Is Treatment Always Necessary For Chlamydia
Yes, treatment is necessary for chlamydia, particularly in women of childbearing age, because it reduces the risk of chlamydia-associated ectopic pregnancy, fertility problems, and the transmission of chlamydia to neonates during birth. In women, of all ages, chlamydia treatment reduces the risk of pelvic inflammatory disease.
In men, treatment for chlamydia stops them from infecting or reinfecting sexual partners with the bacteria.
Treat any person testing positive for chlamydia with a recommended course of antibiotics promptly. Delays in treatment have been associated with complications, such as pelvic inflammatory disease.
Doxycycline Trumps Azithromycin For Asymptomatic Rectal Chlamydia
A 1-week course of doxycycline is more effective than single-dose azithromycin to treat rectal chlamydia in men who have sex with men , according to newly published results in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Chlamydia is the most commonly reported bacterial sexually transmitted infection in the United States, with 4 million cases reported in 2018, and 127 million globally. Most infections are asymptomatic.
Rates of rectal chlamydia among MSM screened for infection range from 3% to 10.5%.
The most recent Centers for Disease Control and Prevention chlamydia guidelines recommend either a single dose of azithromycin or doxycycline 100 mg twice daily for 7 days. These 2015 guidelines were based on a meta-analysis of urogenital chlamydia infections, which showed comparable efficacy of 97% or 98%, respectively.
Study coauthor Jane S. Hocking, PhD, head of the Sexual Health Unit at the University of Melbournes School of Population and Global Health in Australia, told Medscape Medical News that observational studies had suggested that azithromycin was about 20% less effective than doxycycline, prompting this clinical trial.
The study, conducted at five sexual health clinics in Australia, was a double-blind, randomized, controlled trial of doxycycline or azithromycin .
Because 85% of infected men are asymptomatic, the studys primary outcome was a negative nucleic acid amplification test at 4 weeks, confirming a microbiologic cure.
Doxycycline More Effective Than Azithromycin For Chlamydia
Trial finds doxycycline slightly more effective, but researchers not entirely convinced of its superiority.
Clinical research
National Cancer Institute / Science Photo Library
Standard treatment for chlamydia is a single dose of azithromycin or a weeks course of doxycycline twice daily. However, evidence suggests that azithromycin may not be as effective as doxycycline.
To establish efficacy, US researchers randomly assigned adolescents with urogenital Chlamydia trachomatis infection to azithromycin or doxycycline . The participants were residents at youth correctional facilities, which made the chances of reinfection low, say the researchers.
The efficacy of doxycycline was 100%, compared with 97% for azithromycin. The results meant that azithromycin was not deemed as clinically effective as doxycycline.
However, writing in TheNew England Journal of Medicine , the researchers say that the exceptional efficacy of doxycycline may be offset by poorer adherence to the week-long regimen in real-world settings.
Recommended Reading: Does A Zpack Cure Chlamydia
Mass Administration Of Three
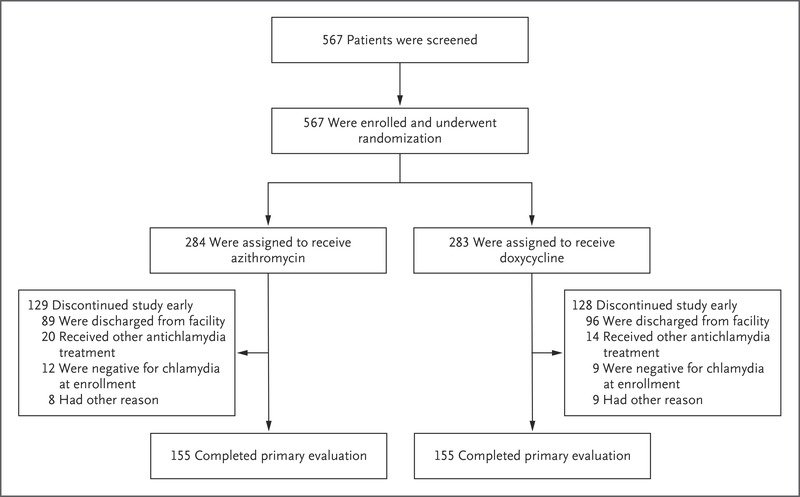
In-Depth : This per-protocol, randomized-controlled trial was conducted in four long-term youth correctional facilities in Los Angeles, USA from December 2009 to May 2014. Inclusion criteria were any correctional resident with a positive screening NAAT on intake. Exclusion criteria included residents who were pregnancy, breast-feeding, had a gonorrhea co-infection among others. Residents were randomized 1:1 to either standard treatment of either azithromycin or doxycycline. The primary outcome of interest was treatment failure, determined by NAAT and C. trachomatis genotyping, at 28 days after treatment. Non-inferiority would be determined if the absolute rate of azithromycin treatment failure would be less than 5% higher than the absolute rate of doxycycline treatment failure.
The 567 participants were randomized 284 to azithromycin and 283 to doxycycline. However, due to numerous reasons, primarily because of discharge from the facility, only 155 residents were included in each primary evaluation. No treatment failures occurred in the doxycycline group . Five participants in the azithromycin group had treatment failure . The difference in failure rate between the two treatments was 3.2% . The upper limit of the 90% was outside of the predetermined 5% rate difference and thus non-inferiority of azithromycin to doxycycline could not be established.
Image: PD/CDC
Sex Partners Need Treatment Too
If you are diagnosed with chlamydia, you will need to tell all of your sexual partners, because they will need the same treatment you are receiving.
In most states, a doctor or other healthcare provider can give you the medicine that your partner or partners will need to take. Then you can deliver it to those partners. This practice is called expedited partner therapy or patient delivered partner therapy.
These options can help a lot if your partner doesnt have a healthcare provider or feels embarrassed about seeking care, says Dr. Dombrowski.
Its natural to feel nervous or upset about having to tell your partner or partners about having an STD. Your healthcare provider can help with this problem. They may even rehearse the conversation with you, says Dombrowksi.
Learning about chlamydia and seeking advice from a healthcare provider about how to discuss it with your partner can help you handle the conversation with less anxiety and more confidence.
Remember, chlamydia is not just common: It is the most common infection reported to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . You are being helpful, mature, and responsible by telling your partners.
Read Also: What Are All The Ways You Can Get Chlamydia
You May Like: How Do They Test For Chlamydia
Doxycycline Trumps Azithromycin For Asymptomatic Rectal Chlamydia In Men Who Have Sex With Men
Judy Stone, MD
A 1-week course of doxycycline is more effective than single-dose azithromycin to treat rectal chlamydia in men who have sex with men , according to newly published results in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Chlamydia is the most commonly reported bacterial sexually transmitted infection in the United States, with 4 million cases reported in 2018, and 127 million globally. Most infections are asymptomatic.
Rates of rectal chlamydia among MSM screened for infection range from 3% to 10.5%.
The most recent Centers for Disease Control and Prevention chlamydia guidelines recommend either a single dose of azithromycin or doxycycline 100 mg twice daily for 7 days. These 2015 guidelines were based on a meta-analysis of urogenital chlamydia infections, which showed comparable efficacy of 97% or 98%, respectively.
Dr Jane S. Hocking
Study coauthor Jane S. Hocking, PhD, head of the Sexual Health Unit at the University of Melbournes School of Population and Global Health in Australia, told Medscape Medical News that observational studies had suggested that azithromycin was about 20% less effective than doxycycline, prompting this clinical trial.
The study, conducted at five sexual health clinics in Australia, was a double-blind, randomized, controlled trial of doxycycline or azithromycin .
Because 85% of infected men are asymptomatic, the studys primary outcome was a negative nucleic acid amplification test at 4 weeks, confirming a microbiologic cure.
Study Sample Collection And Laboratory Analyses
Women collected rectal and vaginal swabs at enrollment immediately prior to treatment, and after 4 weeks at the STI clinic women also collected samples at week 1 and week 2 at home . Individual test results were not available to clinic staff and participants. Samples were tested using commercial NAAT platforms according to manufacturers instructions . The NAAT quantitation cycle values were taken as a proxy for bacterial load . Positive week 0 and 4 samples were cultured . Week 4 NAAT-positive samples with a low Cq value were genotyped by multilocus sequence typing the accompanying week 0 sample was also genotyped .
Read Also: I Took Antibiotics For Chlamydia
What Is Azithromycin And How Does It Work
Azithromycin is used to treat certain bacterial infections . It is a macrolide-type antibiotic. It works by stopping the growth of bacteria.
This medication will not work for viral infections . Unnecessary use or misuse of any antibiotic can lead to its decreased effectiveness.
Azithromycin is available under the following different brand names: Zithromax, and Zmax.
Susceptible organisms
- Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans, Actinomyces israelii, Actinomyces naeslundii, Actinomyces odontolyticus, Afipia felis, Arachnia propionica, Arcanobacterium haemolyticum, Bartonella henselae, Bartonella quintana, Bordetella pertussis, Borrelia burgdorferi, Borrelia recurrentis, Klebsiella granulomatis, Campylobacter jejuni, Chlamydia pneumoniae , Chlamydia trachomatis, Haemophilus ducreyi, Haemophilus influenzae, Legionella spp, Mycobacterium simiae, Mycobacterium scrofulaceum, Mycobacterium xenopi, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Moraxella catarrhalis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus , Streptococcus agalactiae , Streptococcus bovis , Streptococcus intermedius group , Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes , viridans streptococci
- First-line therapy: A felis, B henselae, B quintana, B pertussis, C jejuni, C pneumoniae , C trachomatis, H ducreyi, H influenzae, Legionella spp, M scrofulaceum, M simiae, M xenopi, N gonorrhoeae
- 500 mg/day orally for 3 days or 2 g orally once
Pediatric: Zmax: 2g orally once
- 10 mg/kg of oral suspension orally once daily for 3 days
How Is Chlamydia Treated
The following are the recommended treatment regimens for chlamydia according to the Guidelines for Sexually Transmitted Diseases, released in 2015, but still considered current. Only one regimen should be chosen.
- Azithromycin 1 gram orally as a single dose
- OR
- Ofloxacin 300 mg orally twice a day for 7 days.
Don’t Miss: Can Uti Antibiotics Get Rid Of Chlamydia
Put Sex On Hold During And After Chlamydia Treatment
If you were given a single dose of antibiotics to treat your chlamydia, you should not have any kind of sex for a full seven days after the day you took the medicine. If youre taking antibiotics for a week, wait another seven days after the last day of your treatment. Be sure to take all of the medicine that is prescribed for you.
Not having sex for seven days after treatment is important so you dont spread the infection to your partner or partners.
Medication stops the infection and can keep you from spreading the disease, but it wont cure any permanent damage that the infection caused before you started treatment. In women, such damage can include blocking the fallopian tubes, causing infertility.
If you still have symptoms for more than a few days after you stop taking your medicine, go back to see your doctor or other healthcare provider so they can check you again.
You May Like: Can Chlamydia Cause Kidney Infection
Concerned You May Have Chlamydia Check Your Symptoms For Free And Chat With A Doctor For Just $23
Always follow the directions from your doctor or pharmacist for taking azithromycin.
Azithromycin is taken as a single dose, one time.
It should be taken as soon as you receive the prescription. Azithromycin can be taken with or without food, however, the extended-release form is typically taken on an empty stomach.
If you take the liquid form, shake it well before using and use a dosing spoon to measure an accurate dose. If you are prescribed the powder, mix it with water according to directions.
Don’t Miss: Can You Die From Chlamydia
Definition Of Treatment And Outcome
Per CDC treatment guidelines11, men who tested positive for rectal chlamydia were treated with azithromycin or doxycycline , at the clinician’s discretion. The treatment regimen was recorded by clinic staff on a standardized form. Clinicians treated men presumptively at the time of the initial evaluation if they reported recent sexual contact to a partner diagnosed with gonorrhea, chlamydia, or non-gonococcal urethritis.
We limited the analytic sample to men who were treated within 60 days of diagnosis to minimize the effect of spontaneous resolution of infection15 on our study outcome. We further excluded men who were co-treated with a quinolone or amoxicillin, since both drugs have some activity against C. trachomatis. We also excluded men from the analysis if they were treated with a doxycycline or azithromycin regimen other than those recommended in the 2010 CDC STD Treatment Guidelines11.
How Long Does Azithromycin Take To Cure Chlamydia
It usually takes approximately 7 days for azithromycin to cure chlamydia. However, it can take up to 2 weeks for the infection to go away completely.
Avoid having sex during treatment or until the infection has cleared. Youll want to make sure its completely cured, or else youll risk passing it to someone else.
Recommended Reading: At Home Chlamydia Test Kit Walgreens
What Happens If Chlamydia Is Left Untreated
If left untreated, chlamydia can lead to more serious health problems.
In people assigned female at birth, untreated chlamydia can cause pelvic inflammatory disease , a condition which can scar the fallopian tubes and lead to infertility.
Chlamydia can also be passed on to babies during birth if the parent has the infection while pregnant.
In people assigned male at birth, untreated chlamydia can cause epididymitis, an infection in the prostate gland, and male chlamydial urethritis.
Antibiotics For Treating Genital Chlamydia Trachomatis Infection In Men And Non
Review question
This systematic review assessed the effectiveness and safety of antibiotic treatment for Chlamydia trachomatis genital infection in terms of microbiological or clinical failure in men and non-pregnant women.
Background
CT is the most frequent cause of urinary tract and genital infections in women and men. However, women frequently show no symptoms when they are infected. CT infection can lead to complications or cause further problems in reproductive health in women , and men , or chronic pelvic pain. Clinical guidelines for treating CT do not recommend a preferred antibiotic treatment. This Cochrane review evaluates all randomised controlled studies , that included antibiotics for the treatment of genital CT infection that are recommended by the most up-to-date clinical guidelines.
Search date
We searched for studies published up to June 2018 that provided information about failure to eliminate the CT infection or improve the symptoms, presence of adverse events, antimicrobial resistance, and reinfection. as treatment outcomes
Study characteristics
Study funding sources
One study reported funding from academic grants, another four studies declared having received sponsorship or grants from pharmaceutical companies. The other studies declared that they were self-funded or did not mention funding at all.
Key results
Quality of evidence
To assess the efficacy and safety of antibiotic treatment for CT genital infection in men and non-pregnant women.
Recommended Reading: Can A Uti Lead To Chlamydia
Usual Adult Dose For Tonsillitis/pharyngitis
Immediate-release: 500 mg orally as a single dose on day 1, followed by 250 mg orally once a day on days 2 to 5Use: Treatment of pharyngitis/tonsillitis caused by Streptococcus pyogenes as an alternative to first-line therapy in patients who cannot use first-line therapyIDSA Recommendations:Individuals with penicillin allergy: 12 mg/kg orally once a day-Maximum dose: 500 mg/day-Duration of therapy: 5 daysUse: Treatment of Group A streptococcal pharyngitis
Infant Pneumonia Caused By C Trachomatis
Chlamydial pneumonia among infants typically occurs at age 13 months and is a subacute pneumonia. Characteristic signs of chlamydial pneumonia among infants include a repetitive staccato cough with tachypnea and hyperinflation and bilateral diffuse infiltrates on a chest radiograph. In addition, peripheral eosinophilia occurs frequently. Because clinical presentations differ, all infants aged 13 months suspected of having pneumonia, especially those whose mothers have a history of, are at risk for , or suspected of having a chlamydial infection should be tested for C. trachomatis and treated if infected.
Diagnostic Considerations
Specimens for chlamydial testing should be collected from the nasopharynx. Tissue culture is the definitive standard diagnostic test for chlamydial pneumonia. Nonculture tests can be used. DFA is the only nonculture FDA-cleared test for detecting C. trachomatis from nasopharyngeal specimens however, DFA of nasopharyngeal specimens has a lower sensitivity and specificity than culture. NAATs are not cleared by FDA for detecting chlamydia from nasopharyngeal specimens, and clinical laboratories should verify the procedure according to CLIA regulations . Tracheal aspirates and lung biopsy specimens, if collected, should be tested for C. trachomatis.
Treatment
Erythromycin base or ethylsuccinate 50 mg/kg body weight/day orally divided into 4 doses daily for 14 days
Azithromycin suspension 20 mg/kg body weight/day orally, 1 dose daily for 3 days
Read Also: How Do You Contract Chlamydia
Does Azithromycin Cure Chlamydia
Cure rates of 97% were reported in an analysis of 12 randomized clinical trials that investigated the use of azithromycin 1 gram for the treatment of chlamydia. That means for every 100 people with chlamydia who take azithromycin, 97 will be cured and 3 will not be cured.
This relies on the person with chlamydia taking azithromycin exactly as directed and not sharing the medication with anyone. Any sexual partners must be also treated.
Although azithromycin cures chlamydia in most people, it will not repair any permanent damage done to tissues by the disease.
If you have been symptomatic with chlamydia before treatment and your symptoms continue for more than a few days after receiving treatment, then ask to be re-evaluated by your health care provider.
Unfortunately, repeat infection with chlamydia is common. This means that even though azithromycin has cured your current infection with chlamydia, this does not mean you will not get chlamydia again. If your sexual partners have not been appropriately treated, you are at high-risk for reinfection. Having chlamydia multiple times puts women at high risk of fertility problems, ectopic pregnancy, and pelvic inflammatory disease. Infants born to mothers who are infected with chlamydia may develop chlamydial conjunctivitis and/or pneumonia. Chlamydial infection in infants can be treated with antibiotics.
Trial Of Azithromycin Vs Doxycycline For The Treatment Of Rectal Chlamydia In Msm
| The safety and scientific validity of this study is the responsibility of the study sponsor and investigators. Listing a study does not mean it has been evaluated by the U.S. Federal Government. Read our disclaimer for details. |
| First Posted : August 1, 2018Results First Posted : January 7, 2021Last Update Posted : January 7, 2021 |
- Study Details
| Drug: AzithromycinDrug: DoxycyclineOther: Placebo | Phase 4 |
| Study Type : | |
| Treatment | |
| Official Title: | A Phase 4, Randomized, Double-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Azithromycin Versus Doxycycline for the Treatment of Rectal Chlamydia in Men Who Have Sex With Men |
| Actual Study Start Date : |
Recommended Reading: Garlic Cure Chlamydia How Long