia every year if you are:
- Younger than 25 years old.
- 25 years and older with risk factors, such as new or multiple sex partners, or a sex partner who has a sexually transmitted infection.
Recommended Reading: 1 Dose Treatment For Chlamydia
Chlamydia Cdc Fact Sheet
Chlamydia is a common sexually transmitted disease that can be easily cured. If left untreated, chlamydia can make it difficult for a woman to get pregnant.
Basic Fact Sheet | Detailed Version
Basic fact sheets are presented in plain language for individuals with general questions about sexually transmitted diseases. The content here can be syndicated .
Also Check: How Can You Treat Chlamydia At Home
Use Your Health Insurance Just Like You Normally Would To See Your Doctor
In a 2015 report, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimated that the United States sees 20 million new cases of STDs every year. About half of those are from sexually active youths, age 15 to 24. By the age of 25, its estimated that half of all sexually active people will have had a sexually transmitted infection at some point. Nationally, there are over 110 million total infections, both new and existing, at any given time.
Also Check: What Meds Get Rid Of Chlamydia
Put Sex On Hold During And After Chlamydia Treatment
If you were given a single dose of antibiotics to treat your chlamydia, you should not have any kind of sex for a full seven days after the day you took the medicine. If youre taking antibiotics for a week, wait another seven days after the last day of your treatment. Be sure to take all of the medicine that is prescribed for you.
Not having sex for seven days after treatment is important so you dont spread the infection to your partner or partners.
Medication stops the infection and can keep you from spreading the disease, but it wont cure any permanent damage that the infection caused before you started treatment. In women, such damage can include blocking the fallopian tubes, causing infertility.
If you still have symptoms for more than a few days after you stop taking your medicine, go back to see your doctor or other healthcare provider so they can check you again.
Having Multiple Sexual Partners After Treatment
After treatment, did you engage in unprotected intercourse with multiple sexual partners?
If you did, its likely your new symptoms are due to chlamydia or other sexually transmitted infections like gonorrhea and trichomonas infection.
After chlamydia treatment, boosting your sexual health and minimizing the number of persons you have unprotected intercourse with, is vital to prevent reinfection.
Also Check: What Test Is Done For Chlamydia
Recommended Reading: How Long To Get Chlamydia Results