What Does The Test Result Mean
A positive test indicates you have an active chlamydia infection that requires treatment with antibiotics.
A negative test means only that there is no evidence of infection at the time of the test. If you are at an increased risk, it is important that you have screening tests performed yearly to check for possible infection, especially since re-infection is common, particularly among teenagers.
If you are infected, your sexual partner should be tested and treated as well.
How Can Chlamydia Be Prevented
The most reliable ways to avoid infection with chlamydia or any sexually transmitted disease are to abstain from oral, vaginal, and anal sex or to be in a long-term, mutually monogamous relationship with an uninfected partner. People who are sexually active should correctly and consistently use condoms to reduce the risk of infection with chlamydia and other STDs.
Understanding Of Lab Tests Results
Please visit the site associated with The American Association for Clinical Chemistry for better understanding of tests. There you will find the most detailed and full information regarding lab tests. In “common questions” tab you will find answers on the most common questions.
In addition, you can use a special form to ask the question. It is useful, if there is no answer on your question on the web site. A laboratory scientist will answer your question. It is a part of voluntary service provided by the American Society for Clinical Laboratory Science.
Read Also: Can I Get Chlamydia Medication For My Partner
Question 2 Are Samples Other Than Urogenital Samples Such As Throat And Rectal Swabs Acceptable For C Trachomatis And N Gonorrhoeae Naats
Rectal and throat swabs are acceptable for C trachomatis and N gonorrhoeae NAAT testing. C trachomatis and N gonorrhoeae have been isolated from extra-genital sites in men who have sex with men and sexually active, heterosexuals who engage in unprotected oral or anal sex. The CDC currently recommends oral and anal testing of MSM who have had receptive oral or anal sex, respectively, within the previous year.4 Both C trachomatis and N gonorrhoeae testing are recommended on the anal specimens.
Most persons with C trachomatis detected at oropharyngeal sites do not have oropharyngeal symptoms. Although the clinical significance of oropharyngeal C trachomatis infection is unclear and routine oropharyngeal screening for CT is not recommended, available evidence suggests oropharyngeal C trachomatis can be sexually transmitted to genital sites therefore, per the 2015 guidelines on sexually transmitted diseases, oropharyngeal C trachomatis should be treated with appropriate antimicrobials.4
Quest Diagnostics offers throat- and anal -based testing:
- Test code 16506-Chlamydia trachomatis/Neisseria gonorrhoeae RNA, TMA, Rectal
- Test code 70051-Chlamydia trachomatis/Neisseria gonorrhoeae RNA, TMA, Throat
- Test code 16505-Chlamydia trachomatisRNA, TMA, Rectal
- Test code 70048-Chlamydia trachomatisRNA, TMA, Throat
- Test code 16504-Neisseria gonorrhoeae RNA, TMA, Rectal
- Test code 70049-Neisseria gonorrhoeaeRNA, TMA, Throat
Question 1 Which Specimen Types Are Suitable For C Trachomatis And N Gonorrhoeae Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests
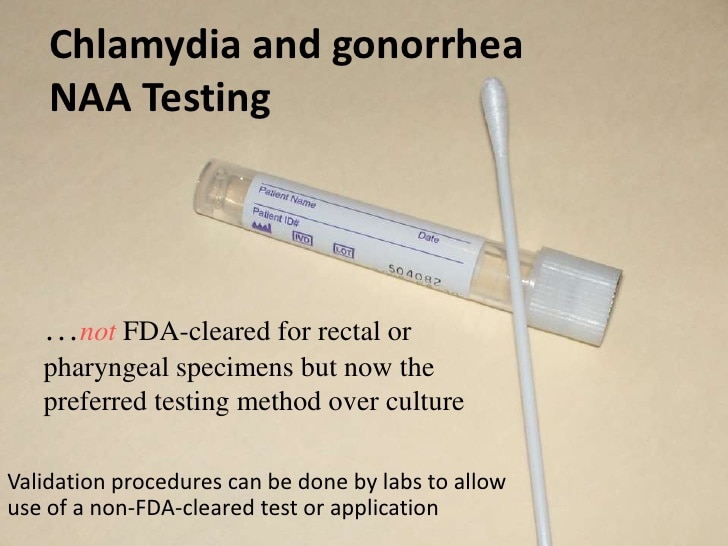
For women, a vaginal sample is recommended in the absence of a pelvic exam. For men, first-catch urine is the recommended specimen.
The following urogenital specimens are suitable:
- First-catch urine sample from a male or a female
- Endocervical, vaginal, SurePath, or ThinPrep® vial with PreservCyt® specimens from a female patient
- Male urethral swab
- Vaginal swab collected by a physician or the patient1-3
For nonurogenital specimens, see Question 2 below.
Recommended Reading: Chlamydia How Fast Can You Get It
Are Test Results Accurate
Although chlamydia testing is an important method of finding and treating this common STD, test results could be impacted by the following:
- The use of antibiotics within several days before testing
- Urinating within one hour of sample collection
- Vaginal douching within 24 hours of testing
- Improper sample collection
- Contamination of rectal samples with fecal matter
Question 3 What Are The Guidelines For Additional Testing Following A Positive Ct/ng Naat Screening Test
Repeat testing of the same positive sample using the same NAAT methodology is usually not recommended and does not improve the positive predictive value when screening with currently available NAATs.5 Positive results from an NAAT-based screening assay are considered presumptive evidence of infection.
If a false-positive CT or NG NAAT result is expected to have adverse medical, social, or psychological consequences, confirmatory testing should be considered.6 Confirmatory testing, using an alternative nucleic acid target region, should also be considered in low-prevalence settings, where the positive predictive value of assays is reduced. Note that testing of asymptomatic people is not recommended in extremely low-prevalence settings.5 Treatment probably should not be withheld while awaiting the results of confirmatory testing.
The following tests target alternative nucleic acid regions and can thus be used to confirm positive CT/NG NAAT screening test results:
- Test Code 15031-Chlamydia trachomatis RNA, TMA, Alternate Target
- Test Code 91046-Chlamydia trachomatis RNA, TMA, Alternate Target, Rectal
- Test Code 15033-Neisseria gonorrhoeae RNA, TMA, Alternate Target
- Test Code 90990-Neisseria gonorrhoeae RNA, TMA, Alternate Target, Rectal
You May Like: How Do They Treat Chlamydia
Why Consider This Test
Sexually Active
Annual chlamydia and gonorrhea screenings are recommended for all sexually active women younger than 25 years, as well as older women with risk factors such as new or multiple sex partners, or a sex partner who has a sexually transmitted infection.1
Sexually Active
Annual screening for syphilis, chlamydia, and gonorrhea is recommended for all sexually active gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men.
References
How Much Does The Test Cost
The cost of chlamydia testing varies based on many factors. Chlamydia testing may be paid for by health insurance when ordered by a doctor. Because health plans vary, its important for patients to discuss the cost of testing, including any copays or deductibles, with their health plan.
For patients without health insurance coverage, the cost of testing may include the cost of the office visit and sample collection as well as technician fees. Testing may also be available for free or at low cost through community-based organizations and local health departments.
Recommended Reading: Can Boric Acid Cure Chlamydia
When To Get Tested
More About Labcorp Urine Chlamydia And Gonorrhea Recipes
GONORRHEA AND CHLAMYDIA ASSOCIATED WOMEN’S HEALTH …
FromEstimated Reading Time
CHLAMYDIA, GONORRHEA & AMP TRICHOMONIASIS | PIXEL BY LABCORP
FromEstimated Reading Time
URINE TESTING FOR SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASES
FromEstimated Reading Time
CHLAMYDIA & AMP GONORRHEA URINE TEST | STD TEST
From
183194: CHLAMYDIA/GONOCOCCUS, NAA | LABCORP
From
CHLAMYDIA/GONOCOCCUS | DEFY MEDICAL
From
DISCOUNTED CHLAMYDIA AND GONORRHEA TESTING | ONLINE STD …
From
CHLAMYDIA, GONORRHEA & AMP TRICH TEST
From
TEST FOR CHLAMYDIA AND GONORRHEA – PRIVATE MD LABS
From
CHLAMYDIA TRACHOMATIS/NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE (CT/GC …
From
CHLAMYDIA TRACHOMATIS AND NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE – NUCLEIC …
From
GONORRHEA TESTING | LABCORP
From
UNIVERSAL SCREENING FOR CHLAMYDIA AND GONORRHEA | LABCORP
From
183160: CHLAMYDIA TRACHOMATIS,NEISSERIA … – LABCORP
From
NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE, NAA | LABCORP – FIND LAB TESTS ONLINE
From
CHLAMYDIA AND GONORRHEA URINE TEST, RANDOM | WALK-IN LAB
From
CHLAMYDIA/GONORRHEA RECOMMENDED TREATMENTS
From
CHLAMYDIA AND GONORRHOEA TESTING – QUEENSLAND HEALTH
From
URINE CHLAMYDIA & AMP GONORRHEA LAB TEST – GC CHLAMYDIA STD TEST
From
DISCOUNTED CHLAMYDIA AND GONORRHEA TESTING | ONLINE STD …
From
CHLAMYDIA/GONOCOCCUS, NAA | LABCORP – FIND LAB TESTS ONLINE
From
URINE TESTS FOR CHLAMYDIA AND GONORRHEA: REQUEST A TEST
From
CHLAMYDIA/GONOCOCCUS, NAA WITH CONFIRMATION | LABCORP …
From
CHLAMYDIA TRACHOMATIS AND NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE BY …
From
CHLAMYDIA, GONORRHEA & AMP TRICH TEST
From
You May Like: What Medication Is Used To Treat Chlamydia And Gonorrhea
Chlamydia Gonorrhea & Trichomoniasis
This panel provides an assessment of sexual health by screening for three common sexually transmitted infections :
- Chlamydia
Preparation
For your urine test, it’s best not to urinate for two hours before your sample collection urinating within this period could affect the accuracy of your results.
How Is The Test Used
Chlamydia testing is used to screen for and diagnose sexually transmitted infections caused by the bacteria Chlamydia trachomatis.
Testing for Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae is often done at the same time since the infections caused by these two bacteria can have similar signs and symptoms. These bacteria may be acquired at the same time, and you may have infections with both. A definitive diagnosis is important since the two infections require different antibiotic treatment.
Repeat testing is recommended to ensure that treatment has been effective. This is done about three months after you have completed treatment.
Read Also: Amoxicillin For Chlamydia And Gonorrhea
When Is It Ordered
Screening
Because many infected people do not have any noticeable symptoms, a number of health organizations recommend regular chlamydia screening for certain people:
Women
All sexually active women younger than age 25 and sexually active women age 25 and older who are at increased risk should get yearly screening for chlamydia, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists . The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force and the American Academy of Pediatrics also recommend routine screening for these women .
Examples of risk factors for chlamydia infection include:
For pregnant women, the CDC recommends screening for chlamydia during the first trimester or first prenatal visit. For women younger than age 25 or at increased risk of infection, testing is repeated in the third trimester. Pregnant women diagnosed with chlamydia should be retested about 3 months after completing treatment.
Diagnosis
Chlamydia testing may also be done when your sex partner has been diagnosed with chlamydia or when you have signs and symptoms of chlamydia.
For women, if symptoms occur, they may include:
For men, symptoms may include:
Question 5 What Do I Do If Test
If an NAAT is positive for C trachomatis or N gonorrhoeae 3 or more weeks after the end of treatment,6 first ensure that the patient has complied with the prescribed therapy and that the patient denies having sex after treatment with an untreated or new sex partner. If these conditions are met, treatment is considered to be a failure. In such cases, the CDC recommends contacting the local or state health department to get guidance and to arrange for antimicrobial susceptibility testing.7
Also Check: How Long Does Chlamydia Last After Treatment
How To Get Tested
Chlamydia testing is usually ordered by a doctor. In people without symptoms, a doctor can evaluate their risk and suggest an appropriate screening schedule. If a patient has symptoms of this infection, a doctor will order testing to diagnose or rule out chlamydia.
Testing for chlamydia can be conducted at a hospital, doctors office, health clinic, or community health program.
Questions For Your Doctor About Test Results
It can be helpful to bring questions to your doctor to learn more about your chlamydia test results. Helpful questions may include:
- What is my chlamydia test result?
- Did my test check for any other STDs?
- Do I need any treatment based on my results?
- How can I talk to my sexual partners about chlamydia?
- When should I be tested for STDs and how often?
You May Like: Is It Possible To Not Pass Chlamydia
Question 6 Is Performance Of One Ct/ng Naat Any Different From That Of Another Ct/ng Naat
There are many FDA-approved CT/NG NAATs with high specificities. However, TMA methods have a higher clinical sensitivity than other NAATs.8 Please consult reference 8 for further details.
References
What Is Being Tested
Chlamydia is one of the most common bacterial sexually transmitted diseases in the United States and can cause serious complications if not treated. Chlamydia testing identifies the bacteria Chlamydia trachomatis as the cause of your infection.
The preferred method for chlamydia testing is the nucleic acid amplification test that detects the genetic material of Chlamydia trachomatis. It is generally more sensitive and specific than other chlamydia tests and can be performed on a vaginal swab on women or urine from both men and women, which eliminates the need for a pelvic exam in women.
Screening for, diagnosing, and treating chlamydia is very important in preventing long-term complications and spread of the infection to others. Chlamydia infections are especially common among people 15 to 24 years of age. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that 2.86 million Americans are infected with chlamydia each year and notes that women are frequently re-infected if their partners don’t get treatment. The actual number of cases may be higher since many people do not experience any symptoms and do not get tested and diagnosed. Still, over one million new cases are reported each year.
Chlamydia is generally spread through sexual contact with an infected partner. Risk factors include having multiple sex partners, infection with another STD at the same time or previous STD infection, and not using a condom correctly and consistently.
Read Also: Can A Urinalysis Detect Chlamydia
Chlamydia / N Gonorrhoeae Rna Tma
Includes: Chlamydia trachomatis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Methodology: Dual Kinetic Assay Target Capture Transcription-Mediated Amplification
This test was performed using the APTIMA® COMBO2 Assay .
Clinical Significance:C. trachomatis infections are the leading cause of sexually transmitted diseases in the United States. C. trachomatis is known to cause cervicitis, pelvic inflammatory disease , epididymitis and proctitis. It is also the most frequent cause of non-gonococcal urethritis in men. Among women, the consequences of Chlamydial infections are severe if left untreated. Approximately half of Chlamydial infections are asymptomatic. Neisseria gonorrhoeae is the causative agent of gonorrhea. In men, this disease generally results in anterior urethritis accompanied by purulent exudate. In women, the disease is most often found in the cervix, but the vagina and uterus may also be infected.
Alternative Name: CT/NG APTIMA®, CT/GC APTIMA®, Hologic, CT/GC TMA, CT/NG TMA
Additional Preferred Specimens Collection for Test Code 11363: 1 ml liquid cytology collected throughThinprep® Broomor Brush/Spatula0.5 ml of Surepath® preservative fluid collected using Broom or Brush/Spatula Vaginal swabs in the APTIMA® Combo 2 Assay Vaginal Swab Collection Kit
Note: Results from the APTIMA® Combo 2 Assay should be interpreted in conjunction with other laboratory and clinical data available to the clinician.
Supply: A01 – APTIMA Urine Collection
Transport temperature: Room temperature
How Is Chlamydia Treated

Your healthcare practitioner will prescribe antibiotics to treat chlamydia. Antibiotics can cure your infection, but damage from the infection may sometimes be permanent. If symptoms do not resolve after a few days, consult your healthcare provider. You should refrain from having sex until you have completed your treatment and should be re-tested three months after treatment.
Recommended Reading: How Long After Being Treated For Chlamydia
Question 4 Can Naats Be Used For Test
Per the CDC guidelines for chlamydial infections, an NAAT can be used for test-of-cure if performed 3 to 4 weeks after the end of treatment.4 This is appropriate when therapeutic adherence is in question, symptoms persist, or reinfection is suspected.4 Testing earlier than 3 to 4 weeks after treatment may produce a clinically false-positive result due to detection of nucleic acids from nonviable organisms.6
For patients with urogenital or rectal gonorrhea, follow-up testing is not needed to prove eradication after treatment with any of the recommended or alternative regimens. However, if symptoms persist, the patient should be evaluated using N gonorrhoeae culture , and any gonococci isolated should be tested for antimicrobial susceptibility. Any person with pharyngeal gonorrhea who is treated with an alternative regimen should return 14 days after treatment for a follow-up with either culture or NAAT. If the NAAT is positive, a confirmatory culture is recommended before retreatment. If the culture is positive, antimicrobial susceptibility testing is recommended.
Routine follow-up testing after chlamydia or gonorrhea therapy can be performed using an NAAT approximately 3 months after treatment. If retesting at 3 months is not possible, clinicians should retest at the next opportunity within the 12-month period following initial treatment.
Can I Take The Test At Home
Tests are available to detect chlamydia at home. Most at-home chlamydia tests are self-collection kits, which allow you to obtain a swab or sample of urine at home and return it to a laboratory by mail. If an at-home chlamydia test returns positive results, a doctor may suggest confirmation testing with a laboratory-based method.
Recommended Reading: Treatment For Chlamydia And Trichomoniasis
What Does The Test Measure
Chlamydia testing looks for evidence of infection with the bacteria Chlamydia trachomatis. There are several types of tests that can be used to detect chlamydia, including molecular testing, also called Nucleic Acid Amplification Test , and cell culture.
NAAT is the preferred method for detecting a chlamydia infection. This type of test detects the genetic material of Chlamydia trachomatis. It can be performed using a urine sample or swab of fluid taken from a site of potential infection such as the urethra, vagina, rectum, or eye.
Traditionally, NAAT takes a day or more to provide results, but there have also been rapid chlamydia tests developed using NAAT methods. Rapid chlamydia tests can often provide a result within 30 to 90 minutes. Rapid chlamydia tests are typically performed on urine samples or swabs of fluid taken from the vagina or cervix.
Although much less commonly used, cell cultures can help diagnose a chlamydia infection. Chlamydia cell cultures may be used in children with a suspected chlamydia infection, when evaluating potential infections in the anus or rectum, and when initial treatment for chlamydia is unsuccessful. In these cases of treatment failure, doctors may use a cell culture to help understand which treatments may be most effective for an individuals infection.
Other types of chlamydia tests are available but are rarely used given the accuracy and availability of NAAT.