Question : How Does Chlamydia Impact My Pregnancy
Chlamydia can cause a number of issues during pregnancy.
Women with untreated chlamydia might develop pelvic inflammatory disease , which can lead to chronic pelvic pain, infertility and increased risk of ectopic pregnancies. Additionally, pregnant women who are infected with chlamydia have an increased risk of their waters breaking prematurely, causing the baby to be born early.
If a mother has chlamydia during pregnancy, her baby can also become infected at childbirth causing lung or eye infections. Because of this, doctors recommend that pregnant women should be tested for chlamydia.
When Should You Call Your Doctor
- Have sores, bumps, rashes, blisters, or warts on or around the genital or anal area or on any area of the body where you think they could be caused by a sexually transmitted infection .
- Think you have been exposed to a STI.
Do not have sexual intercourse or other sexual contact until you have been treated by a doctor. If you are diagnosed with syphilis, your sex partner will need to be treated also.
In most areas, public health clinics or health departments are able to diagnose and provide low-cost assessment and treatment of early syphilis and other STIs.
Question : Can You Get Chlamydia From Sex Toys
Its less likely, but chlamydia can be passed during other types of sex such as sharing sex toys. If you are using and sharing sex toys, play it safe and place condoms and water-based lube on them.
When youre finished, clean them carefully with a bar of mild soap and water. You can also use a 70% isopropyl alcohol solution to clean toys. Do not use anti-bacterial or perfumed soaps as they can leave a residue which can irritate your genitals.
Read Also: Can You Have Chlamydia And Not Know
What Increases Your Risk
Your risk of syphilis increases if you:
- Have unprotected sex . This risk is especially high among men who have sex with other men .
- Have multiple sex partners, particularly if you live in an area of the country where syphilis is more common.
- Have a sex partner who has syphilis.
- Have sex with a partner who has multiple sex partners.
- Exchange sex for drugs or money.
- Have human immunodeficiency virus infection and engage in any of the behaviors listed above.
Syphilis is contagious whenever an open sore or skin rash is present. The risk of being infected with syphilis from a single sexual encounter with an infected partner is approximately 3% to 10%.footnote 3
Infection with syphilis also increases a person’s risk of being infected with HIV. Syphilis causes open sores on the genitals that allow the HIV infection to enter the body easily. Syphilis is in general more common in people who are also infected with HIV.
Disease Watch Focus: Syphilis
TDR | Nature Reviews Microbiology
BACKGROUND
CAUSATIVE AGENTS. Syphilis is a chronic infectious disease caused by the spirochaete Treponema pallidum. Syphilis is usually transmitted by sexual contact or from mother to infant, although endemic syphilis is transmitted by non-sexual contact in communities living under poor hygiene conditions. T. pallidum can also be transmitted by blood transfusion. In spite of provoking a strong humoral and cell-mediated immune response, T. pallidum is able to survive in the human host for several decades. After an incubation period of about 21 days, an ulcer appears at the site of inoculation. This resolves spontaneously and 68 weeks later is followed by the secondary stage, at which time the organism has disseminated via the blood stream and any organ can be affected. Tertiary syphilis, which can affect the skin, bones or central nervous and cardiovascular systems, can occur many years later . In pregnant women, syphilis can lead to stillbirth or congenital infection of the neonate, resulting in neonatal death or late sequelae . Parenteral penicillin remains the treatment of choice, and resistance to it has not been described. As T. pallidum divides slowly, a long-acting preparation is recommended.
RECENT DEVELOPMENTS
References:
You May Like: How Long Does Chlamydia Last With Treatment
How Can Chlamydia Be Prevented
Latex male condoms, when used consistently and correctly, can reduce the risk of getting or giving chlamydia.53 The surest way to avoid chlamydia is to abstain from vaginal, anal, and oral sex, or to be in a long-term mutually monogamous relationship with a partner who has been tested and is known to be uninfected.
How Do I Know If I Have Chlamydia
Most people who have chlamydia have no symptoms. If you do have symptoms, they may not appear until several weeks after you have sex with an infected partner. Even when chlamydia causes no symptoms, it can damage your reproductive system.
Women with symptoms may notice
- An abnormal vaginal discharge
- A burning sensation when urinating.
Symptoms in men can include
- A discharge from their penis
- A burning sensation when urinating
- Pain and swelling in one or both testicles .
Men and women can also get infected with chlamydia in their rectum. This happens either by having receptive anal sex, or by spread from another infected site . While these infections often cause no symptoms, they can cause
- Rectal pain
- Discharge
- Bleeding.
You should be examined by your doctor if you notice any of these symptoms or if your partner has an STD or symptoms of an STD. STD symptoms can include an unusual sore, a smelly discharge, burning when urinating, or bleeding between periods.
Don’t Miss: How Do Guys Get Tested For Chlamydia
How Is Syphilis Diagnosed
If you have sores, bumps, a rash, blisters, or warts on or around your genital or anal area, or if you think you were exposed to an STI, see your doctor.
He or she will do a physical exam and will ask you about your symptoms and your sexual history. You will probably have one or more blood tests to check for the infection. Because the open sores from syphilis make HIV infection more likely, you may also be tested for HIV.
To prevent babies from getting syphilis, experts recommend that all pregnant women have a syphilis blood test.
More Than Just A Simple Infection
Ct has a number of serovars which cause different types of pathology AC are responsible for ocular infections and are a major cause of blindness particularly in the developing world DK cause the common sexually transmitted infection and L1 and L2 cause the severe pathology of lymphogranuloma venereum.
In men, untreated sexual transmitted Ct can cause complications such as urethritis and chronic prostatitis . Studies have also shown that men with Cthave poorer quality sperm compared to healthy counterparts . However, in women infection can have devastating and long-term effects on reproductive health. Ct has been associated with urethritis, pelvic inflammatory disease, scarring in the pelvis , and fertility complications including ectopic pregnancy, infertility, miscarriage and premature rupture of membranes .
You May Like: Is Trich The Same As Chlamydia
Sexually Transmitted Diseases /sexually Transmitted Infections
STDs/STIs infect the mouth, genital and anal areas of the body. Although some STDs/STIs can also be spread through sexual skin-to-skin contact, STDs/STIs are spread mainly through oral, vaginal, or anal sex with an infected partner. Some STDs/STIs can also be spread from an infected mother to her child during the birthing process.
STDs/STIs are either viral or bacterial. A viral infection is caused by a virus and cannot be cured. However, although a virus will remain in the body for life, symptoms of the virus might not be present at all times. A bacterial infection is caused by a bacterial organism, and the active infection can be cured. The infection must be treated early, however, to ensure that the damage it caused to the body can be repaired. Whether an infection is viral or bacterial, the infection can have long-term effects on the body, such as infertility or sterility, and can leave the body vulnerable to more serious diseases, such as HIV. Ultimately, untreated STDs/STIs can affect numerous organ systems in the body.
The Ultimate Guide To Chlamydia
Chlamydia is a sexually transmissible infection , that if left untreated, can lead to serious health problems down the track.
Though chlamydia is easily spread, having good knowledge about the prevention and transmission of this STI will help you maintain a confident and healthy sex life. To assist you, weve answered a range of popular chlamydia questions on this page, fully and factually. Its the Ultimate Guide to Chlamydia. An Encyclopedia of Chlamydia. An STI FYI.
Recommended Reading: Can Chlamydia Be Cured Without Treatment
Classification And Antigenic Types
Several distinct antigenic components have been recognized in Ctrachomatis and C psittaci, some group specific andothers species specific. Detergents have been used to extract antigens fromelementary bodies and reticulate bodies. Chlamydia pneumoniae is serologically unique and differs from C trachomatisspecies and all C psittaci strains tested.
The outer chlamydial cell wall contains several antigenic proteins, including a40-kilodalton major outer membrane protein , a 60- to 62-kDa and 15-kDa,cysteine-rich proteins, a 74 kDa species-specific protein, and 31- and 18-kDaeukaryotic cell-binding proteins, which share the same primary sequence.
Three monoclonal antibodies that recognize epitopes on cysteine-rich membraneproteins interact with all 15 human C trachomatis serotypes,establishing the species specificity of this antigen. Monoclonal antibodies to the15-kDa cysteine-rich protein showed biovar specificity and species specificity. The60- to 62-kDa and 15-kDa cysteine-rich proteins are highly immunogenic in thenatural infection, but the antibodies do not neutralize the infectivity of Ctrachomatis elementary bodies.
How Do You Get Chlamydia

Chlamydia is usually passed on through unprotected vaginal, anal or oral sex.
Chlamydia can be passed on through genital contact. This means you can get chlamydia from someone who has the infection if your genitals touch, even if you dont have sex or ejaculate .
You can also get chlamydia if you come into contact with infected semen or vaginal fluid, or get them in your eye.
Chlamydia cant be passed on through kissing, hugging, sharing towels or using the same toilet as someone with the infection.
Also Check: One Day Pill For Chlamydia
What Causes Syphilis
Bacteria cause syphilis. They usually enter the body through the tissues that line the throat, nose, rectum, and vagina. Syphilis bacteria also can be transmitted by contact with the penis or vulva. A person with syphilis who has a sore or a rash can pass the infection to others. An infected pregnant woman can also pass syphilis to her baby.
Some things increase your chance of getting syphilis. They include:
- Having unprotected sex . This risk is high among men who have sex with other men.
- Having more than one sex partner and living in an area where syphilis is common.
- Having a sex partner who has syphilis.
- Having sex with a partner who has many sex partners.
- Trading sex for drugs or money.
- Having HIV.
What To Think About
In rare cases, the first attempt at treatment does not cure the syphilis infection. Follow-up blood tests are needed to be sure the infection is cured.
Some types of syphilis can’t be treated by certain antibiotics. If your doctor finds that your syphilis is resistant to the drug you are taking, you will be tested so that your doctor can prescribe another antibiotic to cure the infection.
Read Also: How Can You Tell If A Girl Has Chlamydia
What Exactly Causes Chlamydia
A type of bacterium called Chlamydia trachomatis causes chlamydia. This bacterium can take hold in the tissues of your genitals, anus, eyes, or throat.
Its usually transmitted from one person to another during penetrative vaginal or anal sex or oral sex, although sex without penetration can also transmit it.
Chlamydia can also be transmitted to a baby during vaginal delivery if the person giving birth has an untreated chlamydia infection.
What Is The Treatment For Chlamydia
Chlamydia can be easily cured with antibiotics. HIV-positive persons with chlamydia should receive the same treatment as those who are HIV-negative.
Persons with chlamydia should abstain from sexual activity for 7 days after single dose antibiotics or until completion of a 7-day course of antibiotics, to prevent spreading the infection to partners. It is important to take all of the medication prescribed to cure chlamydia. Medication for chlamydia should not be shared with anyone. Although medication will cure the infection, it will not repair any permanent damage done by the disease. If a persons symptoms continue for more than a few days after receiving treatment, he or she should return to a health care provider to be reevaluated.
Repeat infection with chlamydia is common.49 Women whose sex partners have not been appropriately treated are at high risk for re-infection. Having multiple chlamydial infections increases a womans risk of serious reproductive health complications, including pelvic inflammatory disease and ectopic pregnancy.50,51 Women and men with chlamydia should be retested about three months after treatment of an initial infection, regardless of whether they believe that their sex partners were successfully treated.40
Infants infected with chlamydia may develop ophthalmia neonatorum and/or pneumonia.10 Chlamydial infection in infants can be treated with antibiotics.
Also Check: How Can You Get Chlamydia If No One Cheats
Who Is At Risk For Chlamydia
Any sexually active person can be infected with chlamydia. It is a very common STD, especially among young people.3 It is estimated that 1 in 20 sexually active young women aged 14-24 years has chlamydia.5
Sexually active young people are at high risk of acquiring chlamydia for a combination of behavioral, biological, and cultural reasons. Some young people dont use condoms consistently.15 Some adolescents may move from one monogamous relationship to the next more rapidly than the likely infectivity period of chlamydia, thus increasing risk of transmission.16 Teenage girls and young women may have cervical ectopy .17 Cervical ectopy may increase susceptibility to chlamydial infection. The higher prevalence of chlamydia among young people also may reflect multiple barriers to accessing STD prevention services, such as lack of transportation, cost, and perceived stigma.16-20
Men who have sex with men are also at risk for chlamydial infection since chlamydia can be transmitted by oral or anal sex. Among MSM screened for rectal chlamydial infection, positivity has ranged from 3.0% to 10.5%.6.7 Among MSM screened for pharyngeal chlamydial infection, positivity has ranged from 0.5% to 2.3%.7.8
Can You Get Std From Kissing
Although kissing is considered to be low-risk when compared to intercourse and oral sex, its possible for kissing to transmit CMV, herpes, and syphilis. CMV can be present in saliva, and herpes and syphilis can be transmitted through skin-to-skin contact, particularly at times when sores are present.
Read Also: Side Effects To Chlamydia Medication
How Long Can You Have Chlamydia Without Knowing
If youve had intercourse with an infected man or woman, chlamydia symptoms may appear between 1 3 weeks after contact.
However, you may still be asymptomatic after a chlamydia infection. This is because chlamydia can be silent or dormant for months and years without showing symptoms.
In men, about 50 70 percent will show symptoms of chlamydia while only 30 50 percent of women will be symptomatic. Absent symptoms of chlamydia do not mean absent infection. You should take chlamydia test to confirm if you have the infection or not.
Frequently Asked Questions About Hiv/aids
HIV can be detected in several fluids and tissue of a person living with HIV. It is important to understand however, that finding a small amount of HIV in a body fluid or tissue does not mean that HIV is transmitted by that body fluid or tissue. Only specific fluids from an HIV-infected person can transmit HIV. These specific fluids must come in contact with a mucous membrane or damaged tissue or be directly injected into the blood-stream for transmission to possibly occur.
In the United States, HIV is most commonly transmitted through specific sexual behaviors or sharing needles with an infected person. It is less common for HIV to be transmitted through oral sex or for an HIV-infected woman to pass the virus to her baby before or during childbirth or after birth through breastfeeding or by prechewing food for her infant. In the United States, it is also possible to acquire HIV through exposure to infected blood, transfusions of infected blood, blood products, or organ transplantation, though this risk is extremely remote due to rigorous testing of the U.S. blood supply and donated organs.
For more information, see: How safe is the blood supply in the United States?
For more information on latex condoms, see “Male Latex Condoms and Sexually Transmitted Diseases.”
In women, the lining of the vagina can sometimes tear and possibly allow HIV to enter the body. HIV can also be directly absorbed through the mucous membranes that line the vagina and cervix.
Recommended Reading: How Do I Get Antibiotics For Chlamydia
How Long Does It Take To Show Up In The Throat
Symptoms of chlamydia in your throat are typically caused by having oral sex with someone whos contracted the infection.
Its much less common to notice throat symptoms, but they may still appear after a week or so, up to a few months or longer.
STI tests that look for chlamydia arent always done on the throat since its an area that does not carry the infection often. Ask your doctor for a throat swab or other chlamydia test if you think youve been exposed through oral sex.
Here are the most common symptoms of chlamydia in both people with penises and people with vulvas.
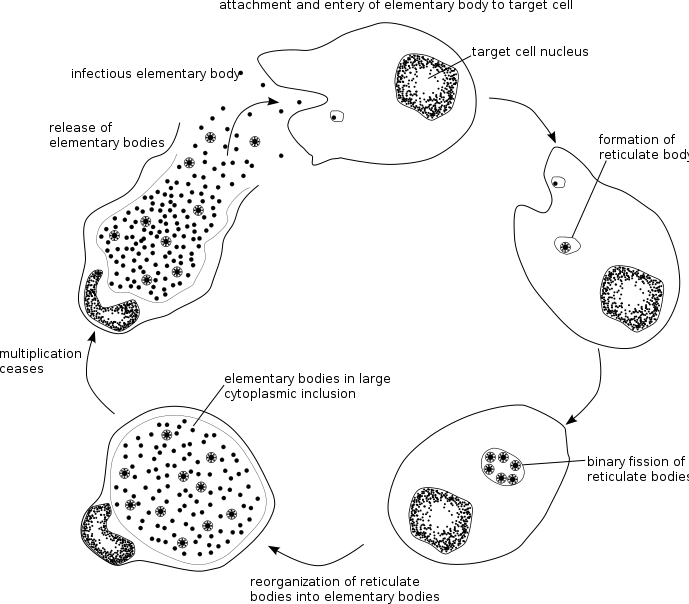
Life Cycle Of Ct In The Human Body
Ct is a Gram-negative bacterium which exists in two forms: the infectious elementary body and the intracellular reticulate body , which is able to replicate and multiply. Infection begins when EBs attach to the membrane of a cell of the inner layer of the urogenital tract . EBs enter the cell and two hours later are transformed into RBs which grow and divide over the next hours, resulting in a rapid increase in number. At this point RBs transform into EBs. Usually, 4872 hours after infection, the host cell bursts to release the infectious EBs .
Figure 1. The life cycle of Chlamydia trachomatis in the female reproductive tract
Also Check: What Are Some Treatments For Chlamydia